Abstract
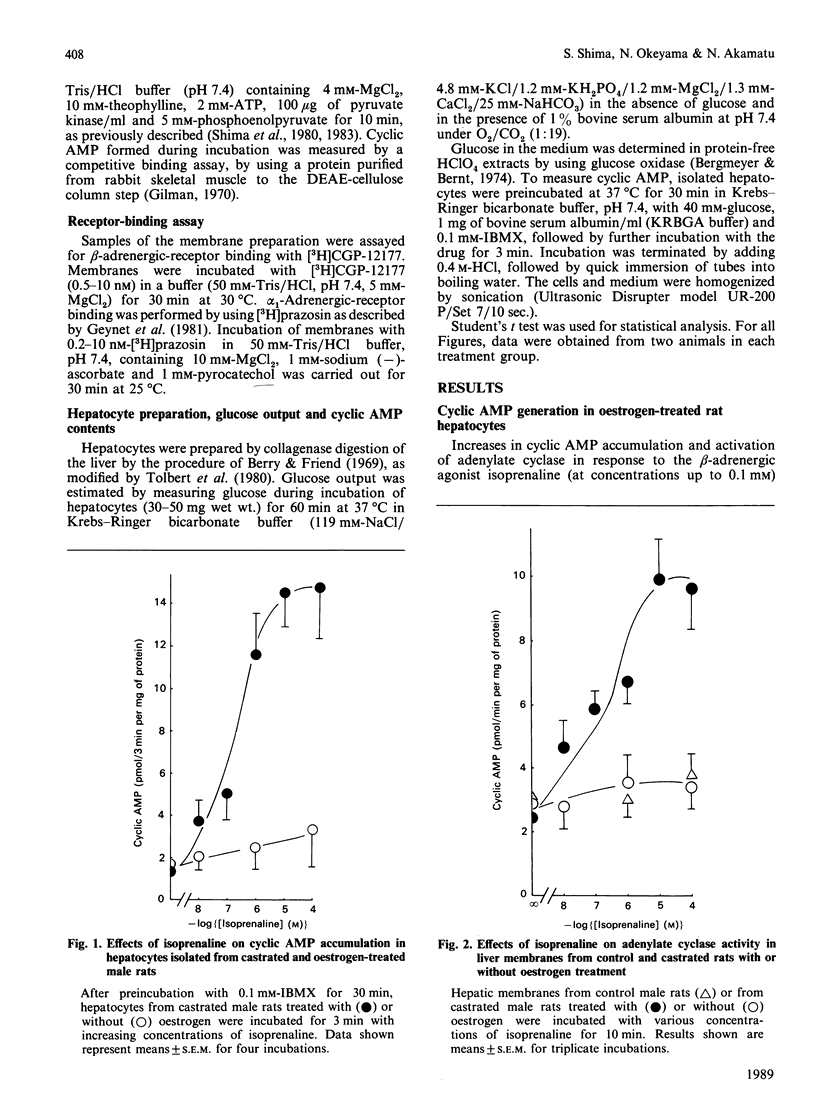
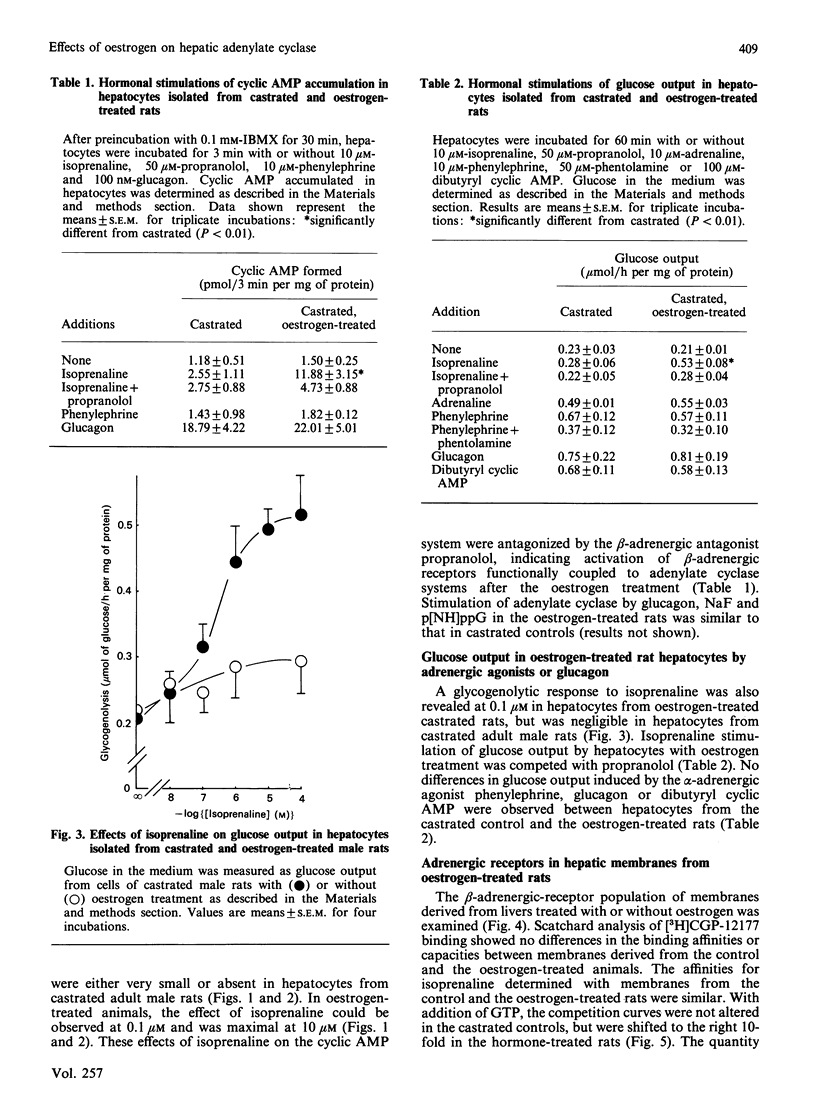
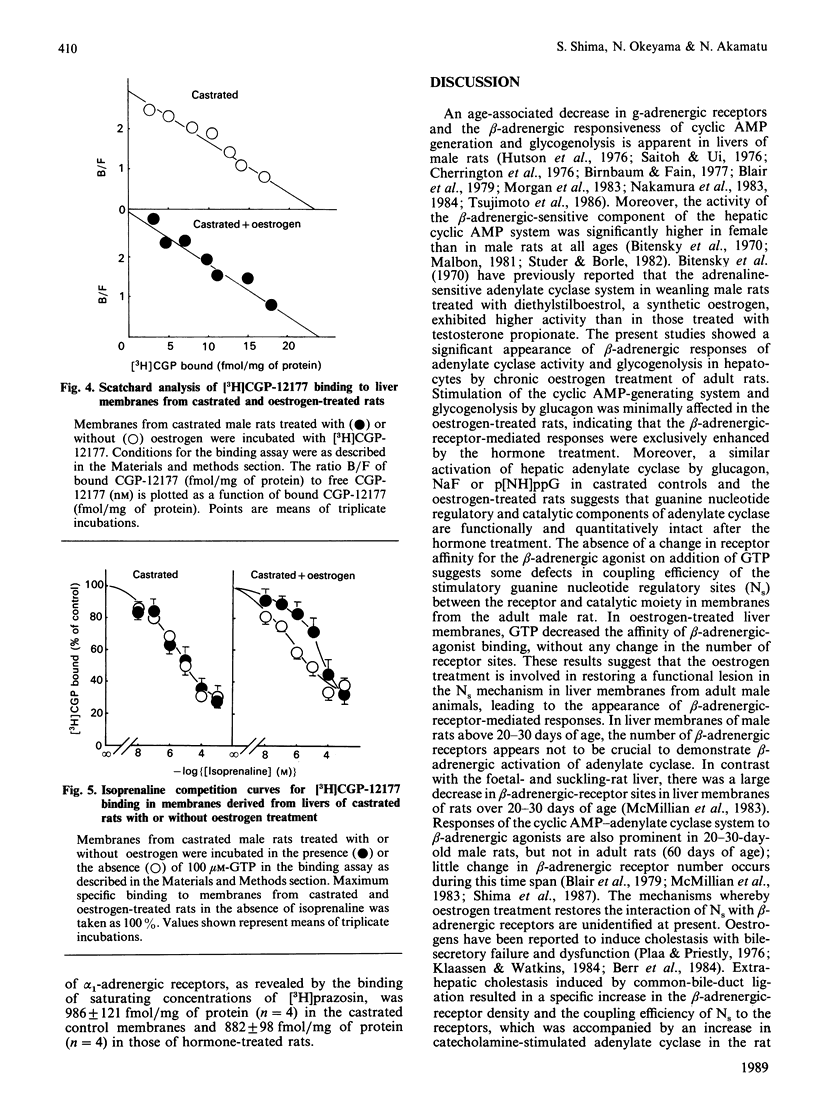
Effects of chronic oestrogen treatment on catecholamine- and glucagon-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity and glucose output in hepatocytes of castrated male rats were studied. In hepatocytes from male intact or castrated rats, the beta-adrenergic agonist isoprenaline did not stimulate adenylate cyclase activity and glycogenolysis, but glucagon markedly stimulated all these activities. Treatment of castrated animals with 17 beta-oestradiol for 7 days led to the appearance of beta-adrenergic-stimulated increases in both cyclic AMP generation and glucose output. The basal, glucagon- or fluoride-stimulated activities of adenylate cyclase of hepatic membranes prepared from oestrogen-treated rats were similar to those of control animals. Treatment with oestrogen did not influence the number or affinity of beta-adrenergic receptors. In hepatic plasma membranes from control rats, GTP failed to decrease the affinity of beta-adrenergic receptors for agonists, whereas the GTP-induced shift was apparently observed in those from oestrogen-treated animals. These results suggest that oestrogen is able to facilitate the coupling of hepatic beta-adrenergic receptors to the enzyme by increasing the effectiveness of receptor-guanine nucleotide regulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck M., Ferry N., Zafrani E. S., Billon M. C., Barouki R., Hanoune J. Adrenergic regulation of glycogenolysis in rat liver after cholestasis. Modulation of the balance between alpha 1 and beta 2 receptors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):476–486. doi: 10.1172/JCI110792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit V., Valette A., Mercier L., Meignen J. M., Boyer J. Potentiation of epinephrine-induced lipolysis in fat cells from estrogen-treated rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1186–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91902-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berr F., Simon F. R., Reichen J. Ethynylestradiol impairs bile salt uptake and Na-K pump function of rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):G437–G443. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.4.G437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Fain J. N. Activation of protein kinase and glycogen phosphorylase in isolated rat liver cells by glucagon and catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):528–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitensky M. W., Russell V., Blanco M. Independent variation of glucagon and epinephrine responsive components of hepatic adenyl cyclase as a function of age, sex and steroid hormones. Endocrinology. 1970 Jan;86(1):154–159. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-1-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. B., James M. E., Foster J. L. Adrenergic control of glucose output and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate levels in hepatocytes from juvenile and adult rats. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7579–7584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Assimacopoulos F. D., Harper S. C., Corbin J. D., Park C. R., Exton J. H. Studies on the alpha-andrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. II. Investigation of the roles of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in the actions of phenylephrine in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5209–5218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debeer L. J., Beynen A. C., Mannaerts G. P., Geelen M. J. Lipolysis of hepatic triacylglycerol stores. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80884-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geynet P., Ferry N., Borsodi A., Hanoune J. Two distinct alpha1-adrenergic receptor sites in rat liver: differential binding of (--)-[3H]dihydroergocryptine. Effects of guanine nucleotides and proteolysis; implications for a two-site model of alpha-receptor regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 15;30(12):1665–1675. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guellaen G., Yates-Aggerbeck M., Vauquelin G., Strosberg D., Hanoune J. Characterization with [3H] dihydroergocryptine of the alpha-adrenergic receptor of the hepatic plasma membrane. Comparison with the beta-adrenergic receptor in normal and adrenalectomized rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Brumley F. T., Assimacopoulos F. D., Harper S. C., Exton J. H. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. I. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase and gluconeogenesis and inactivation of glycogen synthase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5200–5208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen C. D., Watkins J. B., 3rd Mechanisms of bile formation, hepatic uptake, and biliary excretion. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Mar;36(1):1–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Hirata F., Ishac E. J., Tchakarov L. Time-dependent conversion of alpha 1- to beta-adrenoceptor-mediated glycogenolysis in isolated rat liver cells: role of membrane phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6178–6182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C. Beta-adrenergic activity of (+/-)-hydroxybenzylisoproterenol in isolated rat fat cells and hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 5;673(2):203–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Schanberg S. M., Kuhn C. M. Ontogeny of rat hepatic adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Age-related changes in the control of hepatic cyclic AMP levels by alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors in male rats. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5103–5109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomomura A., Kato S., Noda C., Ichihara A. Reciprocal expressions of alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic receptors, but constant expression of glucagon receptor by rat hepatocytes during development and primary culture. J Biochem. 1984 Jul;96(1):127–136. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomomura A., Noda C., Shimoji M., Ichihara A. Acquisition of a beta-adrenergic response by adult rat hepatocytes during primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9283–9289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. Predominance of beta-adrenergic over alpha-adrenergic receptor functions involved in phosphorylase activation in liver cells of cholestatic rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):640–651. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaa G. L., Priestly B. G. Intrahepatic cholestasis induced by drugs and chemicals. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Sep;28(3):207–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh Y., Ui M. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis by epinephrine independent of its beta-adrenergic function in perfused rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Apr 1;25(7):841–845. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelck P. H., Billon M. C., Munnich A., Geynet P., Houssin D., Hanoune J. The effects of common bile duct ligation upon the rat liver beta-adrenergic receptor-adenylate cylase system. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80509-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima S., Kawashima Y., Hirai M., Asakura M. Effect of adrenergic stimulation on adenylate cyclase activity in rat prostate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 20;628(3):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima S., Komoriyama K., Hirai M., Kouyama H. Blockade of heterologous desensitization of prostate adenylate cyclase without blockade of homologous down regulation of receptors or loss of GTP regulation of agonist binding. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2083–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima S., Okeyama N., Oikawa S., Akamatsu N. Effects of chronic propranolol treatment on hepatic adenylate cyclase system in the rat. J Toxicol Sci. 1987 Aug;12(3):309–319. doi: 10.2131/jts.12.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer R. K., Borle A. B. Differences between male and female rats in the regulation of hepatic glycogenolysis. The relative role of calcium and cAMP in phosphorylase activation by catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7987–7993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert M. E., White A. C., Aspry K., Cutts J., Fain J. N. Stimulation by vasopressin and alpha-catecholamines of phosphatidylinositol formation in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1938–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto A., Tsujimoto G., Azhar S., Hoffman B. B. Altered responsiveness to alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor stimulation in hepatocytes cultured in defined medium. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 15;35(8):1400–1404. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


