Abstract
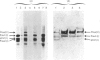
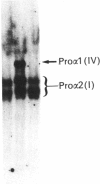
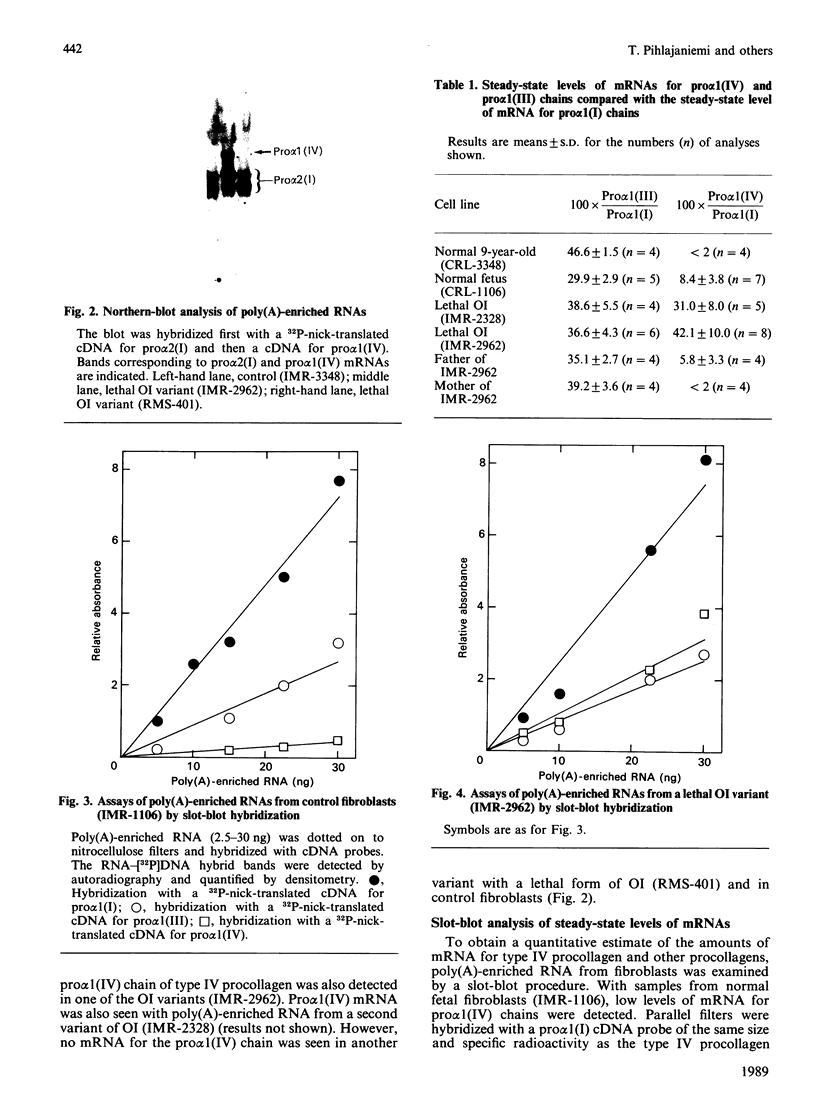
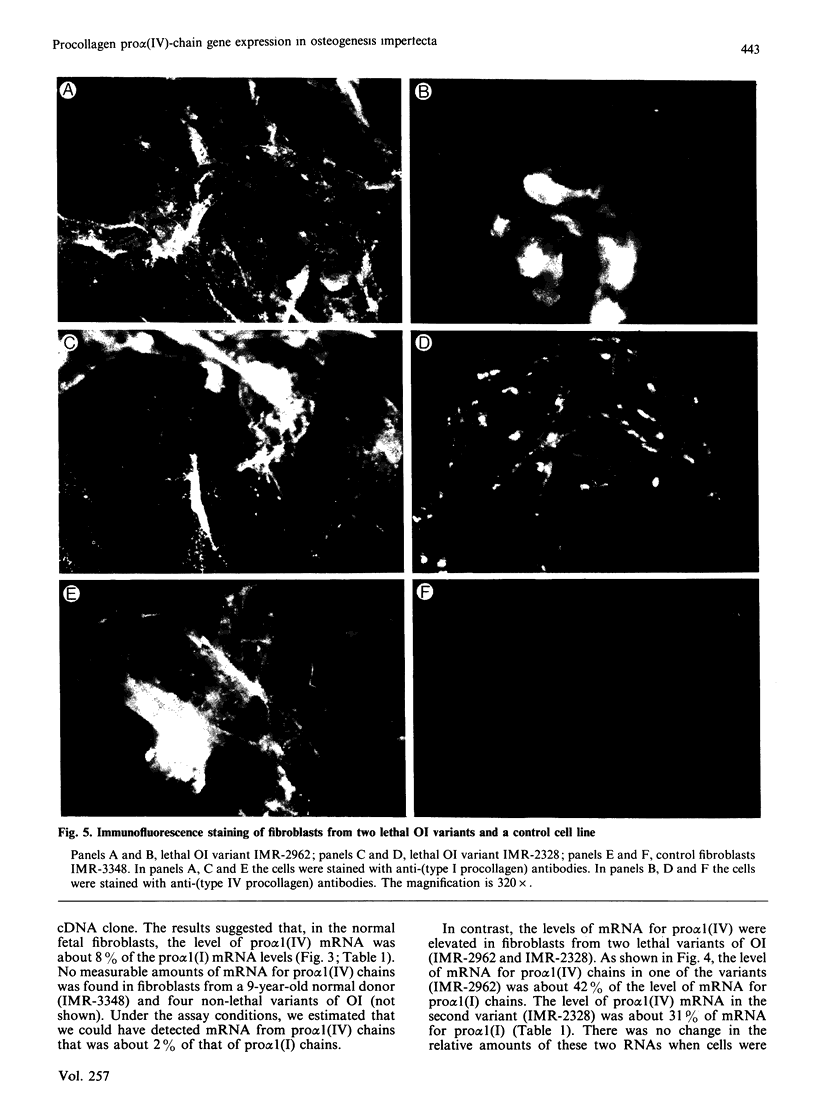
Fibroblasts from two lethal variants of osteogenesis imperfecta were shown to synthesize increased amounts of type IV procollagen. Previous studies established that one of these variants had a non-functional allele for the pro alpha 2 chain of type I procollagen, whereas the other pro alpha 2(I) allele contained a mutation leading to synthesis of shortened pro alpha 2(I) chains. In the two variants, the relative level of mRNA for pro alpha 1(IV) was 31 and 42% of the level of mRNA for pro alpha 1(I) chains. A value of less than 2% was found for a third lethal and four non-lethal variants of osteogenesis imperfecta. Immunofluorescent staining of fibroblasts from the two variants synthesizing increased amounts of type IV procollagen indicated that a homogeneous population of cells synthesized both type IV and type I procollagen. The results suggest that mutations in the type I procollagen genes that result in osteogenesis imperfecta can be associated with increased expression of the genes for type IV procollagen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., David K. E., Byers P. H. Type I osteogenesis imperfecta: a nonfunctional allele for pro alpha 1 (I) chains of type I procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3838–3842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Roush C. L., Bonadio J., Byers P. H., Gelinas R. E. Intron-mediated recombination may cause a deletion in an alpha 1 type I collagen chain in a lethal form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2870–2874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Chan D., Mascara T., Rogers J. G., Cole W. G. Collagen defects in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):699–708. doi: 10.1042/bj2400699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Shapiro J. R., Rowe D. W., David K. E., Holbrook K. A. Abnormal alpha 2-chain in type I collagen from a patient with a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):689–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI110815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. Collagen genes and inherited connective tissue disease. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):287–303. doi: 10.1042/bj2290287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Gargiulo V., Williams C. J., Ramirez F. Multiexon deletion in an osteogenesis imperfecta variant with increased type III collagen mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):691–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Byers P. H., Steinmann B., Gelinas R. E. Lethal osteogenesis imperfecta resulting from a single nucleotide change in one human pro alpha 1(I) collagen allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6045–6047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Bornstein P. Characterization of a type IV procollagen synthesized by human amniotic fluid cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4197–4204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deak S. B., Nicholls A., Pope F. M., Prockop D. J. The molecular defect in a nonlethal variant of osteogenesis imperfecta. Synthesis of pro-alpha 2(I) chains which are not incorporated into trimers of type I procollagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15192–15197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson L. A., Pihlajaniemi T., Deak S., Pope F. M., Nicholls A., Prockop D. J., Myers J. C. Nuclease S1 mapping of a homozygous mutation in the carboxyl-propeptide-coding region of the pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene in a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4524–4528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Fine J. D. Characterization and isolation of poly- and monoclonal antibodies against collagen for use in immunohistochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1987;145:148–167. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)45007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loidl H. R., Brinker J. M., May M., Pihlajaniemi T., Morrow S., Rosenbloom J., Myers J. C. Molecular cloning and carboxyl-propeptide analysis of human type III procollagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9383–9394. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. The structure of fibril-forming collagens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;460:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb51152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Faro S. H., Clark W. J., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Cloning a cDNA for the pro-alpha 2 chain of human type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. K., Lemmen C., Gay S., Meigel W. N. Disturbance in the regulation of the type of collagen synthesized in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. K., Raisch K., Matzen K., Gay S. Presence of type III collagen in bone from a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur J Pediatr. 1977 Apr 26;125(1):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00470603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A. C., Pope F. M., Craig D. An abnormal collagen alpha chain containing cysteine in autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jan 14;288(6411):112–113. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6411.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Lichtenstein J. R., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A. Abnormal collagen metabolism in cultured cells in osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):586–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Dickson L. A., Pope F. M., Korhonen V. R., Nicholls A., Prockop D. J., Myers J. C. Osteogenesis imperfecta: cloning of a pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene with a frameshift mutation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12941–12944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Myers J. C. Characterization of a pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene mutation by nuclease S1 mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1987;145:213–222. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)45011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Tryggvason K., Myers J. C., Kurkinen M., Lebo R., Cheung M. C., Prockop D. J., Boyd C. D. cDNA clones coding for the pro-alpha1(IV) chain of human type IV procollagen reveal an unusual homology of amino acid sequences in two halves of the carboxyl-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7681–7687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope F. M., Nicholls A. C., Eggleton C., Narcissi P., Hey E. N., Parkin J. M. Osteogenesis imperfecta (lethal) bones contain types III and V collagens. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jun;33(6):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.6.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):376–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Shapiro J. R., Poirier M., Schlesinger S. Diminished type I collagen synthesis and reduced alpha 1(I) collagen messenger RNA in cultured fibroblasts from patients with dominantly inherited (type I) osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):604–611. doi: 10.1172/JCI112012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippola M., Kaffe S., Prockop D. J. A heterozygous defect for structurally altered pro-alpha 2 chain of type I procollagen in a mild variant of osteogenesis imperfecta. The altered structure decreases the thermal stability of procollagen and makes it resistant to procollagen N-proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14094–14100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Rao V. H., Vogel A., Bruckner P., Gitzelmann R., Byers P. H. Cysteine in the triple-helical domain of one allelic product of the alpha 1(I) gene of type I collagen produces a lethal form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):11129–11138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Francis M. J., Smith R. Altered relation of two collagen types in osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 26;296(21):1200–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705262962104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Ogilvie D., Wordsworth P., Anderson, Jones N. Osteogenesis imperfecta is linked to both type I collagen structural genes. Lancet. 1986 Jul 12;2(8498):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91609-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryggvason K., Robey P. G., Martin G. R. Biosynthesis of type IV procollagens. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1284–1289. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Børresen A. L., Dickson L. A., Berg K., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Molecular heterogeneity in the mild autosomal dominant forms of osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1172–1179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turakainen H., Larjava H., Saarni H., Penttinen R. Synthesis of hyaluronic acid and collagen in skin fibroblasts cultured from patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 3;628(4):388–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E. Connective tissue diseases: mutations of collagen genes. Ann Clin Res. 1986;18(5-6):234–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. J., Prockop D. J. Synthesis and processing of a type I procollagen containing shortened pro-alpha 1(I) chains by fibroblasts from a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries W. N., de Wet W. J. The molecular defect in an autosomal dominant form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Synthesis of type I procollagen containing cysteine in the triple-helical domain of pro-alpha 1(I) chains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9056–9064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Chu M. L., Prockop D. J. The mRNAs for the pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) chains of type I procollagen are translated at the same rate in normal human fibroblasts and in fibroblasts from two variants of osteogenesis imperfecta with altered steady state ratios of the two mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14385–14389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Pihlajaniemi T., Myers J., Kelly T. E., Prockop D. J. Synthesis of a shortened pro-alpha 2(I) chain and decreased synthesis of pro-alpha 2(I) chains in a proband with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7721–7728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wett W., Sippola M., Tromp G., Prockop D., Chu M. L., Ramirez F. Use of R-loop mapping for the assessment of human collagen mutations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3857–3862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]