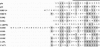Abstract
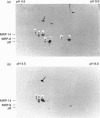
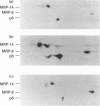
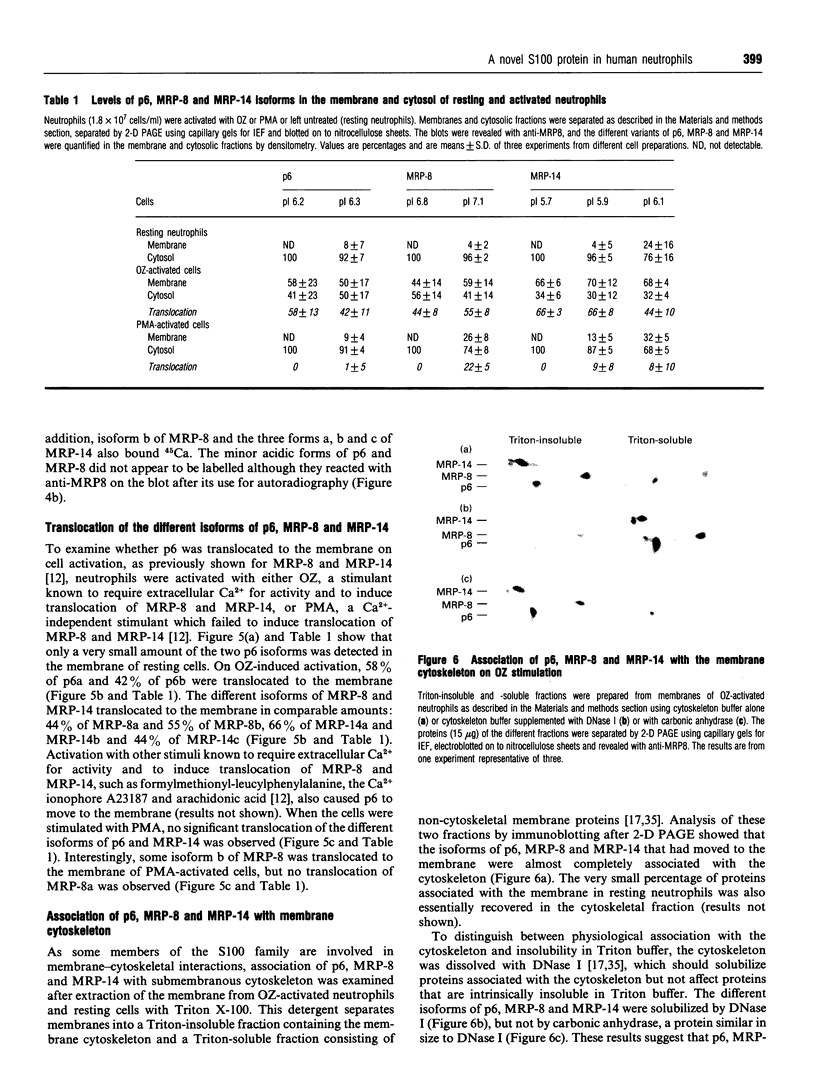
A rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against myeloid-related protein 8 (MRP-8), a protein of the S100 family, recognized another S100 protein (MRP-14) as well as a protein of 6.5 kDa (p6) in the cytosol of resting neutrophils. p6 was found to be a novel member of the S100 family. It consisted of two isoforms with pI values of 6.2 (the minor form, p6a) and 6.3 (the major form, p6b) and constituted 5% of the total cytosolic proteins. Both isoforms were also demonstrated in the cytosol of monocytes, but not in lymphocytes, as previously shown for MRP-8 and MRP-14. Only the major isoform bound radioactive Ca2+, as also observed for MRP-8, whereas the different variants of MRP-14 were all labelled. On neutrophil activation with opsonized zymosan, a stimulant known to require extracellular Ca2+, 58% of p6a and 42% of p6b was translocated to the membrane. With phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, a Ca(2+)-independent stimulant, no translocation was detected. This translocation pattern was similar to that observed with MRP-8 and MRP-14. In addition, p6, MRP-8 and MRP-14 were specifically associated with the cytoskeletal fraction of the membrane. The Ca(2+)-dependent translocation of the novel S100 protein in parallel with MRP-8 and MRP-14 suggests a role for these proteins in regulating the Ca2+ signal to the membrane cytoskeleton and thus in regulating neutrophil activation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel R. D., Hochstrasser D. F., Funk M., Vargas J. R., Pellegrini C., Muller A. F., Scherrer J. R. The MELANIE project: from a biopsy to automatic protein map interpretation by computer. Electrophoresis. 1991 Oct;12(10):722–735. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150121006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker T., Gerke V., Kube E., Weber K. S100P, a novel Ca(2+)-binding protein from human placenta. cDNA cloning, recombinant protein expression and Ca2+ binding properties. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berntzen H. B., Fagerhol M. K. L1, a major granulocyte protein: antigenic properties of its subunits. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;48(7):647–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjellqvist B., Pasquali C., Ravier F., Sanchez J. C., Hochstrasser D. A nonlinear wide-range immobilized pH gradient for two-dimensional electrophoresis and its definition in a relevant pH scale. Electrophoresis. 1993 Dec;14(12):1357–1365. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501401209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell'Angelica E. C., Schleicher C. H., Santomé J. A. Primary structure and binding properties of calgranulin C, a novel S100-like calcium-binding protein from pig granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28929–28936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgeworth J., Freemont P., Hogg N. Ionomycin-regulated phosphorylation of the myeloid calcium-binding protein p14. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):189–192. doi: 10.1038/342189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgeworth J., Gorman M., Bennett R., Freemont P., Hogg N. Identification of p8,14 as a highly abundant heterodimeric calcium binding protein complex of myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7706–7713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelkamp D., Schäfer B. W., Erne P., Heizmann C. W. S100 alpha, CAPL, and CACY: molecular cloning and expression analysis of three calcium-binding proteins from human heart. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 27;31(42):10258–10264. doi: 10.1021/bi00157a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelkamp D., Schäfer B. W., Mattei M. G., Erne P., Heizmann C. W. Six S100 genes are clustered on human chromosome 1q21: identification of two genes coding for the two previously unreported calcium-binding proteins S100D and S100E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6547–6551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell D. J., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Identification of tissue histiocytes on paraffin sections by a new monoclonal antibody. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Nov;35(11):1217–1226. doi: 10.1177/35.11.3309045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Identification of actin-binding protein as the protein linking the membrane skeleton to glycoproteins on platelet plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11970–11977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P., Hogg N., Edgeworth J. Sequence identity. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):516–516. doi: 10.1038/339516b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebeler M., Roth J., Teigelkamp S., Sorg C. The monoclonal antibody MAC387 detects an epitope on the calcium-binding protein MRP14. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Feb;55(2):259–261. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heierli C., Markert M., Lambert P. H., Kuwahara T., Wauters J. P. On the mechanisms of haemodialysis-induced neutropenia: a study with five new and re-used membranes. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1988;3(6):773–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser D. F., Harrington M. G., Hochstrasser A. C., Miller M. J., Merril C. R. Methods for increasing the resolution of two-dimensional protein electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):424–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A., Legon S., Spurr N. K., Walters J. R. Molecular cloning and chromosomal assignment of human calbindin-D9k. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 15;185(2):663–669. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91676-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Bartles J. R., Braiterman L. T. Identification of rat hepatocyte plasma membrane proteins using monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1115–1125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Marshak D. R., Anderson C., Lukas T. J., Watterson D. M. Characterization of human brain S100 protein fraction: amino acid sequence of S100 beta. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):700–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman D., Hilt D. C. The S100 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Tomasetto C., Swisshelm K., Keyomarsi K., Sager R. Down-regulation of a member of the S100 gene family in mammary carcinoma cells and reexpression by azadeoxycytidine treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2504–2508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemarchand P., Vaglio M., Mauël J., Markert M. Translocation of a small cytosolic calcium-binding protein (MRP-8) to plasma membrane correlates with human neutrophil activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19379–19382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert M., Andrews P. C., Babior B. M. Measurement of O2- production by human neutrophils. The preparation and assay of NADPH oxidase-containing particles from human neutrophils. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:358–365. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert M., Glass G. A., Babior B. M. Respiratory burst oxidase from human neutrophils: purification and some properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3144–3148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Jr, Nguyen N. Y., Liu T. Y. Reproducible high yield sequencing of proteins electrophoretically separated and transferred to an inert support. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6005–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murao S., Collart F. R., Huberman E. A protein containing the cystic fibrosis antigen is an inhibitor of protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8356–8360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy A. R., Lehrer R. I., Harwig S. S., Miyasaki K. T. In vitro candidastatic properties of the human neutrophil calprotectin complex. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6291–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odink K., Cerletti N., Brüggen J., Clerc R. G., Tarcsay L., Zwadlo G., Gerhards G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):80–82. doi: 10.1038/330080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertoft H., Johnsson A., Wärmegård B., Seljelid R. Separation of human monocytes on density gradients of Percoll. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. Calcium-binding proteins: the search for functions. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):661–662. doi: 10.1038/339661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F. The O2- -forming NADPH oxidase of the phagocytes: nature, mechanisms of activation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 4;853(1):65–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(86)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Burwinkel F., van den Bos C., Goebeler M., Vollmer E., Sorg C. MRP8 and MRP14, S-100-like proteins associated with myeloid differentiation, are translocated to plasma membrane and intermediate filaments in a calcium-dependent manner. Blood. 1993 Sep 15;82(6):1875–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigelkamp S., Bhardwaj R. S., Roth J., Meinardus-Hager G., Karas M., Sorg C. Calcium-dependent complex assembly of the myeloic differentiation proteins MRP-8 and MRP-14. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13462–13467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace P. J., Packman C. H., Wersto R. P., Lichtman M. A. The effects of sulfhydryl inhibitors and cytochalasin on the cytoplasmic and cytoskeletal actin of human neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Aug;132(2):325–330. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Brightman I. L., Goetzl E. J. Isolation of two polypeptides comprising the neutrophil-immobilizing factor of human leucocytes. Immunology. 1983 Jan;48(1):79–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M. M., Busuttil A., Hayward C., Brock D. J., Dorin J. R., Van Heyningen V. Expression pattern of two related cystic fibrosis-associated calcium-binding proteins in normal and abnormal tissues. J Cell Sci. 1988 Oct;91(Pt 2):221–230. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwadlo G., Brüggen J., Gerhards G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. Two calcium-binding proteins associated with specific stages of myeloid cell differentiation are expressed by subsets of macrophages in inflammatory tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jun;72(3):510–515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Benna J., Ruedi J. M., Babior B. M. Cytosolic guanine nucleotide-binding protein Rac2 operates in vivo as a component of the neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. Transfer of Rac2 and the cytosolic oxidase components p47phox and p67phox to the submembranous actin cytoskeleton during oxidase activation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6729–6734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]