Abstract
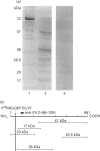
Protein 4.2 (P4.2) is a major component of the erythrocyte plasma membrane accounting for approx. 5% of total membrane protein. The major membrane binding site for P4.2 is contained within the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 (cdb3), although the precise location of the cdb3 binding site is not known. To identify the cdb3 binding site, we used synthetic P4.2 peptides (15-mers) that spanned the entire 721-amino-acid large isoform of P4.2, and determined the binding of these peptides to cdb3 in an in vitro binding assay. One peptide, P8 (L61FVRRGQPFTIILYF), bound strongly to cdb3 and four others bound less strongly (P22, L271LNKRRGSVPILRQW; P27, G346EGQRGRIWIFQTST; P41, L556WRKKLHLTLSANLE; P48, I661HRERSYRFRSVWPE). These peptides have in common a cluster of two or three basic amino acid residues (arginine or lysine), in a region without nearby acidic residues. Cdb3 bound saturably to P8 with a Kd of 0.16 microM and a capacity of 0.56 mol of cdb3 monomer/mol of P8. Use of overlapping synthetic peptides further defined the cdb3 site as being contained within V63RRGQPFTIILYF. Replacement of R64R with R64G, G64R or G64G almost completely abolished cdb3 binding, suggesting that R64R is essential for cdb3 binding. P8 competitively inhibited binding of purified human erythrocyte P4.2 to cdb3. In blot overlay assays, cdb3 bound to a 23 kDa N-terminal P4.2 tryptic peptide containing V63RRGQPFTIILYF but not to other P4.2 tryptic peptides lacking this site. The V63RRGQPFTIILYF site is highly conserved in mouse and human erythrocyte P4.2 as well as between P4.2 and transglutaminase proteins, which are evolutionarily related to P4.2.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Proteins involved in membrane--cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes: spectrin, ankyrin, and band 3. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:313–324. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhassira E. E., Schwartz R. S., Yawata Y., Ata K., Kanzaki A., Qiu J. J., Nagel R. L., Rybicki A. C. An alanine-to-threonine substitution in protein 4.2 cDNA is associated with a Japanese form of hereditary hemolytic anemia (protein 4.2NIPPON). Blood. 1992 Apr 1;79(7):1846–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bütikofer P., Frenkel E. J., Ott P. 'Crossed immunoblotting': identification of proteins after crossed immunoelectrophoresis and electrotransfer to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 28;84(1-2):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerwiński M., Waśniowska K., Steuden I., Duk M., Wiedłocha A., Lisowska E. Degradation of the human erythrocyte membrane band 3 studied with monoclonal antibody directed against an epitope on the cytoplasmic fragment of band 3. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):647–654. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. H., Otto E., Bennett V. Specific 33-residue repeat(s) of erythrocyte ankyrin associate with the anion exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11163–11169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotimas E., Speicher D. W., GuptaRoy B., Cohen C. M. Structural domain mapping and phosphorylation of human erythrocyte pallidin (band 4.2). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 May 14;1148(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90156-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarolim P., Palek J., Rubin H. L., Prchal J. T., Korsgren C., Cohen C. M. Band 3 Tuscaloosa: Pro327----Arg327 substitution in the cytoplasmic domain of erythrocyte band 3 protein associated with spherocytic hemolytic anemia and partial deficiency of protein 4.2. Blood. 1992 Jul 15;80(2):523–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jöns T., Drenckhahn D. Identification of the binding interface involved in linkage of cytoskeletal protein 4.1 to the erythrocyte anion exchanger. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren C., Cohen C. M. Purification and properties of human erythrocyte band 4.2. Association with the cytoplasmic domain of band 3. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren C., Lawler J., Lambert S., Speicher D., Cohen C. M. Complete amino acid sequence and homologies of human erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):613–617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo C. R., Willardson B. M., Low P. S. Localization of the protein 4.1-binding site on the cytoplasmic domain of erythrocyte membrane band 3. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9540–9546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S. Structure and function of the cytoplasmic domain of band 3: center of erythrocyte membrane-peripheral protein interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 22;864(2):145–167. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak E. K., Hui S. W., Swank R. T. Platelet storage pool deficiency in mouse pigment mutations associated with seven distinct genetic loci. Blood. 1984 Mar;63(3):536–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybicki A. C., Heath R., Wolf J. L., Lubin B., Schwartz R. S. Deficiency of protein 4.2 in erythrocytes from a patient with a Coombs negative hemolytic anemia. Evidence for a role of protein 4.2 in stabilizing ankyrin on the membrane. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):893–901. doi: 10.1172/JCI113400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybicki A. C., Qiu J. J., Musto S., Rosen N. L., Nagel R. L., Schwartz R. S. Human erythrocyte protein 4.2 deficiency associated with hemolytic anemia and a homozygous 40glutamic acid-->lysine substitution in the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 (band 3Montefiore). Blood. 1993 Apr 15;81(8):2155–2165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybicki A. C., Schwartz R. S., Qiu J. J., Gilman J. G. Molecular cloning of mouse erythrocyte protein 4.2: a membrane protein with strong homology with the transglutaminase supergene family. Mamm Genome. 1994 Jul;5(7):438–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00357005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung L. A., Chien S., Chang L. S., Lambert K., Bliss S. A., Bouhassira E. E., Nagel R. L., Schwartz R. S., Rybicki A. C. Molecular cloning of human protein 4.2: a major component of the erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):955–959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. C., Pasternack G. R., Marchesi V. T. The structural basis of ankyrin function. II. Identification of two functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6170–6175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Peters L. L., Adkison L. R., Korsgren C., Cohen C. M., Lux S. E. The murine pallid mutation is a platelet storage pool disease associated with the protein 4.2 (pallidin) gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):80–83. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Steck T. L. Isolation and characterization of band 3, the predominant polypeptide of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9170–9175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]