Abstract
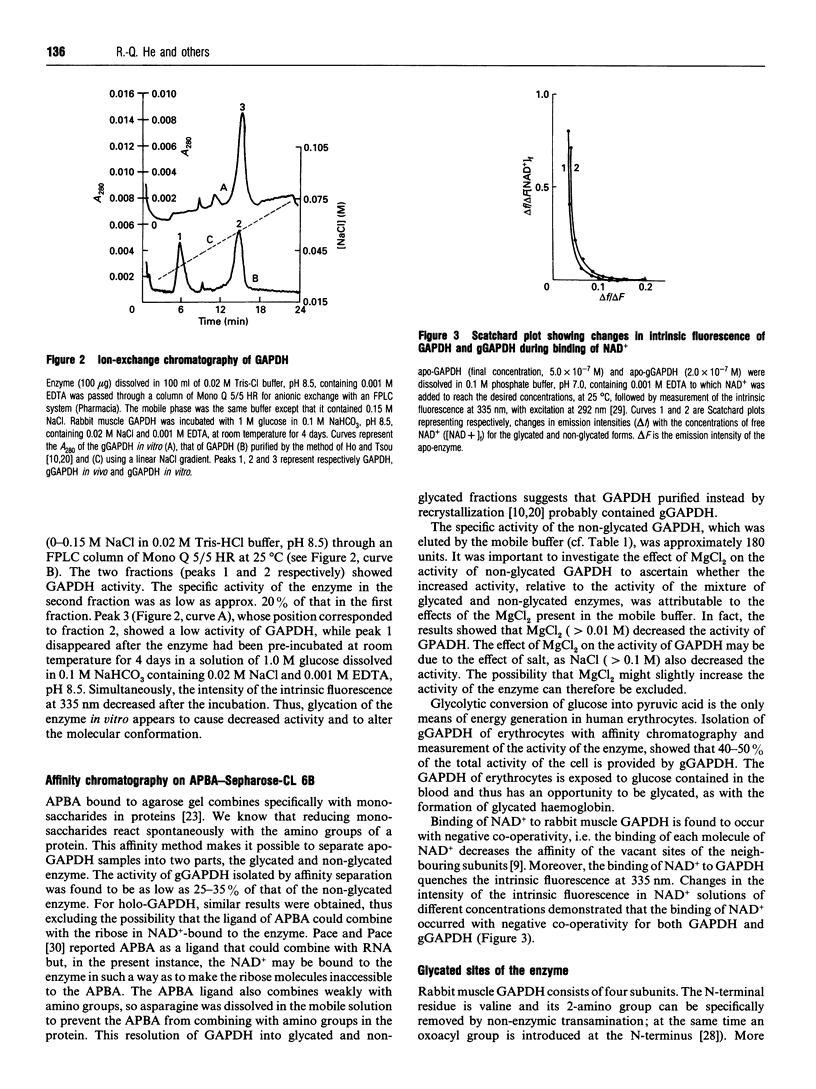
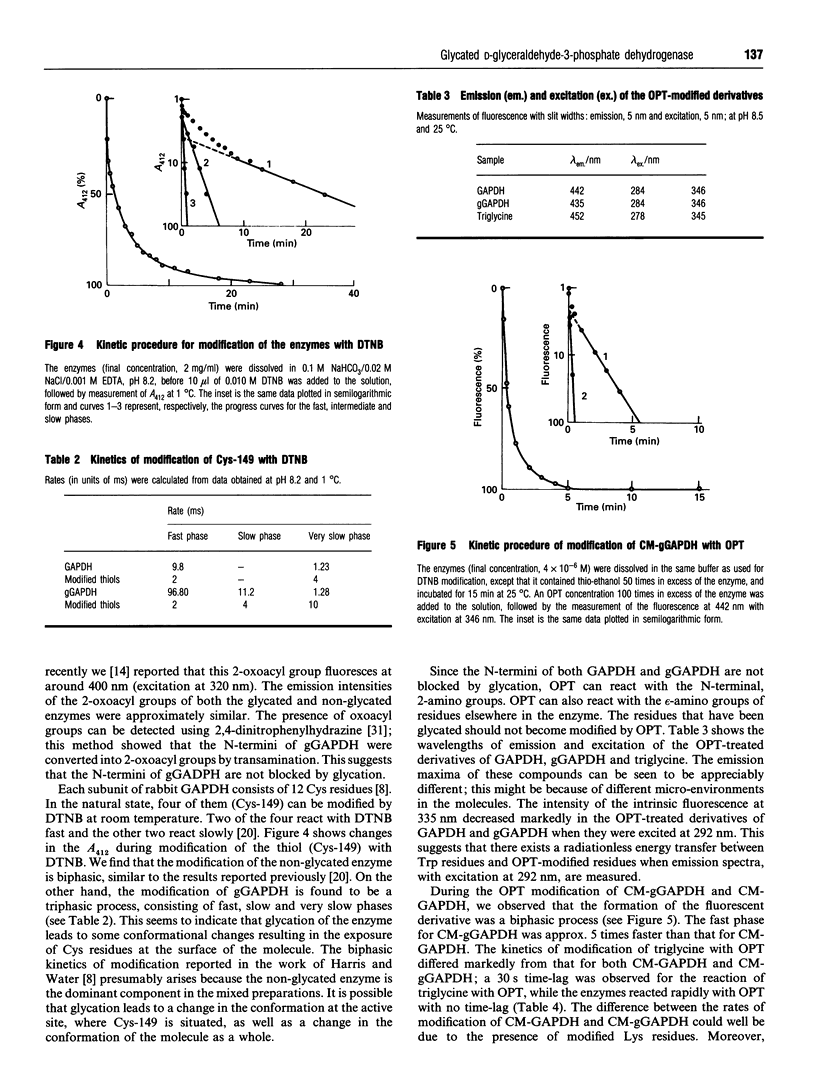
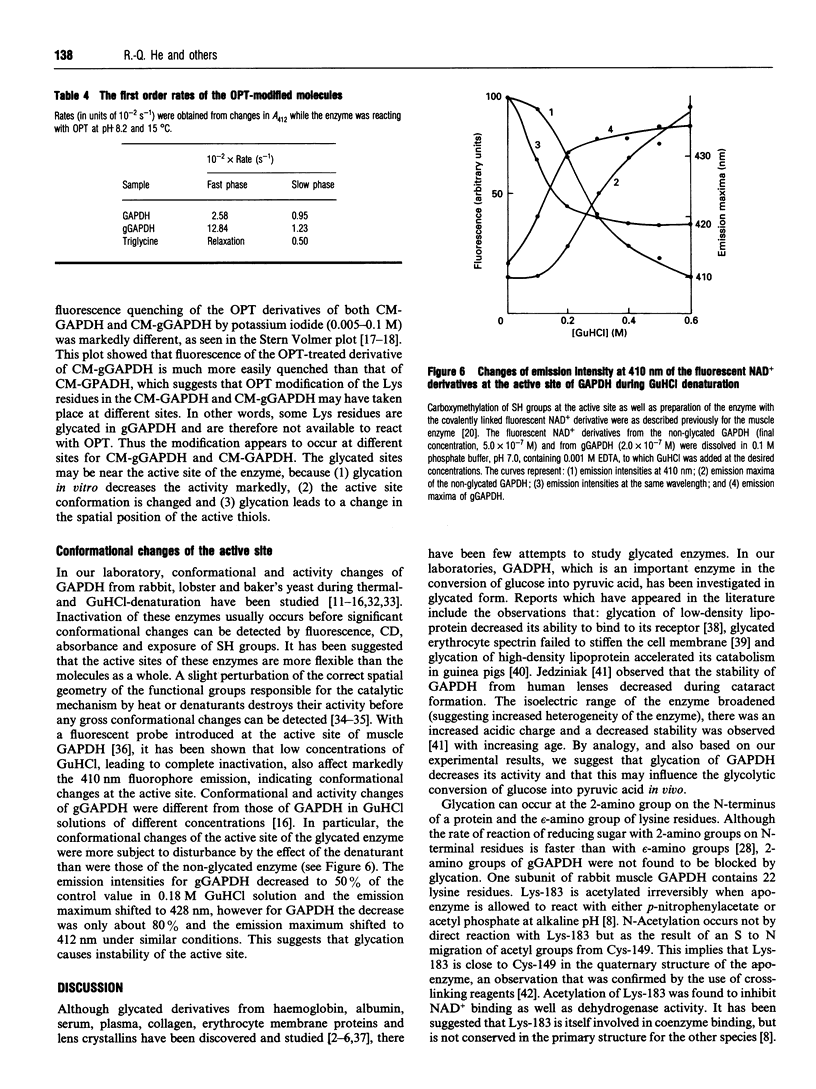
Glycated D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (GAPDH) from rabbit muscle and human erythrocytes have been investigated. The specific activity of the non-glycated GAPDH from rabbit muscle is approx. 180 units. (One unit is defined as the specific activity required to convert 1 microM of substrate/min per mg of enzyme.) The activity of the glycated enzyme, consisting of two sugars per tetramer, is lower than that of the non-glycated GAPDH. Non-enzymic transamination of the N-termini of glycated GAPDH (gGAPDH) indicates that they are not blocked by glycation. The rate of modification of thiols (Cys-149) with 5,5'-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) was greater for the glycated than the non-glycated enzymes. The rate of modification of amino groups of Lys residues of gGAPDH with o-phthalaldehyde was greater for the non-glycated enzyme. In 0.18 M guanidine-HC1 solution, the emission intensity at 410 nm of a fluorescent NAD+ derivative introduced into the active site decreased to 80%, whereas that of gGAPDH decreased to 50%. This suggests that the glycated sites are near the active site; glycation of the enzyme leads to a change of the microenvironment of Cys-149, alters the conformation of the active site and decreases the activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey A. J., Robins S. P., Tanner M. J. Reducible components in the proteins of human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 20;434(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Gabbay K. H., Gallop P. M. The glycosylation of hemoglobin: relevance to diabetes mellitus. Science. 1978 Apr 7;200(4337):21–27. doi: 10.1126/science.635569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes-Laurean D., Minter D. E., Jacobson E. L., Jacobson M. K. Protein glycation by ADP-ribose: studies of model conjugates. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 16;32(6):1528–1534. doi: 10.1021/bi00057a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway A., Koshland D. E., Jr Negative cooperativity in enzyme action. The binding of diphosphopyridine nucleotide to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4011–4023. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H. B. A reaction of glucose with peptides. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):203–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1290203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS C., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 4. The determination of mannose in hen's-egg albumin by radioisotope dilution. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:335–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0830335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields R., Dixon H. B. Micro method for determination of reactive carbonyl groups in proteins and peptides, using 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):587–589. doi: 10.1042/bj1210587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He R. Q., Zhao K. Y., Yan Z. Z., Li M. An asynchronous unfolding among molecular different regions of lobster D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and maltotetraose-forming amylase from an Alcaligenes sp. during guanidine denaturation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 4;1163(3):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(93)90168-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He R., Tsou C. L. Fluorescence of peptide N-terminal 2-oxoacyl and quinoxaline derivatives. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 1;287(Pt 3):1001–1005. doi: 10.1042/bj2871001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann H-D, Pfleiderer G. On the role of tryptophan residues in the mechanism of action of glyceraldehyde-3phosphate dehydrogenase as tested by specific modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Liang S. J., Tsou C. L. Formation and energy transfer of a fluorescent derivative of B. stearothermophilus glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Tsou C. L. Formation of a new fluorophore on irradiation of carboxymethylated D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):245–246. doi: 10.1038/277245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking J. D., Harris J. I. D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Amino-acid sequence of the enzyme from the extreme thermophile Thermus aquaticus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):567–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist W. R., Schroeder W. A. A new N-terminal blocking group involving a Schiff base in hemoglobin AIc. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2489–2503. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedziniak J. A., Arredondo L. M., Meys M. Human lens enzyme alterations with age and cataract: glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase and triose phosphate isomerase. Curr Eye Res. 1986 Feb;5(2):119–126. doi: 10.3109/02713688609015100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer F. B., Chen Y. D., Cheung R. M., Reaven G. M. Are the binding and degradation of low density lipoprotein altered in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus? Diabetologia. 1982 Jul;23(1):28–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00257726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang S. J., Lin Y. Z., Zhou J. M., Tsou C. L., Wu P. Q., Zhou Z. K. Dissociation and aggregation of D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase during denaturation by guanidine hydrochloride. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 19;1038(2):240–246. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90211-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald L. J., Moss J. Nitric oxide-independent, thiol-associated ADP-ribosylation inactivates aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17878–17882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald L. J., Moss J. Stimulation by nitric oxide of an NAD linkage to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6238–6241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moras D., Olsen K. W., Sabesan M. N., Buehner M., Ford G. C., Rossmann M. G. Studies of asymmetry in the three-dimensional structure of lobster D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9137–9162. doi: 10.2210/pdb1gpd/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton A. R., Hill E. G. Inactivation of Nutrients by Heating With Glucose. Science. 1948 Jan 16;107(2768):68–69. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2768.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Bailey A. J. Age-related changes in collagen: the identification of reducible lysine-carbohydrate condensation products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S., Tauber-Finkelstein M. Introduction of an intramolecular crosslink at the active site of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):484–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90627-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., McManus M. J., Zalut C., Bunn H. F. Sites of nonenzymatic glycosylation of human hemoglobin A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3120–3127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Rouzer C. A., Monnier V. M., Cerami A. Diabetic cataract formation: potential role of glycosylation of lens crystallins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strambini G. B., Gabellieri E. Phosphorescence properties and protein structure surrounding tryptophan residues in yeast, pig, and rabbit glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):160–166. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou C. L., Xu G. Q., Zhou J. M., Zhao K. Y. A new fluorescent probe for the study of the allosteric properties of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Aug;11(4):425–429. doi: 10.1042/bst0110425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Fisher M., Pietro T., Steinbrecher U. P., Elam R. L. Nonenzymatic glucosylation of high-density lipoprotein accelerates its catabolism in guinea pigs. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):1029–1032. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie G. F., Tsou C. L. Conformational and activity changes during guanidine denaturation of D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 5;911(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]