Abstract
Two ribosome-inactivating proteins, trichosanthin and alpha-momorcharin, have been studied in the forms of complexes with ATP or formycin, by an X-ray-crystallographic method at 1.6-2.0 A (0.16-0.20 nm) resolution. The native alpha-momorcharin had been studied at 2.2 A resolution. Structures of trichosanthin were determined by a multiple isomorphous replacement method. Structures of alpha-momorcharin were determined by a molecular replacement method using refined trichosanthin as the searching model. Small ligands in all these complexes have been recognized and built on the difference in electron density. All these structures have been refined to achieve good results, both in terms of crystallography and of ideal geometry. These two proteins show considerable similarity in their three-dimensional folding and to that of related proteins. On the basis of these structures, detailed geometries of the active centres of these two proteins are described and are compared with those of related proteins. In all complexes the interactions between ligand atoms and protein atoms, including hydrophobic forces, aromatic stacking interactions and hydrogen bonds, are found to be specific towards the adenine base. The relationship between the sequence conservation of ribosome-inactivating proteins and their active-centre geometry was analysed. A depurinating mechanism of ribosome-inactivating proteins is proposed on the basis of these results. The N-7 atom of the substrate base group is proposed to be protonated by an acidic residue in the active centre.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chow T. P., Feldman R. A., Lovett M., Piatak M. Isolation and DNA sequence of a gene encoding alpha-trichosanthin, a type I ribosome-inactivating protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8670–8674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. The RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of ricin A-chain with ribosomes and with rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8735–8739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Z., Li W. W., Yeung H. W., Chen S. Z., Wang Y. P., Lin X. Y., Dong Y. C., Wang J. H. Crystals of alpha-momorcharin. A new ribosome-inactivating protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):625–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90277-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. R., Mehta P. J. Solvolysis of adenine nucleosides. I. Effects of sugars and adenine substituents on acid solvolyses. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Nov 29;94(24):8532–8541. doi: 10.1021/ja00779a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habuka N., Miyano M., Kataoka J., Tsuge H., Noma M. Specificities of RNA N-glycosidase activity of Mirabilis antiviral protein variants. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7758–7760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling K. C., Halling A. C., Murray E. E., Ladin B. F., Houston L. L., Weaver R. F. Genomic cloning and characterization of a ricin gene from Ricinus communis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8019–8033. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W. K., Liu S. C., Shaw P. C., Yeung H. W., Ng T. B., Chan W. Y. Cloning of the cDNA of alpha-momorcharin: a ribosome inactivating protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 16;1088(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. R., Nishida H., Funatsu G. Complete amino acid sequence of luffin-a, a ribosome-inactivating protein from the seeds of Luffa cylindrica. Agric Biol Chem. 1990 May;54(5):1343–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzin B. J., Collins E. J., Robertus J. D. Structure of ricin A-chain at 2.5 A. Proteins. 1991;10(3):251–259. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita H., Hondo R., Taguchi F., Yogo Y. Variation of R1 repeated sequence present in open reading frame 11 of varicella-zoster virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1097–1100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1097-1100.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. S., Kimura M., Funatsu G. The complete amino acid sequence of antiviral protein from the seeds of pokeweed (Phytolacca americana). Agric Biol Chem. 1990 Dec;54(12):3301–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Huang P. L., Kung H. F., Li B. Q., Huang P. L., Huang P., Huang H. I., Chen H. C. TAP 29: an anti-human immunodeficiency virus protein from Trichosanthes kirilowii that is nontoxic to intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6570–6574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Huang S., Huang P. L., Nara P. L., Chen H. C., Kung H. F., Huang P., Huang H. I., Huang P. L. MAP 30: a new inhibitor of HIV-1 infection and replication. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):12–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80438-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X. Q., Wang Y. P., Wang J. H. An X-ray analysis of the orthorhombic crystal form of trichosanthin at 5 angstrom. Sci Sin B. 1987 Jul;30(7):692–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. S., Hwang K. M., Caldwell S. E., Gaston I., Luk K. C., Wu P., Ng V. L., Crowe S., Daniels J., Marsh J. GLQ223: an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus replication in acutely and chronically infected cells of lymphocyte and mononuclear phagocyte lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentch F., Parkin D. W., Schramm V. L. Transition-state structures for N-glycoside hydrolysis of AMP by acid and by AMP nucleosidase in the presence and absence of allosteric activator. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 10;26(3):921–930. doi: 10.1021/bi00377a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami Y., Funatsu G. The complete amino acid sequence of momordin-a, a ribosome-inactivating protein from the seeds of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1993 Jul;57(7):1141–1144. doi: 10.1271/bbb.57.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzingo A. F., Robertus J. D. X-ray analysis of substrate analogs in the ricin A-chain active site. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1136–1145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90526-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner P., Brennan T., Sundaralingam M. Crystal structure and molecular conformation of formycin monohydrates. Possible origin of the anomalous circular dichroic spectra in formycin mono- and polynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1196–1202. doi: 10.1021/bi00730a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready M. P., Kim Y., Robertus J. D. Site-directed mutagenesis of ricin A-chain and implications for the mechanism of action. Proteins. 1991;10(3):270–278. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Selitrennikoff C. P. Plant proteins that inactivate foreign ribosomes. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jan;6(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01145175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutenber E., Katzin B. J., Ernst S., Collins E. J., Mlsna D., Ready M. P., Robertus J. D. Crystallographic refinement of ricin to 2.5 A. Proteins. 1991;10(3):240–250. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutenber E., Robertus J. D. Structure of ricin B-chain at 2.5 A resolution. Proteins. 1991;10(3):260–269. doi: 10.1002/prot.340100310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L., Battelli M. G., Soria M., Lappi D. A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: present status and future prospects. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Apr;10(4):405–412. doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L. Ribosome-inactivating proteins up to date. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
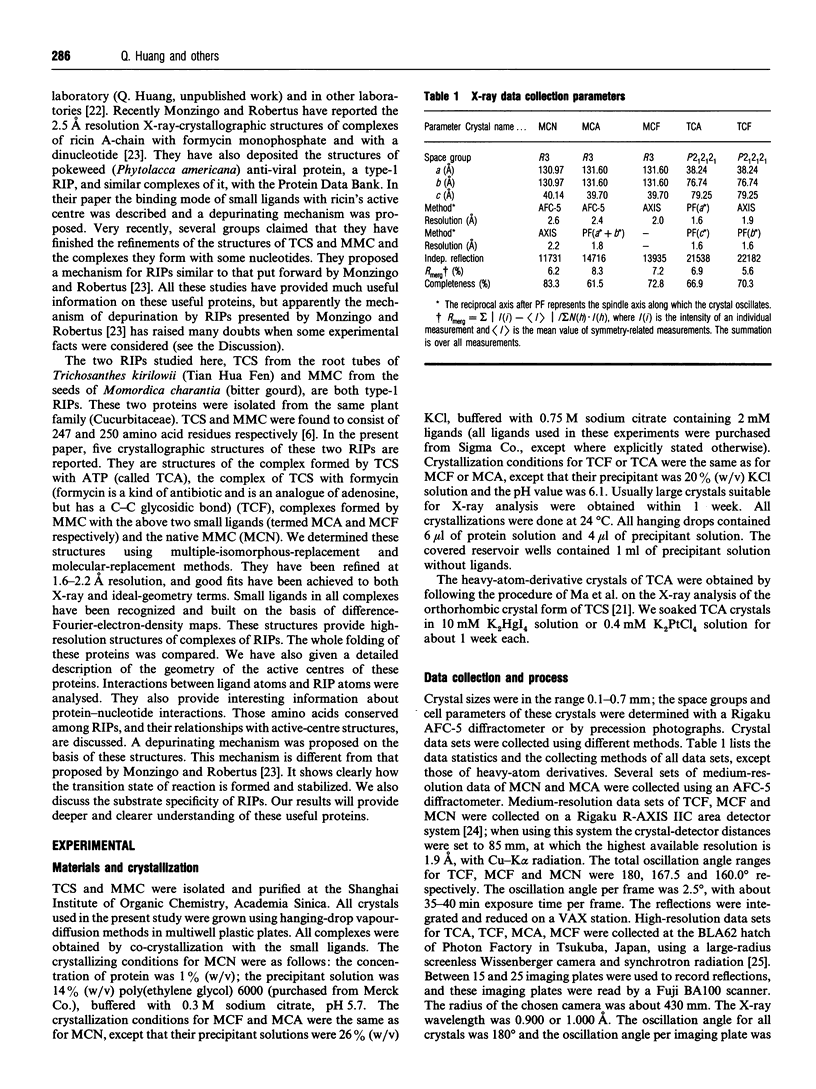
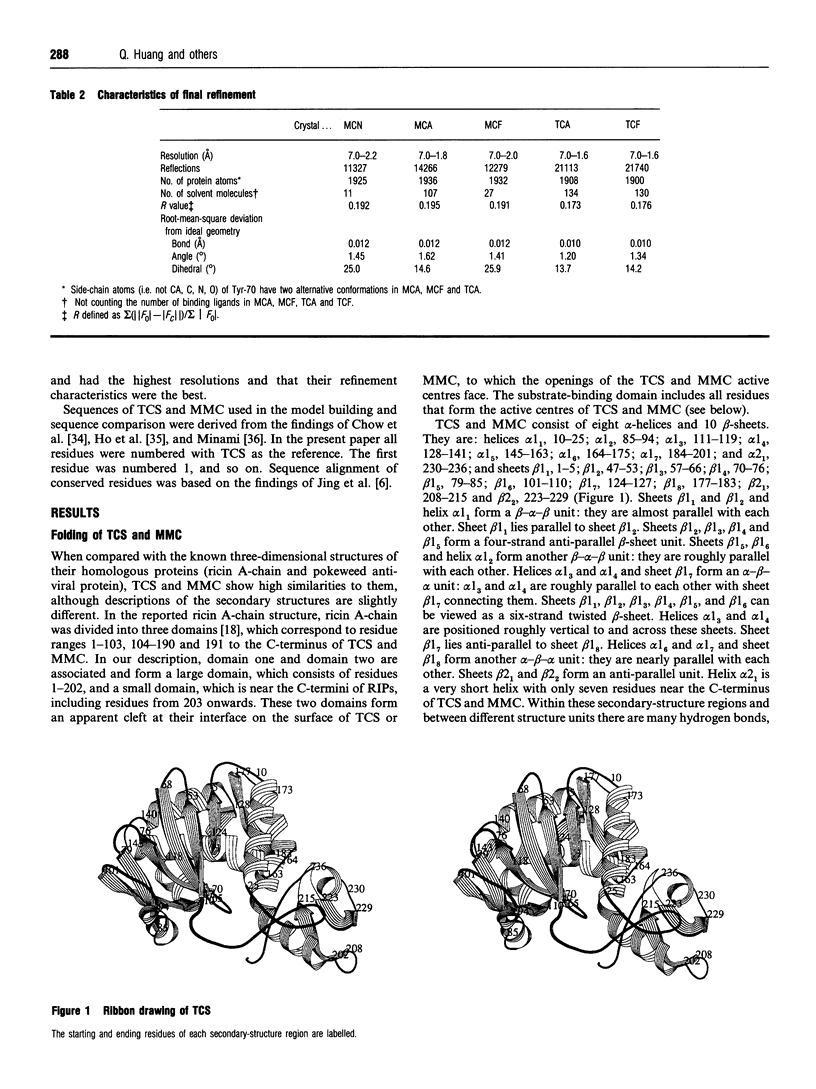
- Vitetta E. S., Fulton R. J., May R. D., Till M., Uhr J. W. Redesigning nature's poisons to create anti-tumor reagents. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1098–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.3317828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung H. W., Li W. W., Feng Z., Barbieri L., Stirpe F. Trichosanthin, alpha-momorcharin and beta-momorcharin: identity of abortifacient and ribosome-inactivating proteins. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1988 Mar;31(3):265–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1988.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. J., Wang J. H. Homology of trichosanthin and ricin A chain. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):477–478. doi: 10.1038/321477b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]