Abstract
Gall-bladder mucin is a densely glycosylated macromolecule which is the primary secretory product of the gall-bladder epithelium. It has been shown to bind cholesterol and other biliary lipids and to promote cholesterol crystal nucleation in vitro. In order to understand the molecular basis for mucin-lipid interactions, bovine gall-bladder mucin cDNAs were identified by expression cloning and were isolated and sequenced. The nucleotide sequences of these cDNAs revealed two distinct tandem repeating domains. One of these domains contained a 20-amino acid tandem repeating sequence enriched in threonine, serine and proline. This sequence was similar to, but not identical with, the short tandem repeating sequences identified previously in other mammalian mucins. The other domain contained a 127-amino acid tandem repeating sequence enriched in cysteine and glycine. This repeat displayed considerable sequence similarity to a family of receptor- and ligand-binding proteins containing scavenger receptor cysteine-rich repeats. By analogy with other proteins containing these cysteine-rich repeats, it is possible that, in gall-bladder mucin, this domain serves as a binding site for hydrophobic ligands such as bilirubin, cholesterol and other biliary lipids.
Full text
PDF




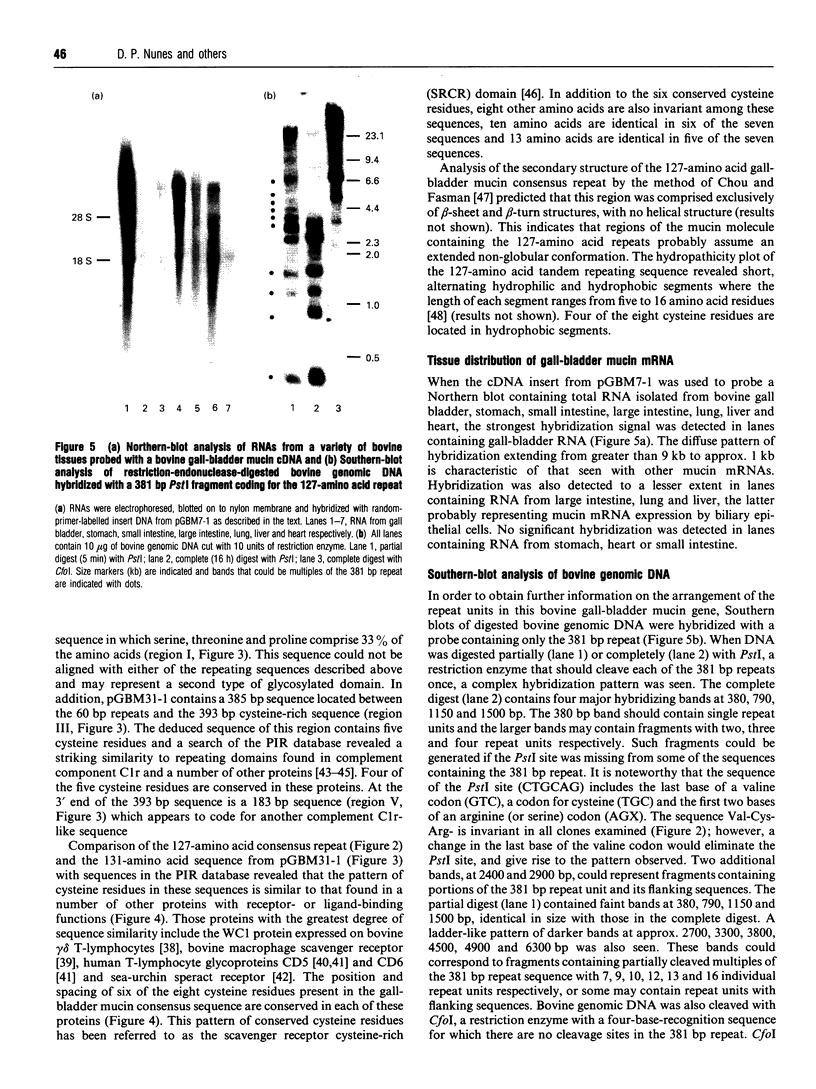


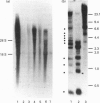
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afdhal N. H., Offner G. D., Murray F. E., Troxler R. F., Smith B. F. Isolation and characterization of peptides from the protein core of bovine gallbladder mucin. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jun;98(6):1633–1641. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91101-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afdhal N. H., Offner G. D., Smith B. F. Characterization of bovine gallbladder mucin. Amino acid sequences of tryptic peptides from the glycosylated domain of the protein core. Gastroenterology. 1990 Nov;99(5):1493–1501. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afdhal N. H., Smith B. F. Cholesterol crystal nucleation: a decade-long search for the missing link in gallstone pathogenesis. Hepatology. 1990 Apr;11(4):699–702. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Melnick M. B., Linsley P. S., Seed B. The lymphocyte glycoprotein CD6 contains a repeated domain structure characteristic of a new family of cell surface and secreted proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):949–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert J. P., Porchet N., Crepin M., Duterque-Coquillaud M., Vergnes G., Mazzuca M., Debuire B., Petitprez D., Degand P. Evidence for different human tracheobronchial mucin peptides deduced from nucleotide cDNA sequences. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Aug;5(2):178–185. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A. E., Sellers L. A., Allen A., Cunliffe W. J., Morris E. R., Ross-Murphy S. B. Properties of gastric and duodenal mucus: effect of proteolysis, disulfide reduction, bile, acid, ethanol, and hypertonicity on mucus gel structure. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava A. K., Woitach J. T., Davidson E. A., Bhavanandan V. P. Cloning and cDNA sequence of a bovine submaxillary gland mucin-like protein containing two distinct domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6798–6802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobek L. A., Tsai H., Biesbrock A. R., Levine M. J. Molecular cloning, sequence, and specificity of expression of the gene encoding the low molecular weight human salivary mucin (MUC7). J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20563–20569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Cahalane M. J. Whither biliary sludge? Gastroenterology. 1988 Aug;95(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90513-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of beta-turns. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85259-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangott L. J., Jordan J. E., Bellet R. A., Garbers D. L. Cloning of the mRNA for the protein that crosslinks to the egg peptide speract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2128–2132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufosse J., Porchet N., Audie J. P., Guyonnet Duperat V., Laine A., Van-Seuningen I., Marrakchi S., Degand P., Aubert J. P. Degenerate 87-base-pair tandem repeats create hydrophilic/hydrophobic alternating domains in human mucin peptides mapped to 11p15. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):329–337. doi: 10.1042/bj2930329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt A. E., Timpte C. S., Abernethy J. L., Zhao Y., Hill R. L. Porcine submaxillary mucin contains a cystine-rich, carboxyl-terminal domain in addition to a highly repetitive, glycosylated domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9678–9686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M., Ashkenas J., Rees D. J., Kingsley D. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Krieger M. An ancient, highly conserved family of cysteine-rich protein domains revealed by cloning type I and type II murine macrophage scavenger receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8810–8814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendler S. J., Lancaster C. A., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Duhig T., Peat N., Burchell J., Pemberton L., Lalani E. N., Wilson D. Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor-associated polymorphic epithelial mucin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15286–15293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Byrd J. C., Hicks J. W., Toribara N. W., Lamport D. T., Kim Y. S. Molecular cloning of human intestinal mucin cDNAs. Sequence analysis and evidence for genetic polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6480–6487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Hicks J. W., Swallow D. M., Lagace R. L., Byrd J. C., Lamport D. T., Siddiki B., Kim Y. S. Molecular cloning of cDNAs derived from a novel human intestinal mucin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91408-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Jr, Hicks J. W., Lagace R. E., Byrd J. C., Toribara N. W., Siddiki B., Fearney F. J., Lamport D. T., Kim Y. S. Molecular cloning of rat intestinal mucin. Lack of conservation between mammalian species. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22733–22738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Jr, Hicks J. W., Toribara N. W., Rothe E. M., Lagace R. E., Kim Y. S. The human MUC2 intestinal mucin has cysteine-rich subdomains located both upstream and downstream of its central repetitive region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21375–21383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Jr, Hicks J. W., Toribara N. W., Siddiki B., Kim Y. S. Molecular cloning of human intestinal mucin (MUC2) cDNA. Identification of the amino terminus and overall sequence similarity to prepro-von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2440–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gum J. R., Jr Mucin genes and the proteins they encode: structure, diversity, and regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Dec;7(6):557–564. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.6.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Hoffmann W. P-domains as shuffled cysteine-rich modules in integumentary mucin C.1 (FIM-C.1) from Xenopus laevis. Polydispersity and genetic polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24620–24624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W. A new repetitive protein from Xenopus laevis skin highly homologous to pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7686–7690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huan L. J., Xu G., Forstner G., Forstner J. A serine, threonine and proline-rich region near the carboxyl-terminus of a rat intestinal mucin peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 17;1132(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. H., Clabby M. L., Dialynas D. P., Huang H. J., Herzenberg L. A., Strominger J. L. Isolation of complementary DNA clones encoding the human lymphocyte glycoprotein T1/Leu-1. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):346–349. doi: 10.1038/323346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journet A., Tosi M. Cloning and sequencing of full-length cDNA encoding the precursor of human complement component C1r. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):783–787. doi: 10.1042/bj2400783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Gum J. R., Jr, Byrd J. C., Toribara N. W. The structure of human intestinal apomucins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 2):S10–S14. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_pt_2.S10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Freeman M., Rohrer L., Zabrecky J., Matsudaira P., Krieger M. Type I macrophage scavenger receptor contains alpha-helical and collagen-like coiled coils. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):531–535. doi: 10.1038/343531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Carey M. C., LaMont J. T. Aspirin prevention of cholesterol gallstone formation in prairie dogs. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.7466399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., LaMont J. T., Carey M. C. Role of gallbladder mucus hypersecretion in the evolution of cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1712–1723. doi: 10.1172/JCI110209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Kurachi K., Sakariassen K. S., Davie E. W. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA coding for human complement C1r. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4855–4863. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meezaman D., Charles P., Daskal E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Martin B. M., Rose M. C. Cloning and analysis of cDNA encoding a major airway glycoprotein, human tracheobronchial mucin (MUC5). J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12932–12939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porchet N., Nguyen V. C., Dufosse J., Audie J. P., Guyonnet-Duperat V., Gross M. S., Denis C., Degand P., Bernheim A., Aubert J. P. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of a novel human tracheo-bronchial mucin cDNA containing tandemly repeated sequences of 48 base pairs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst J. C., Gertzen E. M., Hoffmann W. An integumentary mucin (FIM-B.1) from Xenopus laevis homologous with von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 3;29(26):6240–6244. doi: 10.1021/bi00478a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers L. A., Allen A., Morris E. R., Ross-Murphy S. B. Mucus glycoprotein gels. Role of glycoprotein polymeric structure and carbohydrate side-chains in gel-formation. Carbohydr Res. 1988 Jul 15;178:93–110. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(88)80104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar V., Tan S., Gilmore M. S., Sachdev G. P. Molecular cloning of the carboxy terminus of a canine tracheobronchial mucin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):958–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92297-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimell M. J., Ferguson E. L., Childs S. R., O'Connor M. B. The Drosophila dorsal-ventral patterning gene tolloid is related to human bone morphogenetic protein 1. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90522-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui J., Abe M., Hayes D., Shani E., Yunis E., Kufe D. Isolation and sequencing of a cDNA coding for the human DF3 breast carcinoma-associated antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2320–2323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. F. Human gallbladder mucin binds biliary lipids and promotes cholesterol crystal nucleation in model bile. J Lipid Res. 1987 Sep;28(9):1088–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. F., LaMont J. T. Hydrophobic binding properties of bovine gallbladder mucin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12170–12177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Dekker J. Mucin-type glycoproteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(1-2):57–92. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toribara N. W., Gum J. R., Jr, Culhane P. J., Lagace R. E., Hicks J. W., Petersen G. M., Kim Y. S. MUC-2 human small intestinal mucin gene structure. Repeated arrays and polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):1005–1013. doi: 10.1172/JCI115360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toribara N. W., Roberton A. M., Ho S. B., Kuo W. L., Gum E., Hicks J. W., Gum J. R., Jr, Byrd J. C., Siddiki B., Kim Y. S. Human gastric mucin. Identification of a unique species by expression cloning. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5879–5885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Velde H., von Hoegen I., Luo W., Parnes J. R., Thielemans K. The B-cell surface protein CD72/Lyb-2 is the ligand for CD5. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):662–665. doi: 10.1038/351662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma M., Davidson E. A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a canine tracheobronchial mucin cDNA containing a cysteine-rich domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7144–7148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijngaard P. L., Metzelaar M. J., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I., Clevers H. C. Molecular characterization of the WC1 antigen expressed specifically on bovine CD4-CD8- gamma delta T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3273–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreschner D. H., Hareuveni M., Tsarfaty I., Smorodinsky N., Horev J., Zaretsky J., Kotkes P., Weiss M., Lathe R., Dion A. Human epithelial tumor antigen cDNA sequences. Differential splicing may generate multiple protein forms. Eur J Biochem. 1990 May 20;189(3):463–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G., Huan L. J., Khatri I. A., Wang D., Bennick A., Fahim R. E., Forstner G. G., Forstner J. F. cDNA for the carboxyl-terminal region of a rat intestinal mucin-like peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5401–5407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]