Abstract
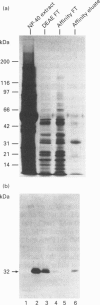
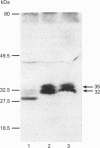
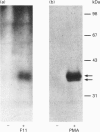
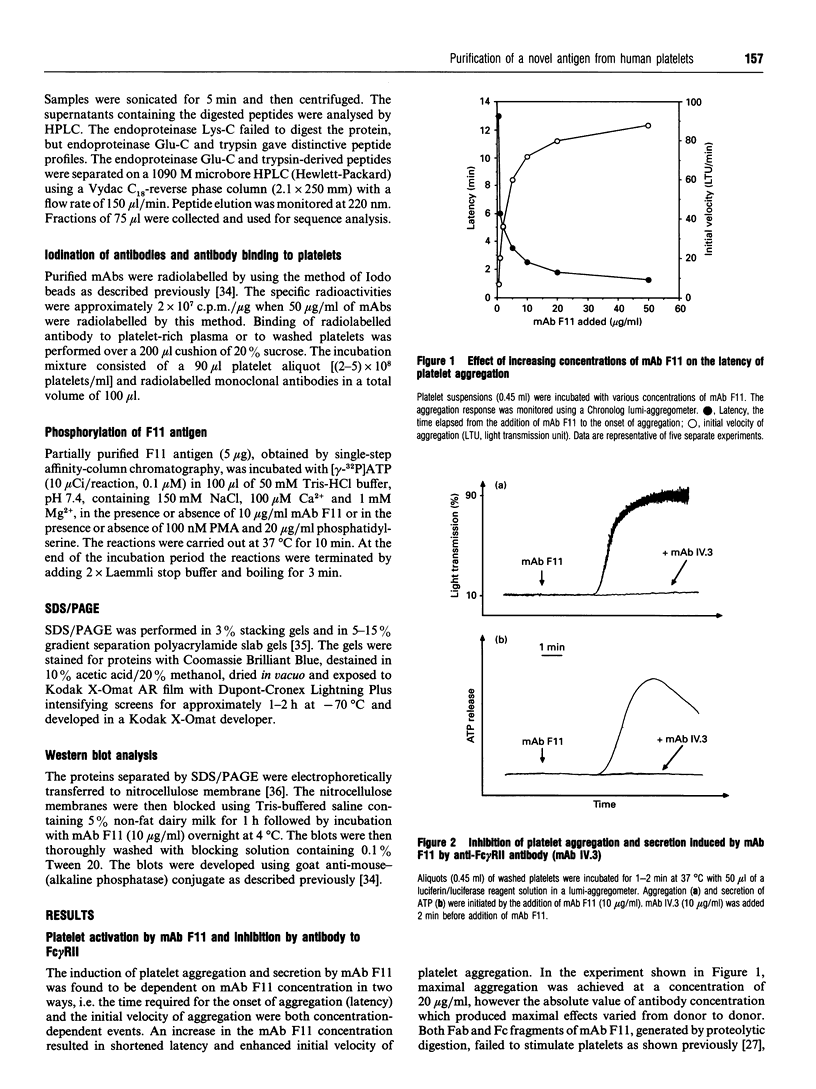
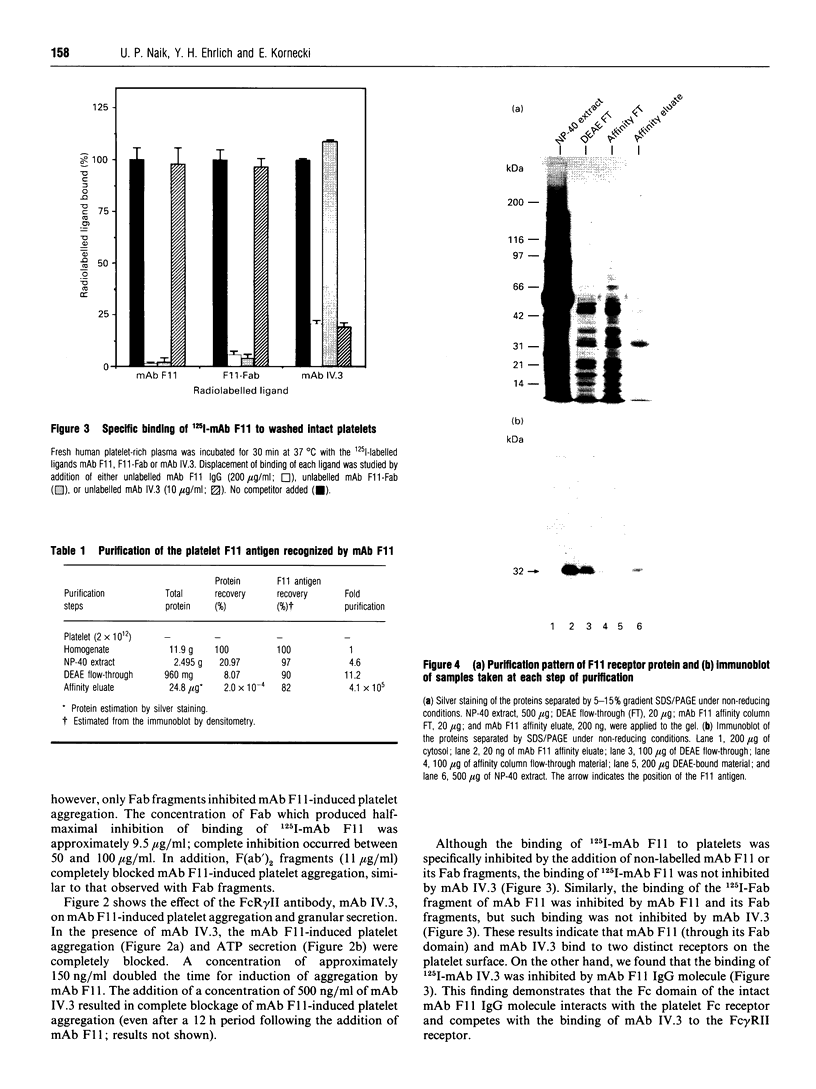
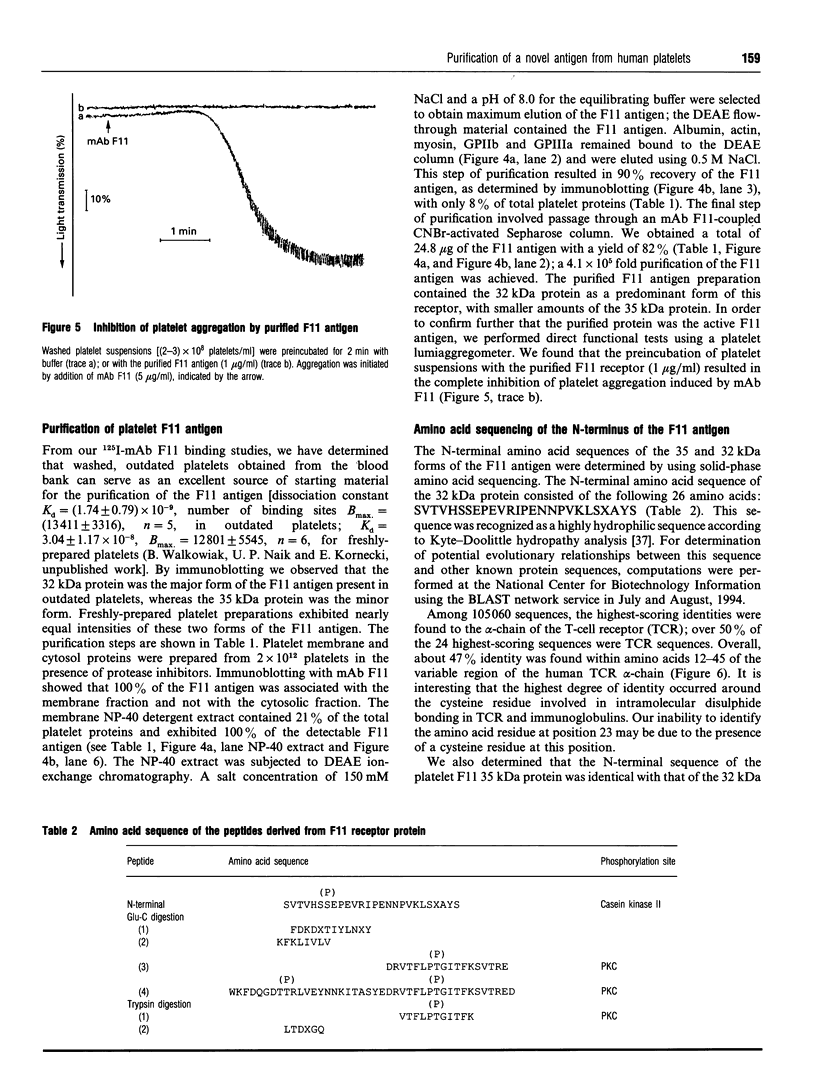
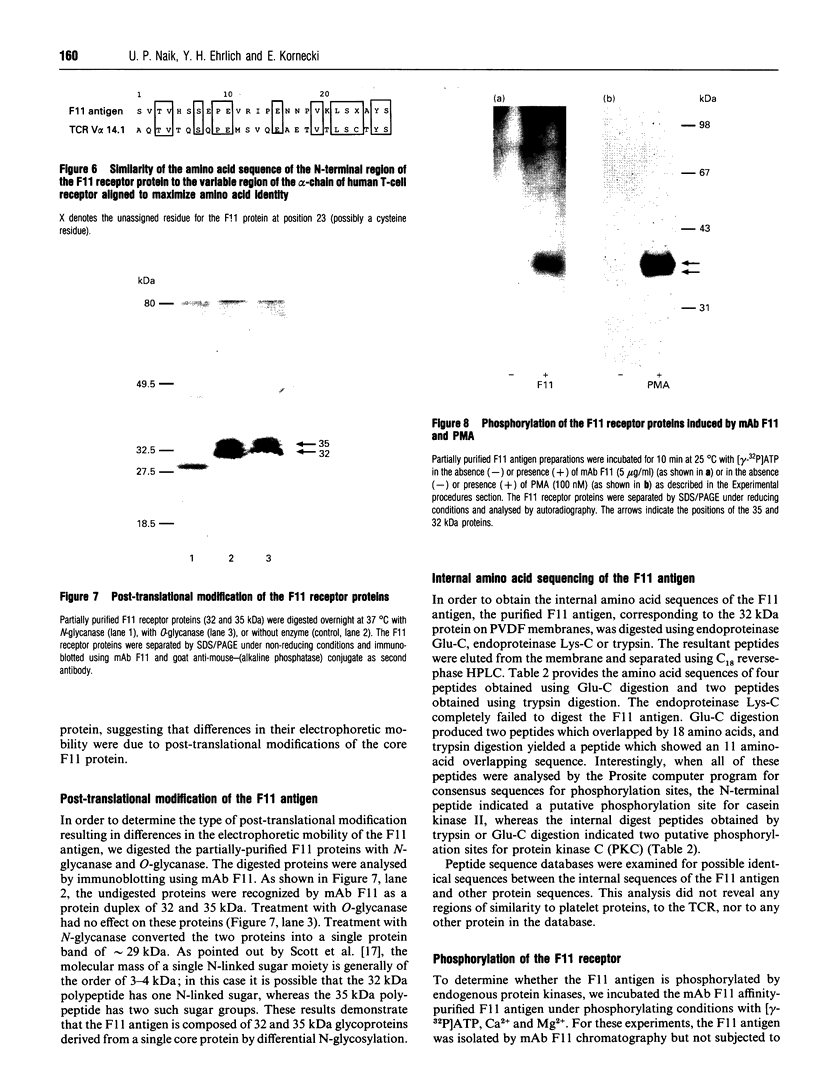
The mechanisms by which a stimulatory monoclonal antibody (mAb), called mAb F11, induces granular secretion and aggregation in human platelets have been characterized. Fab fragments of mAb F11, as well as an mAb directed against the platelet Fc gamma RII receptor (mAb IV.3) were found to inhibit mAb F11-induced platelet secretion and aggregation, indicating that the mAb F11 IgG molecule interacts with the Fc gamma RII receptor through its Fc domain and with its own antigen through its Fab domain. The mAb F11 recognized two platelet proteins of 32 and 35 kDa on the platelet membrane surface, as identified by Western blot analysis. We purified both proteins from human platelet membranes using DEAE-Sepharose chromatography followed by mAb F11 affinity chromatography. When added to platelet-rich plasma, the purified proteins dose-dependently inhibited mAb F11-induced platelet aggregation. The purified protein preparation also competitively inhibited the binding of 125I-labelled mAb F11 to intact platelets. The N-terminal 26 amino acid sequences of both the 32 and 35 kDa proteins were identical and contained a single unblocked serine in the N-terminal position. When digested with N-glycanase, the 32 and 35 kDa proteins were converted into a single approximately 29 kDa protein, indicating that these two proteins are derived from the same core protein but differ in their degree of glycosylation. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of the F11 antigen provided information concerning 68 amino acids and suggested two consensus phosphorylation sites for protein kinase C (PKC). The phosphorylation by PKC of the isolated F11 antigen was observed following stimulation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Databank analysis of the N-terminal and internal amino acid sequences of the F11 antigen indicated that the N-terminal sequence exhibited the highest degree of similarity to the variable region of the alpha-chain of human T-cell receptors (TCR). In contrast, the F11 internal sequences did not exhibit any similarity to the TCR. Our results demonstrate that the F11 antigen is a novel platelet membrane surface glycoprotein which becomes cross-linked with the Fc gamma RII receptor when platelets are activated by the stimulatory mAb F11. These mechanisms may be relevant to the production of immune thrombocytopenia by platelet-activating antibodies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. P., Anderson C. L. Signal transduction by the platelet Fc receptor. Blood. 1990 Sep 15;76(6):1165–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. P., van de Winkel J. G., Anderson C. L. Anti-GPIIb/IIIa (CD41) monoclonal antibody-induced platelet activation requires Fc receptor-dependent cell-cell interaction. Br J Haematol. 1991 Sep;79(1):75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb08010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelot C., Sulpice J. C., Giraud F., Rendu F. Mechanisms involved in platelet activation induced by a monoclonal antibody anti glycoprotein IIb-IIIa: inositol phosphate production is not the primary event. Cell Signal. 1991;3(6):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucheix C., Benoit P., Frachet P., Billard M., Worthington R. E., Gagnon J., Uzan G. Molecular cloning of the CD9 antigen. A new family of cell surface proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J. Homogenization by nitrogen cavitation technique applied to platelet subcellular fractionation. Methods Enzymol. 1992;215:21–32. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)15049-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. C., Worthington R. E., Boucheix C. Stimulus-response coupling in human platelets activated by monoclonal antibodies to the CD9 antigen, a 24 kDa surface-membrane glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):527–535. doi: 10.1042/bj2660527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Reys S., Hoylaerts M. F., De Ley M., Vermylen J., Deckmyn H. Fc-independent cross-linking of a novel platelet membrane protein by a monoclonal antibody causes platelet activation. Blood. 1994 Jul 15;84(2):547–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J., DeMott M., Atherton D., Mische S. M. Internal protein sequence analysis: enzymatic digestion for less than 10 micrograms of protein bound to polyvinylidene difluoride or nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1992 Mar;201(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Leung B., Phillips D. R. A method for purifying the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;151(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Lo S. S., Phillips D. R. Protein sequence of endothelial glycoprotein IIIa derived from a cDNA clone. Identity with platelet glycoprotein IIIa and similarity to "integrin". J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3936–3939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Du X. P., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Monoclonal antibodies to ligand-occupied conformers of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (glycoprotein IIb-IIIa) alter receptor affinity, specificity, and function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17106–17111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Nielsen E. A., Kavaler J., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. Sequence relationships between putative T-cell receptor polypeptides and immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):153–158. doi: 10.1038/308153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara M., Maeda H., Shibata Y., Kume S., Ohashi T. A monoclonal anti-human platelet antibody: a new platelet aggregating substance. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):382–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara M., Takahata K., Yatomi Y., Nakahara K., Kurokawa K. Purification and partial characterization of CD9 antigen of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):270–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80265-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsewood P., Hayward C. P., Warkentin T. E., Kelton J. G. Investigation of the mechanisms of monoclonal antibody-induced platelet activation. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):1019–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Fox C. F., Kouns W. C., McKay C. P., Ballou L. R., Schultz H. E. The activation of human platelets mediated by anti-human platelet p24/CD9 monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Phillips D. R., Walker W. S. Monoclonal antibodies to human platelet glycoprotein IIb beta that initiate distinct platelet responses. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1112–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornecki E., Walkowiak B., Naik U. P., Ehrlich Y. H. Activation of human platelets by a stimulatory monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10042–10048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouns W. C., Jennings L. K. Activation-independent exposure of the GPIIb-IIIa fibrinogen receptor. Thromb Res. 1991 Aug 1;63(3):343–354. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90137-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouns W. C., Wall C. D., White M. M., Fox C. F., Jennings L. K. A conformation-dependent epitope of human platelet glycoprotein IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20594–20601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F., Wolf D., Fox C. F., Kieffer N., Seyer J. M., Fried V. A., Coughlin S. R., Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K. cDNA cloning and expression of platelet p24/CD9. Evidence for a new family of multiple membrane-spanning proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10638–10645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney R. J., Anderson C. L., Ryan D. H., Rosenfeld S. I. Structural polymorphism of the human platelet Fc gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2680–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel M. C., Lecompte T., Champeix P., Favier R., Potevin F., Samama M., Salmon C., Kaplan C. PL2-49, a monoclonal antibody against glycoprotein IIb which is a platelet activator. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jan;71(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb06275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik U. P., Kornecki E., Ehrlich Y. H. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of human platelet surface proteins by an ecto-protein kinase/phosphatase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 17;1092(2):256–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90165-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Magowan C., Chulay J. D. Activation of monocytes and platelets by monoclonal antibodies or malaria-infected erythrocytes binding to the CD36 surface receptor in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):468–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI114188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oquendo P., Hundt E., Lawler J., Seed B. CD36 directly mediates cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Looney R. J., Leddy J. P., Phipps D. C., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Human platelet Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G. Identification as a 40,000-molecular-weight membrane protein shared by monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2317–2322. doi: 10.1172/JCI112242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Ryan D. H., Looney R. J., Anderson C. L., Abraham G. N., Leddy J. P. Human Fc gamma receptors: stable inter-donor variation in quantitative expression on platelets correlates with functional responses. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2869–2873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein E., Boucheix C., Urso I., Carroll R. C. Fc gamma receptor-mediated interplatelet activation by a monoclonal antibody against beta 2 microglobulin. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3040–3046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein E., Kouns W. C., Jennings L. K., Boucheix C., Carroll R. C. Interaction of two GPIIb/IIIa monoclonal antibodies with platelet Fc receptor (Fc gamma RII). Br J Haematol. 1991 May;78(1):80–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. L., Dunn S. M., Jin B., Hillam A. J., Walton S., Berndt M. C., Murray A. W., Krissansen G. W., Burns G. F. Characterization of a novel membrane glycoprotein involved in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13475–13482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of beta-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;221:253–273. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7618-7_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon N. N., Lipsky R. H., Burgess W. H., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of platelet glycoprotein IV (CD36). J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7570–7575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyama Y., Kunicki T. J., Zipf T. F., Ford S. B., Aster R. H. Response of human platelets to activating monoclonal antibodies: importance of Fc gamma RII (CD32) phenotype and level of expression. Blood. 1992 Nov 1;80(9):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkowiak B., Naik U. P., Lange M., Kornecki E. Preferred use of primary radiolabeled anti-platelet monoclonal antibodies. Comparison of immunoblotting methods for the analysis of functional domains on human platelets. Thromb Res. 1992 Dec 1;68(4-5):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(92)90091-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanabu M., Nomura S., Fukuroi T., Soga T., Kondo K., Sone N., Kitada C., Nagata H., Kokawa T., Yasunaga K. Synergistic action in platelet activation induced by an antiplatelet autoantibody in ITP. Br J Haematol. 1991 May;78(1):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]