Abstract
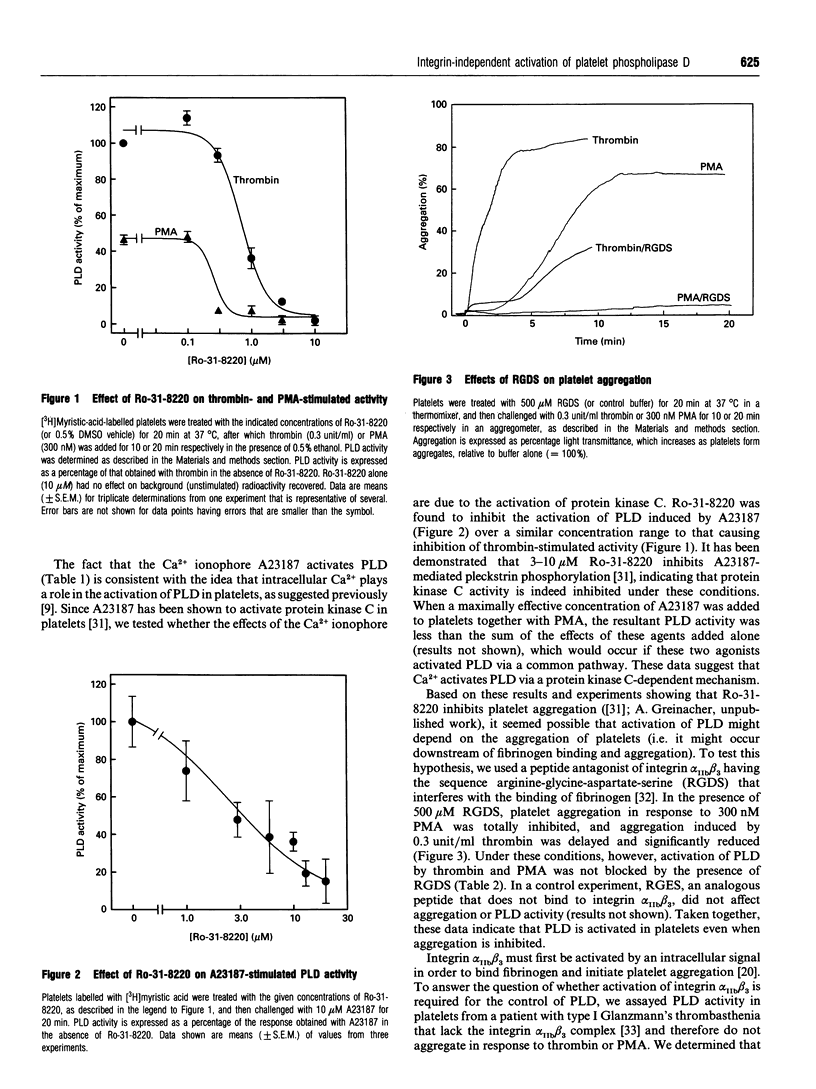
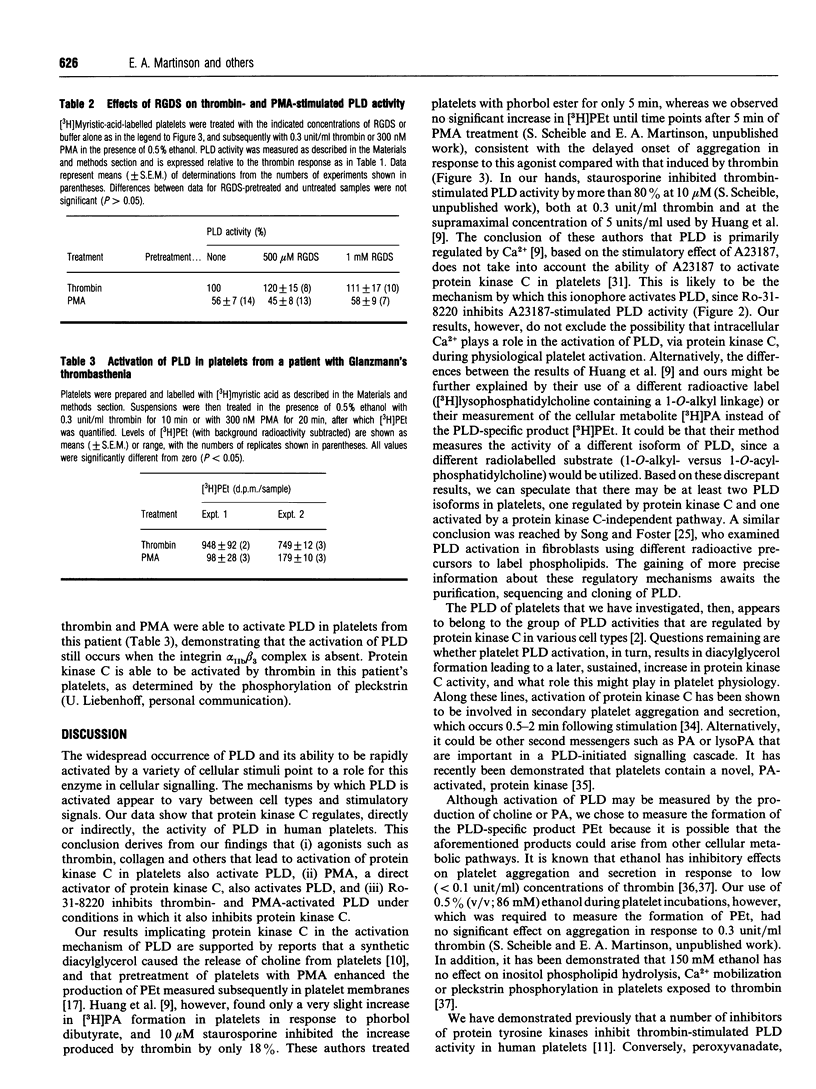
Blood platelets contain phospholipase D (PLD) that is rapidly activated following platelet stimulation. It is currently unclear, however, where PLD fits into the signalling cascade that leads to aggregation and secretion. Therefore we investigated the mechanism of activation of PLD in human platelets, using the formation of the PLD-specific product phosphatidylethanol as a measure of PLD activity. PLD was activated by a number of platelet agonists that also cause the activation of protein kinase C, including thrombin, collagen, the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 and the thromboxane A2-mimetic U46619. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), a direct activator of protein kinase C, also increased PLD activity. A selective inhibitor of protein kinase C, Ro-31-8220, totally blocked the stimulation of PLD by thrombin or PMA under conditions in which it also inhibited phosphorylation of pleckstrin, the major protein kinase C substrate in platelets. Ro-31-8220 additionally inhibited A23187-stimulated PLD activity, indicating that Ca2+ activation of PLD also occurs via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. In the presence of the fibrinogen antagonist peptide RGDS, which inhibits fibrinogen binding to integrin alpha IIb beta 3 and allows little or no aggregation to occur, thrombin- and PMA-stimulated PLD activity was still observed, indicating that PLD activation is not simply a consequence of platelet aggregation. Furthermore, these agonists were able to stimulate PLD in platelets from a Glanzmann's thrombasthenia type I patient lacking the integrin alpha IIb beta 3 complex, which indicates that activation of PLD is also independent of the recruitment of integrin alpha IIb beta 3. Taken together, our results show that PLD is activated by a pathway involving protein kinase C, and suggest that PLD might be involved in signal transduction events occurring upstream of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 activation and fibrinogen binding, which are prerequisites for full platelet aggregation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelot C., Cano E., Grelac F., Saleun S., Druker B. J., Levy-Toledano S., Fischer S., Rendu F. Functional implications of tyrosine protein phosphorylation in platelets. Simultaneous studies with different agonists and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):923–928. doi: 10.1042/bj2840923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benistant C., Rubin R. Ethanol inhibits thrombin-induced secretion by human platelets at a site distinct from phospholipase C or protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):489–497. doi: 10.1042/bj2690489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M. Phospholipase D and cell signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90090-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin S., Grinstein S. Peroxides of vanadate induce activation of phospholipase D in HL-60 cells. Role of tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11908–11916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Brugge J. S. Redistribution of activated pp60c-src to integrin-dependent cytoskeletal complexes in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1863–1871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Thomas G. M., Fensome A., Geny B., Cunningham E., Gout I., Hiles I., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J. Phospholipase D: a downstream effector of ARF in granulocytes. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):523–526. doi: 10.1126/science.8290961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coorssen J. R., Haslam R. J. GTP gamma S and phorbol ester act synergistically to stimulate both Ca(2+)-independent secretion and phospholipase D activity in permeabilized human platelets. Inhibition by BAPTA and analogues. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 25;316(2):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81209-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Keech E., Lawton G., Nixon J. S., Sedgwick A. D., Wadsworth J., Westmacott D., Wilkinson S. E. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. The formation of phosphatidylglycerol and other phospholipids by the transferase activity of phospholipase D. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):205–210. doi: 10.1042/bj1020205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. S., Springer T. A. The dynamic regulation of integrin adhesiveness. Curr Biol. 1994 Jun 1;4(6):506–517. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durieux M. E., Lynch K. R. Signalling properties of lysophosphatidic acid. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jun;14(6):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichholtz T., Jalink K., Fahrenfort I., Moolenaar W. H. The bioactive phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid is released from activated platelets. Biochem J. 1993 May 1;291(Pt 3):677–680. doi: 10.1042/bj2910677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 14;1212(1):26–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greinacher A., Liebenhoff U., Kiefel V., Presek P., Mueller-Eckhardt C. Heparin-associated thrombocytopenia: the effects of various intravenous IgG preparations on antibody mediated platelet activation--a possible new indication for high dose i.v. IgG. Thromb Haemost. 1994 May;71(5):641–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greinacher A., Michels I., Kiefel V., Mueller-Eckhardt C. A rapid and sensitive test for diagnosing heparin-associated thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Dec 2;66(6):734–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha K. S., Exton J. H. Activation of actin polymerization by phosphatidic acid derived from phosphatidylcholine in IIC9 fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1789–1796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha K. S., Exton J. H. Differential translocation of protein kinase C isozymes by thrombin and platelet-derived growth factor. A possible function for phosphatidylcholine-derived diacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10534–10539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillery C. A., Smyth S. S., Parise L. V. Phosphorylation of human platelet glycoprotein IIIa (GPIIIa). Dissociation from fibrinogen receptor activation and phosphorylation of GPIIIa in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14663–14669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A. R., Muszbek L., Kellie S. Translocation of pp60c-src to the cytoskeleton during platelet aggregation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Cabot M. C. Phospholipase D activity in nontransformed and transformed fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 19;1127(3):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90227-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Lynham J. A., Haslam R. J. Purification and characterization of the 47,000-dalton protein phosphorylated during degranulation of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11404–11414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W. A., Blobe G. C., Richards A. L., Hannun Y. A. Identification, partial purification, and characterization of a novel phospholipid-dependent and fatty acid-activated protein kinase from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9729–9735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebenhoff U., Greinacher A., Presek P. The protein tyrosine kinase pp60c-src is activated upon platelet stimulation. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1994 Jul;40(5):645–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luber K., Siess W. Integrin-dependent protein dephosphorylation on tyrosine induced by activation of the thrombin receptor in human platelets. Cell Signal. 1994 Mar;6(3):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson E. A., Goldstein D., Brown J. H. Muscarinic receptor activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Relationship to phosphoinositide hydrolysis and diacylglycerol metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14748–14754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson E. A., Scheible S., Presek P. Inhibition of phospholipase D of human platelets by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1994 Jul;40(5):627–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson E. A., Trilivas I., Brown J. H. Rapid protein kinase C-dependent activation of phospholipase D leads to delayed 1,2-diglyceride accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22282–22287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nofer J. R., Walter M., Kehrel B., Seedorf U., Assmann G. HDL3 activates phospholipase D in normal but not in glycoprotein IIb/IIIa-deficient platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 6;207(1):148–154. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Activation of phospholipase D by chemotactic peptide in HL-60 granulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin M. S., Raben D. M. Molecular species analysis of 1,2-diglycerides stimulated by alpha-thrombin in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8729–8738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. L., Packham M. A., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Fraser Mustard J. Effects of ethanol on pathways of platelet aggregation in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Jun 16;59(3):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. Phosphatidylethanol formation in human platelets: evidence for thrombin-induced activation of phospholipase D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1090–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80744-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher K. A., Classen H. G., Späth M. Platelet aggregation evoked in vitro and in vivo by phosphatidic acids and lysoderivatives: identity with substances in aged serum (DAS). Thromb Haemost. 1979 Aug 31;42(2):631–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Cunningham M., Wiedmer T., Zhao J., Sims P. J., Brass L. F. Regulation of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor function studied with platelets permeabilized by the pore-forming complement proteins C5b-9. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18424–18431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J. Regulation of platelet anchorage and signaling by integrin alpha IIb beta 3. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):224–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth S. S., Hillery C. A., Parise L. V. Fibrinogen binding to purified platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (integrin alpha IIb beta 3) is modulated by lipids. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15568–15577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J., Foster D. A. v-Src activates a unique phospholipase D activity that can be distinguished from the phospholipase D activity activated by phorbol esters. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):711–717. doi: 10.1042/bj2940711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Ezumi Y., Ichinohe T., Okuma M. Involvement of GPIIb-IIIa on human platelets in phosphotyrosine-specific dephosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 15;194(1):472–477. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uings I. J., Thompson N. T., Randall R. W., Spacey G. D., Bonser R. W., Hudson A. T., Garland L. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in receptor coupling to phospholipase D but not phospholipase C in the human neutrophil. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):597–600. doi: 10.1042/bj2810597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meulen J., Haslam R. J. Phorbol ester treatment of intact rabbit platelets greatly enhances both the basal and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated phospholipase D activities of isolated platelet membranes. Physiological activation of phospholipase D may be secondary to activation of phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):693–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2710693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. R., Watson S. P. Synergy between Ca2+ and protein kinase C is the major factor in determining the level of secretion from human platelets. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):277–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2890277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Bielawska A. E., Hannun Y. A. Multiphasic generation of diacylglycerol in thrombin-activated human platelets. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):815–820. doi: 10.1042/bj2820815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


