Abstract
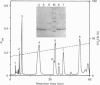
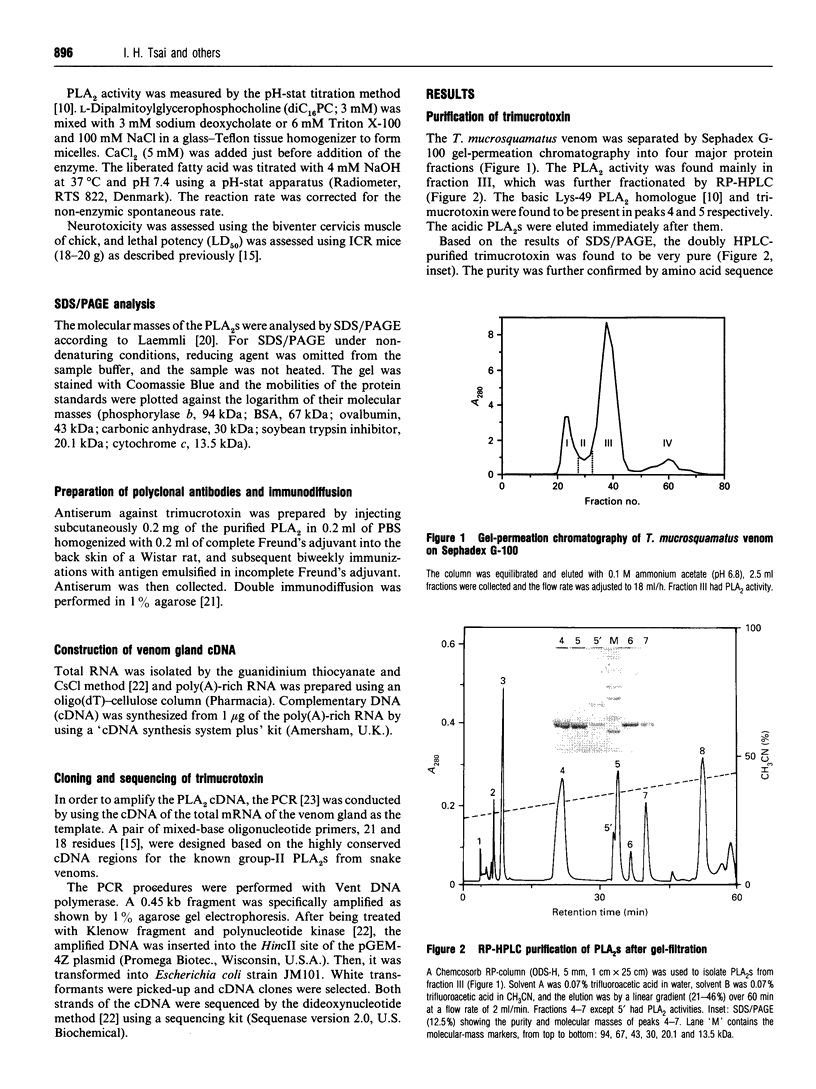
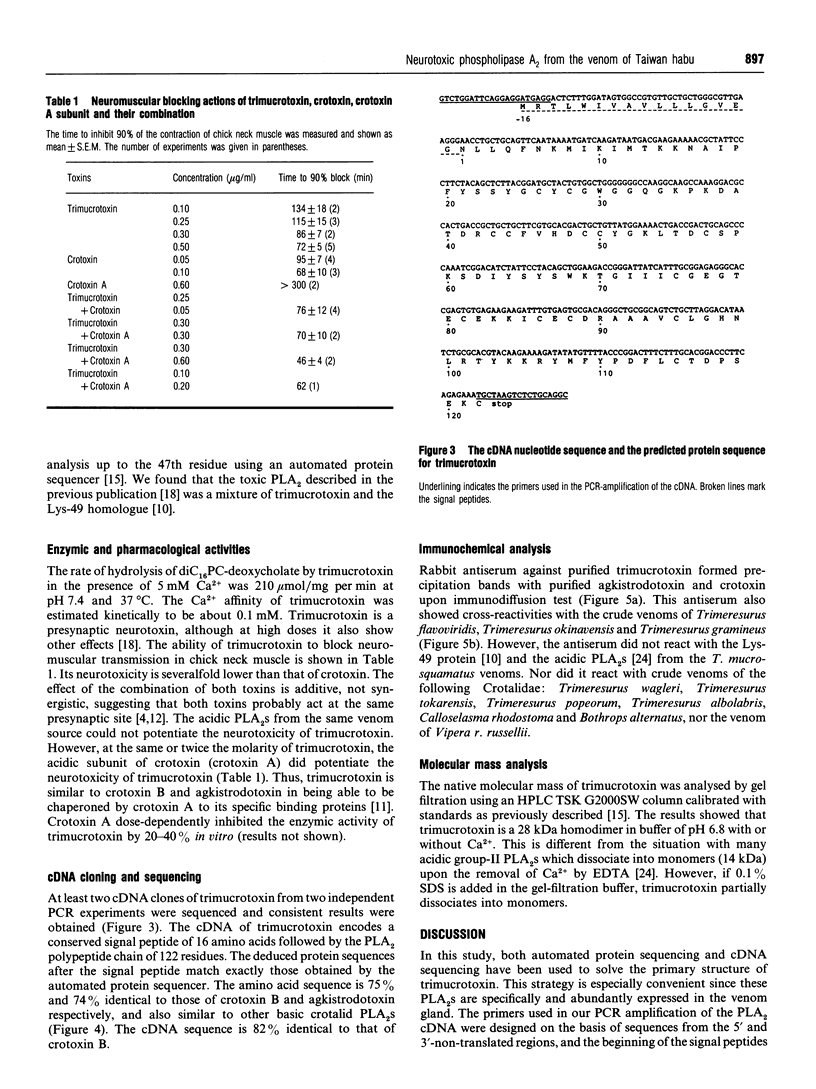
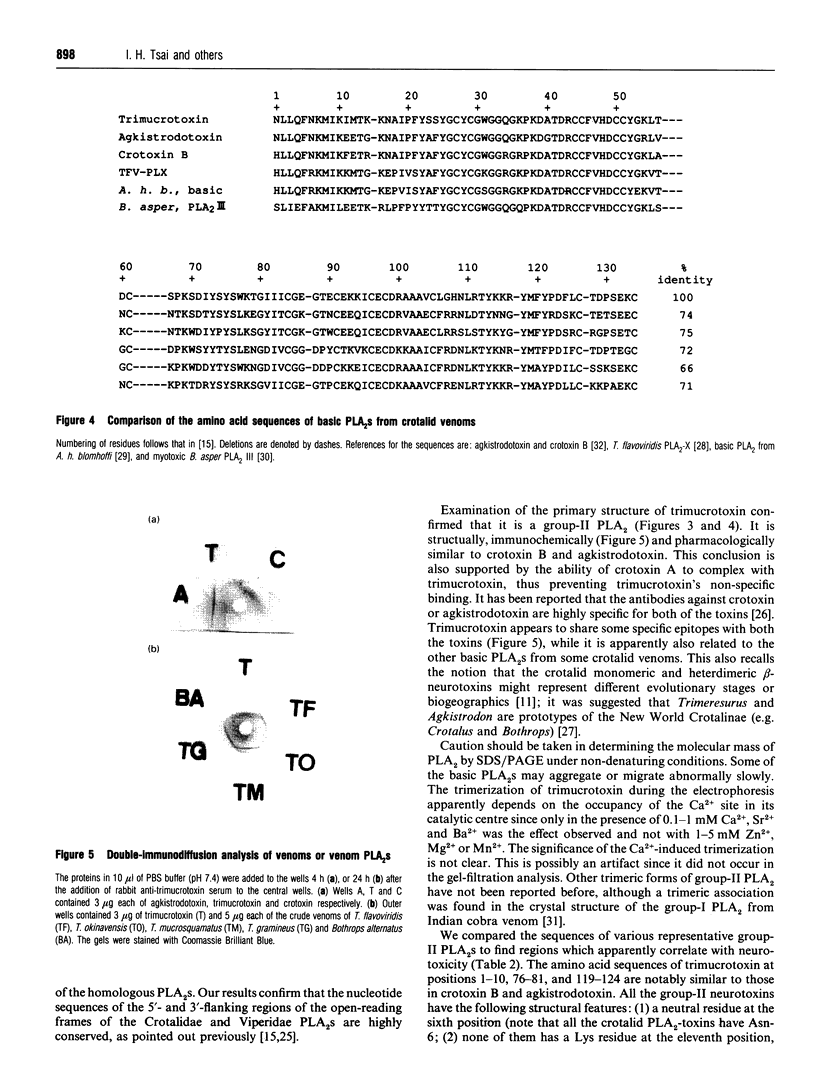
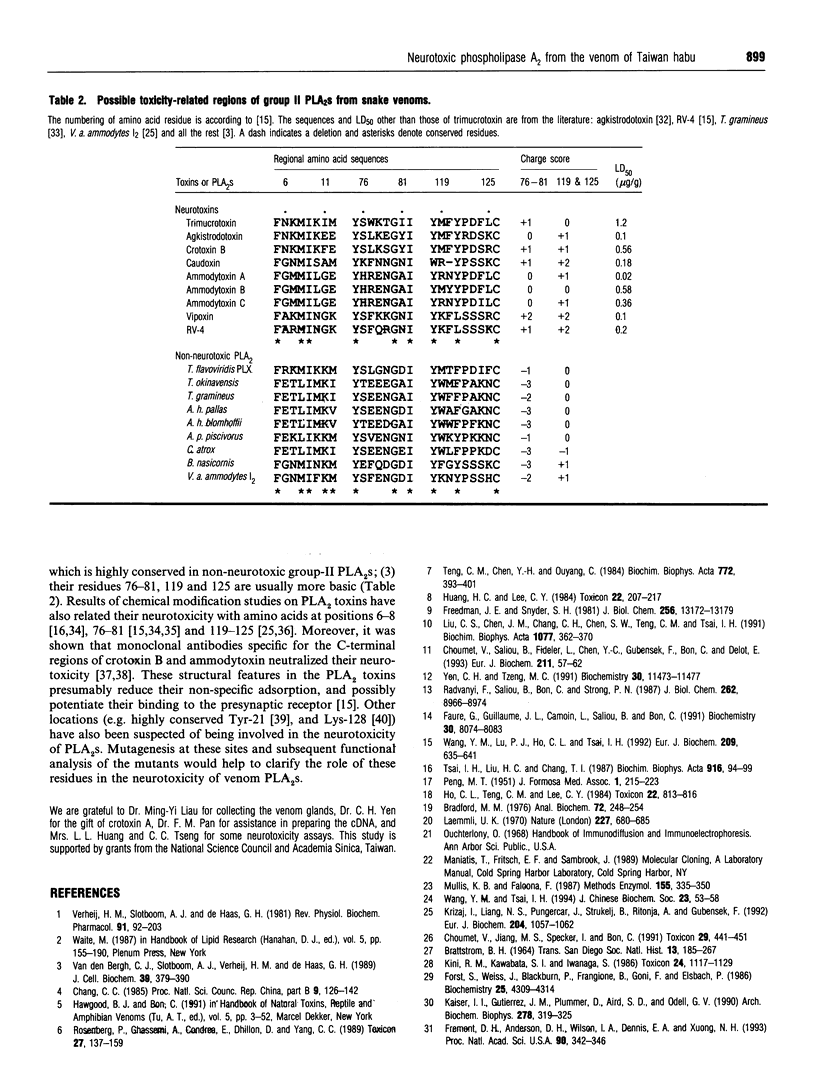
Using gel-filtration chromatography and reverse-phase (RP) HPLC we have purified a presynaptic neurotoxin (designated as trimucrotoxin) from the crude venom of Taiwan habu (Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus). Its complete primary structure was solved by an automated N-terminal sequencing and cDNA sequencing method. The enzyme inhibited the twitch of the chick biventer cervicis muscle at 0.1-1 micrograms/ml and showed lethality in mice (LD50 = 1.2 micrograms/g, when given intravenously). Trimucrotoxin exists mainly as a homodimer of 14 kDa subunits as shown by a gel-filtration experiment, and dissociates into monomers during SDS/PAGE in the absence of Ca2+. However, most of trimucrotoxin migrated as slowly as a trimer during nondenaturing SDS/PAGE in the presence of Ca2+ or Sr2+. Its amino acid sequence identity to crotoxin B and agkistrodotoxin is about 75%, and its cDNA sequence is 82% identical to that of crotoxin B. Rabbit antiserum against trimucrotoxin also cross-reacted with the other crotalid neurotoxic phospholipases A2. Furthermore, the purified acidic subunit of crotoxin potentiated the neurotoxicity of trimucrotoxin. A comparison of the sequences of these crotalid neurotoxins revealed some common features of the possible neurotoxic sites, including residues 6, 11, 76-81 and 119-125.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C. Neurotoxins with phospholipase A2 activity in snake venoms. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1985 Apr;9(2):126–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
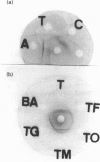
- Choumet V., Faure G., Robbe-Vincent A., Saliou B., Mazié J. C., Bon C. Immunochemical analysis of a snake venom phospholipase A2 neurotoxin, crotoxin, with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1992 Jul-Aug;29(7-8):871–882. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(92)90125-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choumet V., Jiang M. S., Specker I., Bon C. Immunochemical cross-reactivity of two phospholipase A2 neurotoxins, agkistrodotoxin and crotoxin. Toxicon. 1991;29(4-5):441–451. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90018-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choumet V., Saliou B., Fideler L., Chen Y. C., Gubensek F., Bon C., Delot E. Snake-venom phospholipase A2 neurotoxins. Potentiation of a single-chain neurotoxin by the chaperon subunit of a two-component neurotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb19869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curin-Serbec V., Délot E., Faure G., Saliou B., Gubensek F., Bon C., Choumet V. Antipeptide antibodies directed to the C-terminal part of ammodytoxin A react with the PLA2 subunit of crotoxin and neutralize its pharmacological activity. Toxicon. 1994 Nov;32(11):1337–1348. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(94)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure G., Guillaume J. L., Camoin L., Saliou B., Bon C. Multiplicity of acidic subunit isoforms of crotoxin, the phospholipase A2 neurotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom, results from posttranslational modifications. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):8074–8083. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Blackburn P., Frangione B., Goni F., Elsbach P. Amino acid sequence of a basic Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii phospholipase A2. Possible role of NH2-terminal lysines in action on phospholipids of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4309–4314. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman J. E., Snyder S. H. Vipoxin. A protein from Russell's viper venom with high affinity for biogenic amine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13172–13179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremont D. H., Anderson D. H., Wilson I. A., Dennis E. A., Xuong N. H. Crystal structure of phospholipase A2 from Indian cobra reveals a trimeric association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):342–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa T., Nose T., Shimohigashi Y., Ogawa T., Oda N., Nakashima K., Chang C. C., Ohno M. Purification, sequencing and characterization of single amino acid-substituted phospholipase A2 isozymes from Trimeresurus gramineus (green habu snake) venom. Toxicon. 1993 Aug;31(8):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(93)90255-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. L., Teng C. M., Lee C. Y. Presynaptic and musculotropic effects of a basic phospholipase A2 from the Formosan habu (Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus) venom. Toxicon. 1984;22(5):813–816. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Lee C. Y. Isolation and pharmacological properties of phospholipases A2 from Vipera russelli (Russell's viper) snake venom. Toxicon. 1984;22(2):207–217. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser I. I., Gutierrez J. M., Plummer D., Aird S. D., Odell G. V. The amino acid sequence of a myotoxic phospholipase from the venom of Bothrops asper. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 1;278(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Kawabata S. I., Iwanaga S. Comparison of amino terminal region of three isoenzymes of phospholipases A2 (TFV PL-Ia, TFV PL-Ib, TFV PL-X) from Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu snake) venom and the complete amino acid sequence of the basic phospholipase, TFV PL-X. Toxicon. 1986;24(11-12):1117–1129. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Zhang J., Xu K., Kagamiyama H. Amino acid sequence of a presynaptic neurotoxin, agkistrodotoxin, from the venom of Agkistrodon halys Pallas. J Biochem. 1989 Feb;105(2):196–203. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. S., Chen J. M., Chang C. H., Chen S. W., Teng C. M., Tsai I. H. The amino acid sequence and properties of an edema-inducing Lys-49 phospholipase A2 homolog from the venom of Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 29;1077(3):362–370. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90552-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollier P., Chwetzoff S., Bouet F., Harvey A. L., Ménez A. Tryptophan 110, a residue involved in the toxic activity but not in the enzymatic activity of notexin. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radvanyi F., Saliou B., Bon C., Strong P. N. The interaction between the presynaptic phospholipase neurotoxins beta-bungarotoxin and crotoxin and mixed detergent-phosphatidylcholine micelles. A comparison with non-neurotoxic snake venom phospholipases A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):8966–8974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P., Ghassemi A., Condrea E., Dhillon D., Yang C. C. Do chemical modifications dissociate between the enzymatic and pharmacological activities of beta bungarotoxin and notexin? Toxicon. 1989;27(2):137–159. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki C., Sugama A., Yanagita A., Tamiya N., Rowan E. G., Harvey A. L. Effects of chemical modifications of Pa-11, a phospholipase A2 from the venom of Australian king brown snake (Pseudechis australis), on its biological activities. Toxicon. 1990;28(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90012-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. M., Chen Y. H., Ouyang C. Biphasic effect on platelet aggregation by phospholipase a purified from Vipera russellii snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 30;772(3):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai I. H., Liu H. C., Chang T. Toxicity domain in presynaptically toxic phospholipase A2 of snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 5;916(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Yen C. H., Hseu M. J., Dupureur C. M., Tsai M. D. Conversion of bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at a single site into a competitor of neurotoxic phospholipases A2 by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 3;270(5):2120–2123. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij H. M., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H. Structure and function of phospholipase A2. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;91:91–203. doi: 10.1007/3-540-10961-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. M., Lu P. J., Ho C. L., Tsai I. H. Characterization and molecular cloning of neurotoxic phospholipases A2 from Taiwan viper (Vipera russelli formosensis). Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Chang L. S. Dissociation of lethal toxicity and enzymic activity of notexin from Notechis scutatus scutatus (Australian-tiger-snake) venom by modification of tyrosine residues. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):739–744. doi: 10.1042/bj2800739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C. H., Tzeng M. C. Identification of a new binding protein for crotoxin and other neurotoxic phospholipase A2s on brain synaptic membranes. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 3;30(48):11473–11477. doi: 10.1021/bi00112a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bergh C. J., Slotboom A. J., Verheij H. M., de Haas G. H. The role of Asp-49 and other conserved amino acids in phospholipases A2 and their importance for enzymatic activity. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Apr;39(4):379–390. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]