Abstract
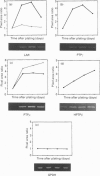
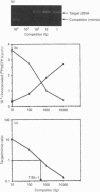
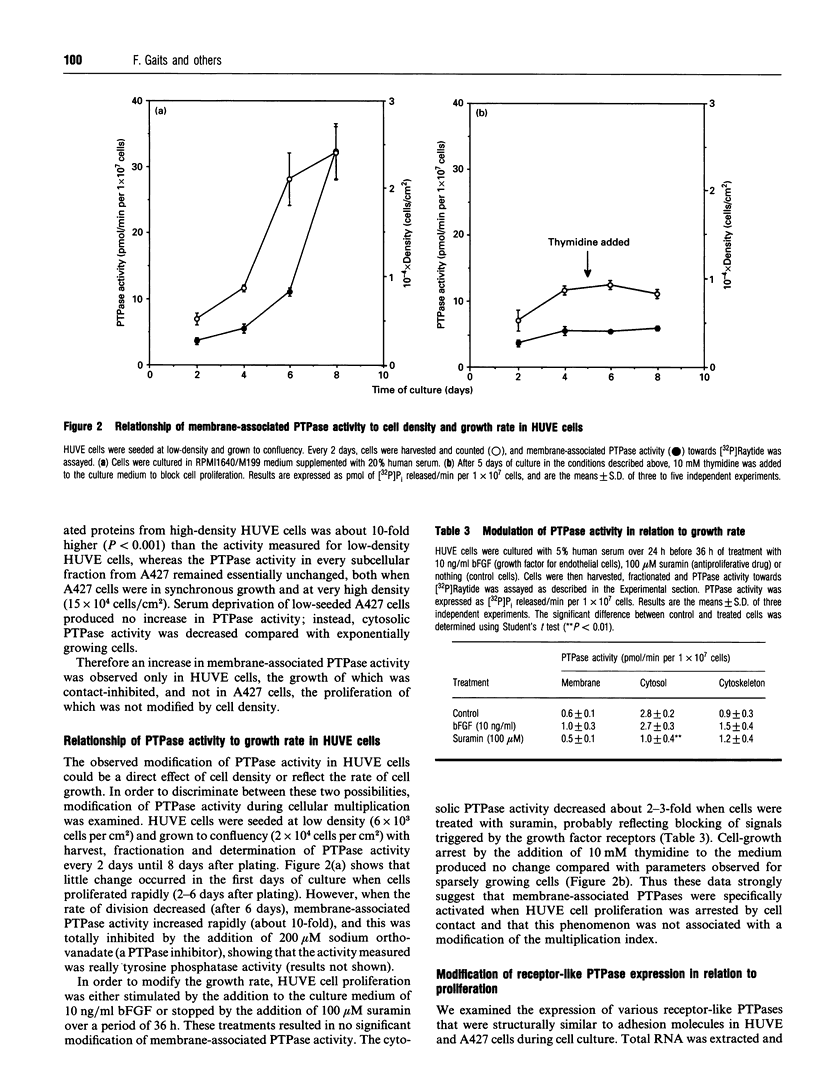
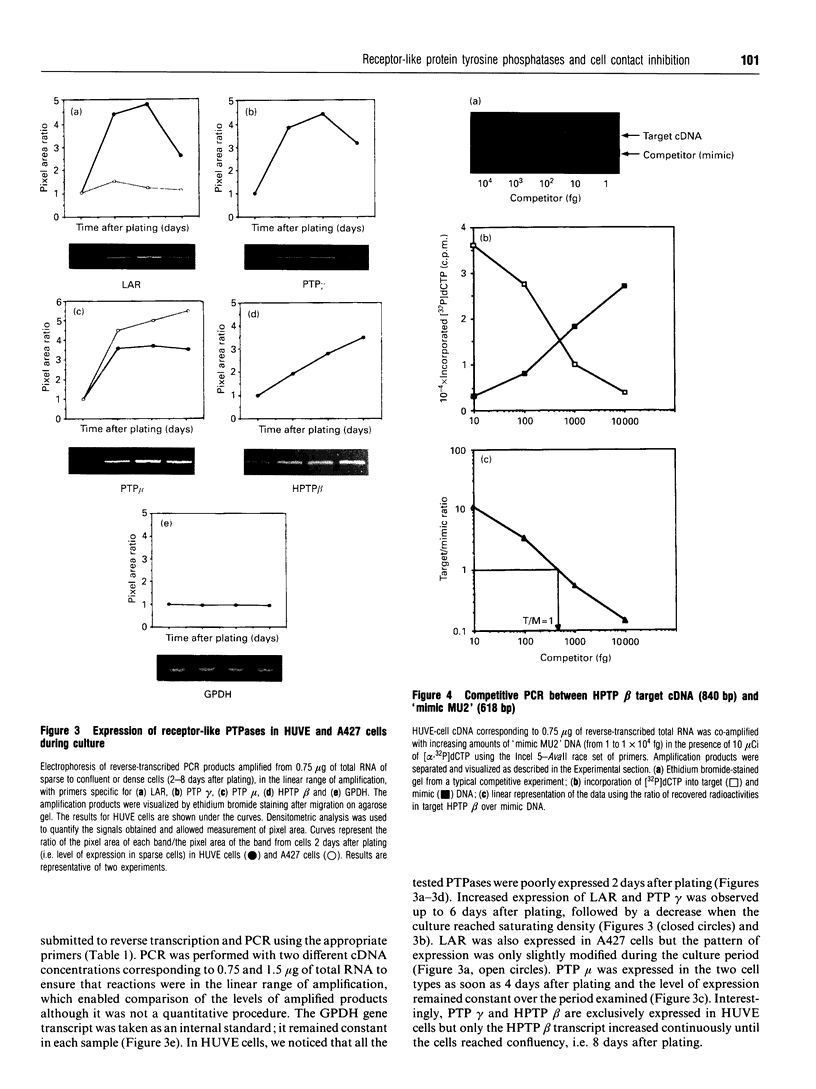
Protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) activity was examined in two cell lines: human umbilical vein endothelial (HUVE) cells, which display contact inhibition of cell growth, and A427 human adenocarcinoma cells, which have lost this ability. HUVE cells harvested at high density displayed a 10-fold increase in membrane-associated PTPase activity. A427 cells exhibited no such phenomenon. Moreover, modification of HUVE cell growth rate by a stimulating agent such as basic fibroblast growth factor or by blocking compounds such as thymidine or suramin resulted in no change in PTPase activity, suggesting that the observed increase in membrane-associated activity at confluency was specific for cell-cell-contact-directed growth arrest. The expression of various PTPase mRNAs was examined in HUVE and A427 cells. Of the receptor-like PTPases tested, two were exclusively expressed in HUVE cells (PTP gamma and HPTP beta). Only HPTP beta, which is structurally similar in its extracellular region to cell-adhesion receptors of the immunoglobulin superfamily, displayed a pattern of expression related to the increase in PTPase activity. Competitive PCR was used to quantify its expression during cell culture. A 12-fold increase in HPTP beta mRNA expression was detected and it parallelled the time course of PTPase activity. This observation strongly implicates receptor-like PTPases in density-dependent growth arrest.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brady-Kalnay S. M., Flint A. J., Tonks N. K. Homophilic binding of PTP mu, a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, can mediate cell-cell aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):961–972. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady-Kalnay S. M., Tonks N. K. Identification of the homophilic binding site of the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP mu. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28472–28477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady-Kalnay S. M., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: from structure to function. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;4(3):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Shimer S., Johnson K. A., Hill D. E., Bruskin A. M. Effect of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B expression on transformation by the human neu oncogene. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 15;52(2):478–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. D., Piccione E., Wolf G., Benett A. M., Lechleider R. J., Neel B. G., Shoelson S. E. SH-PTP2/Syp SH2 domain binding specificity is defined by direct interactions with platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor, epidermal growth factor receptor, and insulin receptor substrate-1-derived phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10467–10474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaits F., Li R. Y., Ragab A., Selves J., Ragab-Thomas J. M., Chap H. Implication of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase in human lung cancer. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1994 Jul;40(5):677–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebbink M. F., Zondag G. C., Wubbolts R. W., Beijersbergen R. L., van Etten I., Moolenaar W. H. Cell-cell adhesion mediated by a receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16101–16104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Bieber A. J., Rehm E. J., Snow P. M., Traquina Z. R., Hortsch M., Patel N. H., Goodman C. S. Molecular genetics of neuronal recognition in Drosophila: evolution and function of immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:327–340. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Broyles S. S., Dixon J. E. A Tyr/Ser protein phosphatase encoded by vaccinia virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):359–362. doi: 10.1038/350359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder K. W., Owen P., Wong L. K., Aebersold R., Clark-Lewis I., Jirik F. R. Characterization and kinetic analysis of the intracellular domain of human protein tyrosine phosphatase beta (HPTP beta) using synthetic phosphopeptides. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 1;298(Pt 2):395–401. doi: 10.1042/bj2980395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hullin F., Raynal P., Ragab-Thomas J. M., Fauvel J., Chap H. Effect of dexamethasone on prostaglandin synthesis and on lipocortin status in human endothelial cells. Inhibition of prostaglandin I2 synthesis occurring without alteration of arachidonic acid liberation and of lipocortin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3506–3513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh M., Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Saito H. Purification and characterization of the catalytic domains of the human receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases HPTP beta, leukocyte common antigen (LCA), and leukocyte common antigen-related molecule (LAR). J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12356–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K. Transformation of cells by an inhibitor of phosphatases acting on phosphotyrosine in proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourembanas S., Faller D. V. Platelet-derived growth factor production by human umbilical vein endothelial cells is regulated by basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4456–4459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger N. X., Streuli M., Saito H. Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3241–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhné M. R., Pawson T., Lienhard G. E., Feng G. S. The insulin receptor substrate 1 associates with the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11479–11481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaForgia S., Morse B., Levy J., Barnea G., Cannizzaro L. A., Li F., Nowell P. C., Boghosian-Sell L., Glick J., Weston A. Receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase gamma is a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome region 3p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R. Y., Gaits F., Ragab A., Ragab-Thomas J. M., Chap H. Translocation of an SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SH-PTP1) to the cytoskeleton of thrombin-activated platelets. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 18;343(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R. Y., Gaits F., Ragab A., Ragab-Thomas J. M., Chap H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of an SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase is coupled to platelet thrombin receptor via a pertussis toxin-sensitive heterotrimeric G-protein. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2519–2526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz U., Ravichandran K. S., Pei D., Walsh C. T., Burakoff S. J., Neel B. G. Lck-dependent tyrosyl phosphorylation of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP1 in murine T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1824–1834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Activation of phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity by reduction of cell-substrate adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11177–11181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell proliferation by vanadate is specific for microvascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jun;151(3):549–554. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041510314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Suzuki T., Uchida T., Inazawa J., Ariyama T., Matsuda K., Horita K., Noguchi H., Mizuno H., Sakamoto C. Molecular cloning of a human transmembrane-type protein tyrosine phosphatase and its expression in gastrointestinal cancers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2075–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., DeChavigny A., Johnson C. E., Hamada J., Stein C. A., Nicolson G. L. Suramin. A potent inhibitor of melanoma heparanase and invasion. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9661–9666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oon S. H., Hong A., Yang X., Chia W. Alternative splicing in a novel tyrosine phosphatase gene (DPTP4E) of Drosophila melanogaster generates two large receptor-like proteins which differ in their carboxyl termini. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23964–23971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostman A., Yang Q., Tonks N. K. Expression of DEP-1, a receptor-like protein-tyrosine-phosphatase, is enhanced with increasing cell density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9680–9684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen C. J., Tan Y. H., Guy G. R. Protein phosphatases in cell signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):1000–1007. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90132-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen C. J., Tong P. H. Elevation of membrane tyrosine phosphatase activity in density-dependent growth-arrested fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6996–7000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pötgens A. J., Lubsen N. H., van Altena G., Schoenmakers J. G., Ruiter D. J., de Waal R. M. Measurement of tissue factor messenger RNA levels in human endothelial cells by a quantitative RT-PCR assay. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Feb;71(2):208–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramponi G., Ruggiero M., Raugei G., Berti A., Modesti A., Degl'Innocenti D., Magnelli L., Pazzagli C., Chiarugi V. P., Camici G. Overexpression of a synthetic phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase gene inhibits normal and transformed cell growth. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jun 19;51(4):652–656. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southey M. C., Findlay D. M., Kemp B. E. Regulation of membrane-associated tyrosine phosphatases in UMR 106.06 osteoblast-like cells. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 15;305(Pt 2):485–490. doi: 10.1042/bj3050485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Thai T., Tang M., Saito H. Distinct functional roles of the two intracellular phosphatase like domains of the receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases LCA and LAR. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2399–2407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto S., Wandless T. J., Shoelson S. E., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Activation of the SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase, SH-PTP2, by phosphotyrosine-containing peptides derived from insulin receptor substrate-1. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13614–13622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Wharram B. L., Goyal M., Wiggins J. E., Holzman L. B., Wiggins R. C. GLEPP1, a renal glomerular epithelial cell (podocyte) membrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Identification, molecular cloning, and characterization in rabbit. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19953–19962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian S. S., Tsoulfas P., Zinn K. Three receptor-linked protein-tyrosine phosphatases are selectively expressed on central nervous system axons in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):675–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Takahashi T., Ueda R., Hibi K., Saito H., Takahashi T. Molecular analysis of the protein tyrosine phosphatase gamma gene in human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 15;52(12):3506–3509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Matozaki T., Noguchi T., Yamao T., Horita K., Suzuki T., Fujioka Y., Sakamoto C., Kasuga M. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of Tyr538 and the catalytic activity of PTP1C, a protein tyrosine phosphatase with Src homology-2 domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12220–12228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. M., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:101–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Pallen C. J. Expression and characterization of wild type, truncated, and mutant forms of the intracellular region of the receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase HPTP beta. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16696–16702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. H., Seow K. T., Bahri S. M., Oon S. H., Chia W. Two Drosophila receptor-like tyrosine phosphatase genes are expressed in a subset of developing axons and pioneer neurons in the embryonic CNS. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):661–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung Y. G., Berg K. L., Pixley F. J., Angeletti R. H., Stanley E. R. Protein tyrosine phosphatase-1C is rapidly phosphorylated in tyrosine in macrophages in response to colony stimulating factor-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23447–23450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zander N. F., Cool D. E., Diltz C. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Suppression of v-fms-induced transformation by overexpression of a truncated T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1175–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Wang Y., Pallen C. J. Cell transformation and activation of pp60c-src by overexpression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):336–339. doi: 10.1038/359336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]