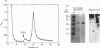Abstract
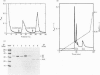
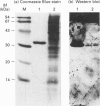
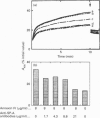
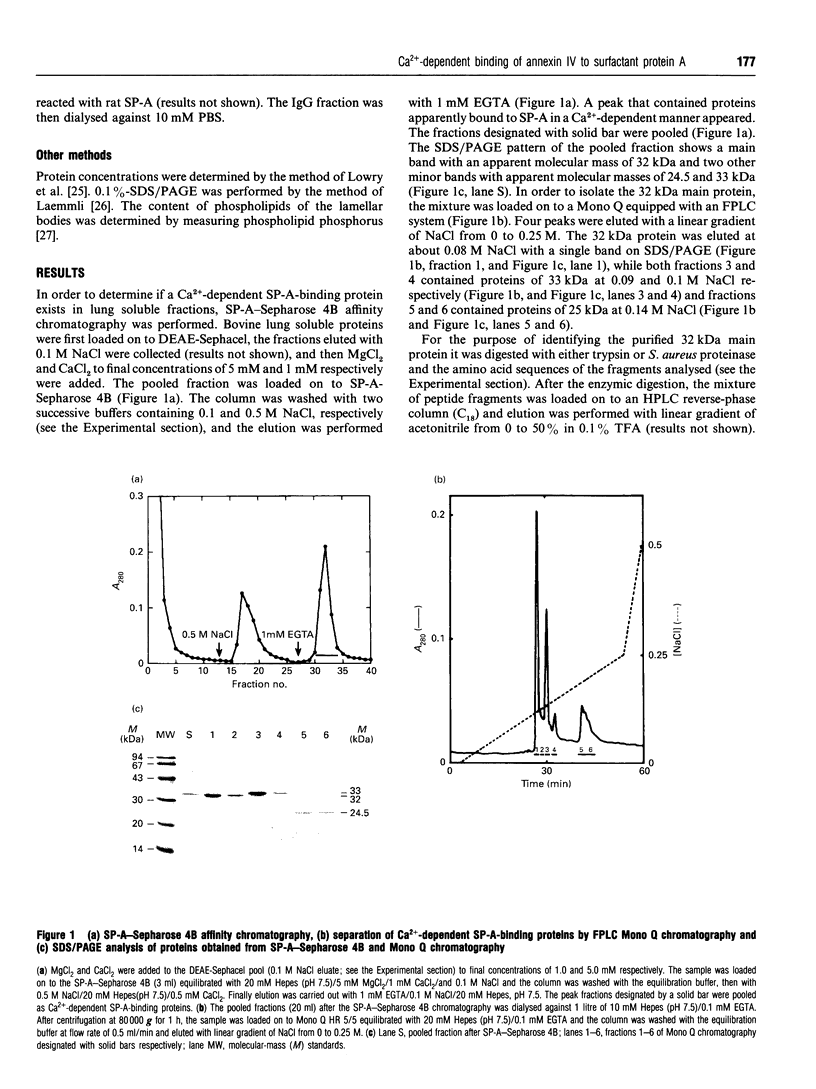
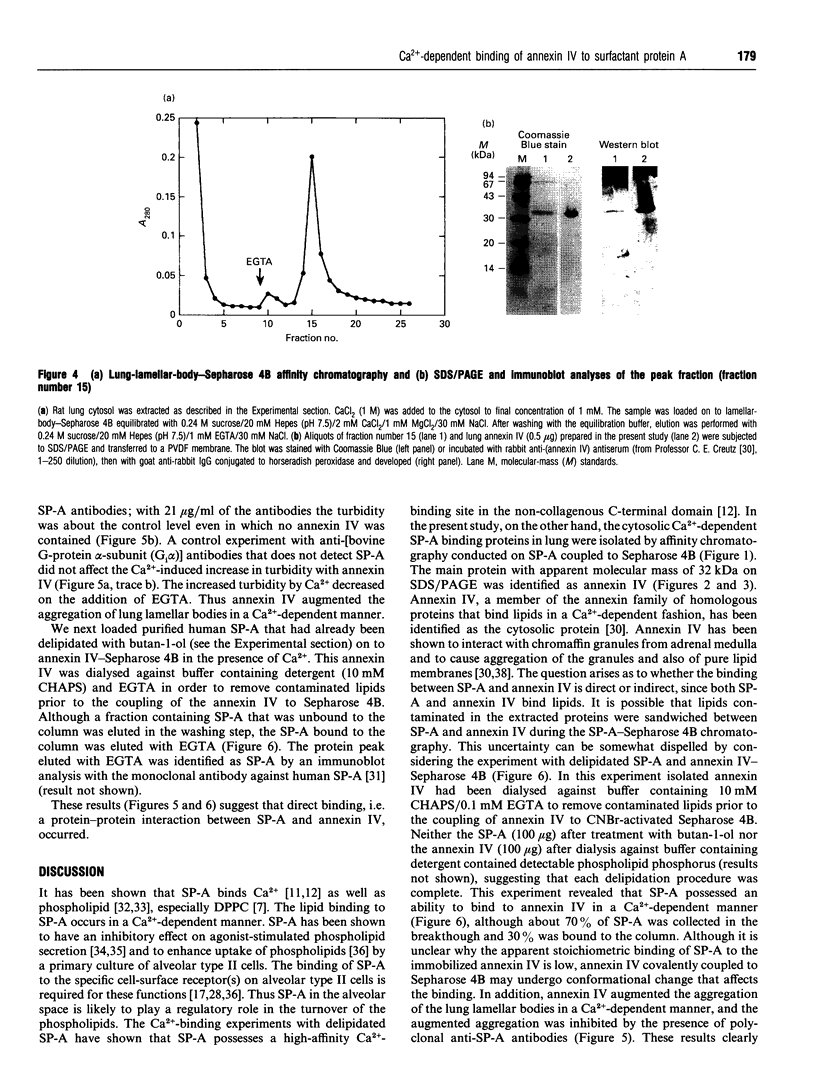
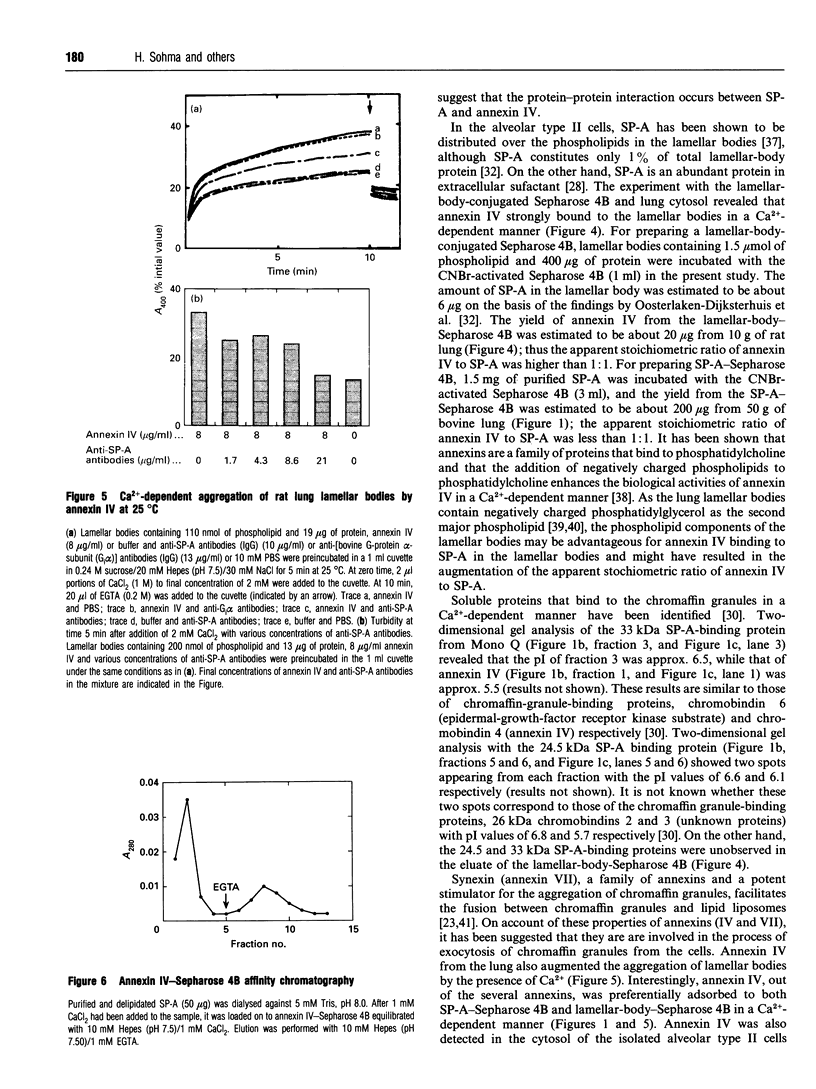
Surfactant protein A (SP-A), a lung-specific glycoprotein in pulmonary surfactant, is synthesized and secreted from the alveolar type II cells. It has been shown that SP-A is a Ca(2+)-binding protein with several binding sites and that the high-affinity site(s) is located in the C-terminal region of SP-A. In the present study we isolated the proteins from bovine lung soluble fraction that bind to SP-A in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner using DEAE-Sephacel and SP-A-conjugated Sepharose 4B. At least three different protein bands with molecular masses of 24.5, 32, and 33 kDa were observed on SDS/PAGE. The main protein, with molecular mass of 32 kDa, was identified as annexin IV by the partial-amino-acid-sequence analyses and an immunoblot analysis with anti-(annexin IV) antiserum. We also found from the immunoblot analysis that the cytosolic fraction of isolated rat alveolar type II cells contains annexin IV. In addition, when rat lung cytosol was loaded on to the lung lamellar body-conjugated Sepharose 4B in the presence of Ca2+, two proteins, with molecular masses of 32 and 60 kDa on SDS/PAGE respectively, were eluted with EGTA. The 32 kDa protein was shown to be annexin IV by an immunoblot analysis with the antiserum against annexin IV. The lung annexin IV augmented the Ca(2+)-induced aggregation of the lung lamellar bodies from rats. However, the augmentation of aggregation of the lung lamellar bodies by annexin IV was attenuated when the lamellar bodies were preincubated with polyclonal anti-SP-A antibodies. SP-A bound to annexin IV under conditions where contaminated lipid was removed. These results suggest that SP-A bound to annexin IV based on protein-protein interaction, though both proteins are phospholipid-binding proteins. All these findings suggest that the interaction between SP-A and annexin IV may have some role in alveolar type II cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi H., Hayashi H., Sato H., Dempo K., Akino T. Characterization of phospholipids accumulated in pulmonary-surfactant compartments of rats intratracheally exposed to silica. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 15;262(3):781–786. doi: 10.1042/bj2620781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggaram V., Qing K., Mendelson C. R. The major apoprotein of rabbit pulmonary surfactant. Elucidation of primary sequence and cyclic AMP and developmental regulation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2939–2947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. J., Winter V. T., Martin H. M., King R. J. Colloidal gold immunoultrastructural localization of rat surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):230–237. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. Secretory vesicle - cytosol interactions in exocytosis: isolation by Ca2+-dependent affinity chromatography of proteins that bind to the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1395–1400. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. The annexins and exocytosis. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):924–931. doi: 10.1126/science.1439804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Zaks W. J., Hamman H. C., Crane S., Martin W. H., Gould K. L., Oddie K. M., Parsons S. J. Identification of chromaffin granule-binding proteins. Relationship of the chromobindins to calelectrin, synhibin, and the tyrosine kinase substrates p35 and p36. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1860–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):247–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lisle R. C., Williams J. A. Regulation of membrane fusion in secretory exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:225–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Mason R. J. Pulmonary alveolar type II cells isolated from rats. Release of phosphatidylcholine in response to beta-adrenergic stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):378–387. doi: 10.1172/JCI109313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duck-Chong C. G. The isolation of lamellar bodies and their membranous content from rat lung, lamb tracheal fluid and human amniotic fluid. Life Sci. 1978 Jun 12;22(22):2025–2030. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90549-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornstedt N., Porath J. Characterization studies on a new lectin found in seeds of Vicia ervilia. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagsman H. P., Sargeant T., Hauschka P. V., Benson B. J., Hawgood S. Binding of calcium to SP-A, a surfactant-associated protein. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 25;29(38):8894–8900. doi: 10.1021/bi00490a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagsman H. P., White R. T., Schilling J., Lau K., Benson B. J., Golden J., Hawgood S., Clements J. A. Studies of the structure of lung surfactant protein SP-A. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L421–L429. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamman H. C., Gaffey L. C., Lynch K. R., Creutz C. E. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding bovine endonexin (chromobindin 4). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):660–667. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker M., Creutz C. E. Ca(2+)-dependent binding of endonexin (annexin IV) to membranes: analysis of the effects of membrane lipid composition and development of a predictive model for the binding interaction. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 2;33(30):8930–8940. doi: 10.1021/bi00196a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Clements J. A. Surface active materials from dog lung. I. Method of isolation. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):707–714. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Klass D. J., Gikas E. G., Clements J. A. Isolation of apoproteins from canine surface active material. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):788–795. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn J., Wilchek M. A new approach (cyano-transfer) for cyanogen bromide activation of Sepharose at neutral pH, which yields activated resins, free of interfering nitrogen derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):878–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90604-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Akino T. Pulmonary surfactant protein A (SP-A) specifically binds dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3068–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Fukada Y., Takahashi H., Akino T. Monoclonal antibodies against human pulmonary surfactant apoproteins: specificity and application in immunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 11;836(2):201–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Alveolar type II cells express a high-affinity receptor for pulmonary surfactant protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5566–5570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montfoort A., van Golde L. M., van Deenen L. L. Molecular species of lecithins from various animal tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 16;231(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterlaken-Dijksterhuis M. A., van Eijk M., van Buel B. L., van Golde L. M., Haagsman H. P. Surfactant protein composition of lamellar bodies isolated from rat lung. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):115–119. doi: 10.1042/bj2740115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizackerley P. J., Town M. H., Newman G. E. Hydrophobic proteins of lamellated osmiophilic bodies isolated from pig lung. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):731–736. doi: 10.1042/bj1830731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Ross G. F., Singleton F. M., Dingle S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):692–698. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. F., Notter R. H., Meuth J., Whitsett J. A. Phospholipid binding and biophysical activity of pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (SAP)-35 and its non-collagenous COOH-terminal domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14283–14291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Fisher J., Mason R. J., Kuroki Y., Schilling J., Benson B., Voelker D. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for the rat pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (PSP-A). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):367–374. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohma H., Hashimoto H., Ohguro H., Akino T. Two gamma-subunits, gamma-I and gamma-II, complex with the same beta-subunits in bovine brain G-proteins (Gi/o). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91175-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohma H., Hattori A., Kuroki Y., Akino T. Calcium and dithiothreitol dependent conformational changes in beta-sheet structure of collagenase resistant fragment of human surfactant protein A. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1993 Jun;30(2):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohma H., Watanabe T., Kuroki Y., Yoshino H., Matsushima N., Yazawa M., Akino T. Calcium dependent conformational changes of surfactant protein A (SP-A) and its collagenase resistant fragment with or without dithiothreitol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 23;1159(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90019-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Fujita Y., Kogishi K. Reconstitution of tubular myelin from synthetic lipids and proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):75–81. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. T., Damm D., Miller J., Spratt K., Schilling J., Hawgood S., Benson B., Cordell B. Isolation and characterization of the human pulmonary surfactant apoprotein gene. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):361–363. doi: 10.1038/317361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Borchelt J. D., Hawgood S. Lung surfactant apoprotein SP-A (26-36 kDa) binds with high affinity to isolated alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5410–5414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]