Abstract
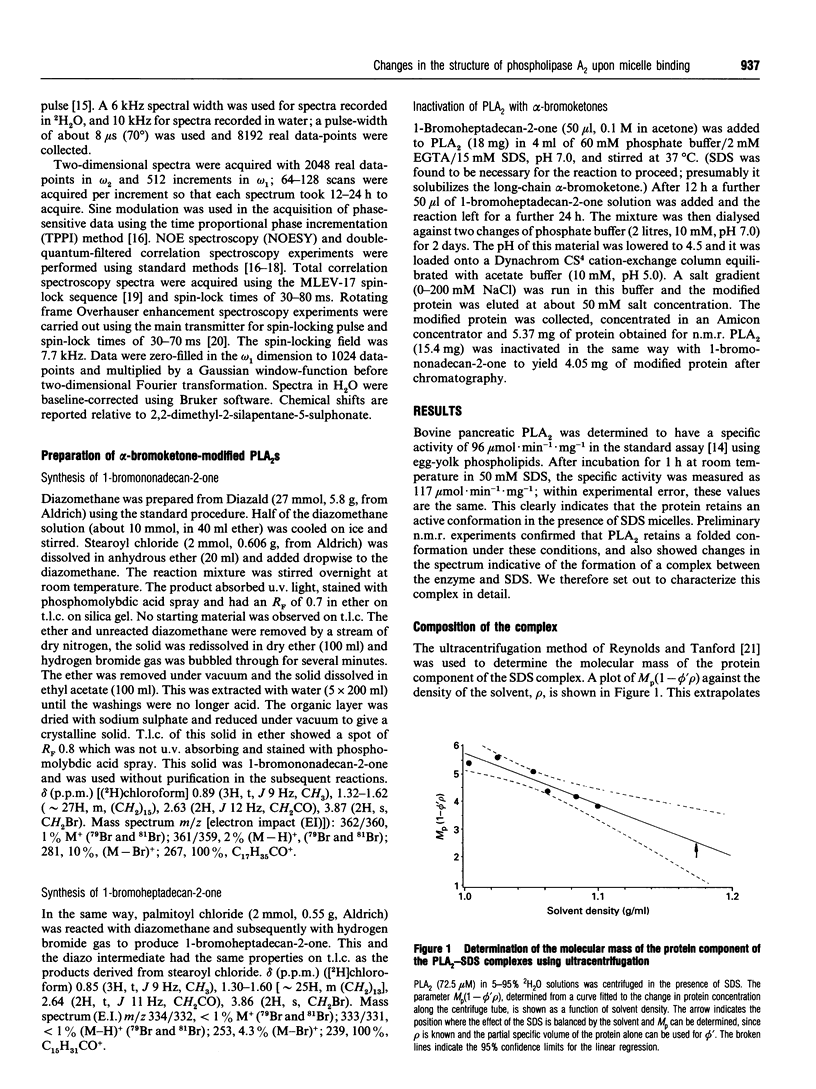
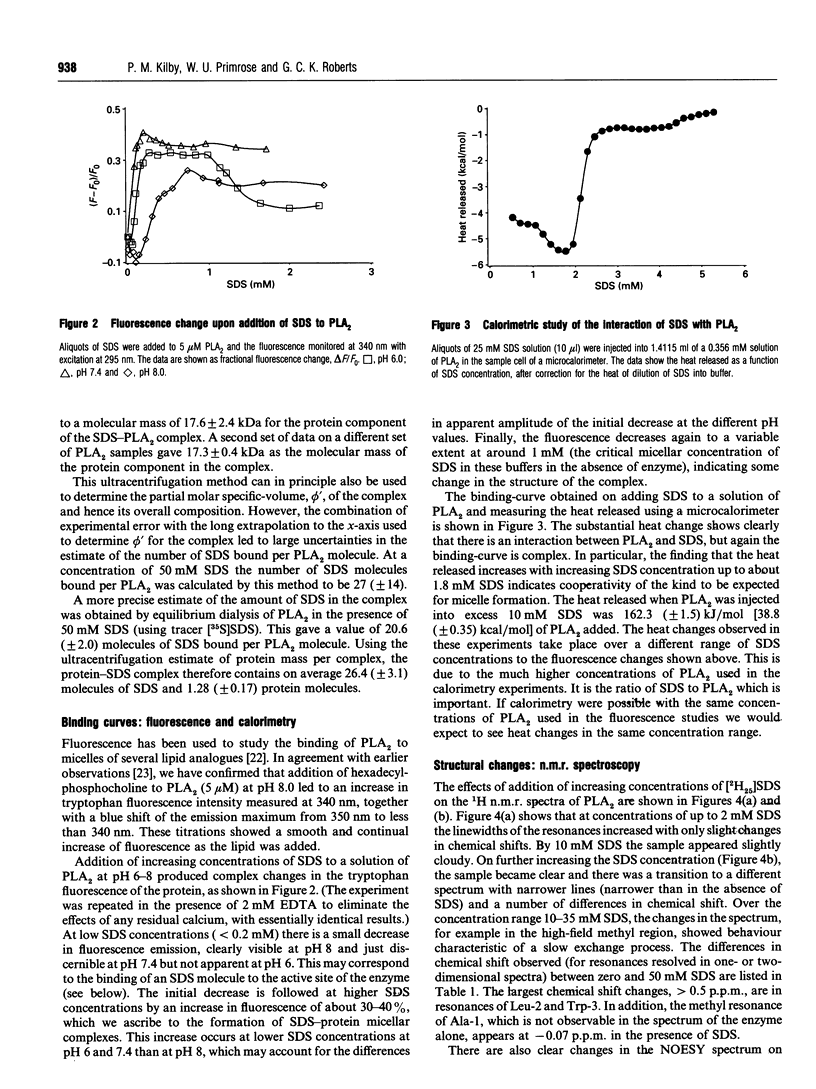
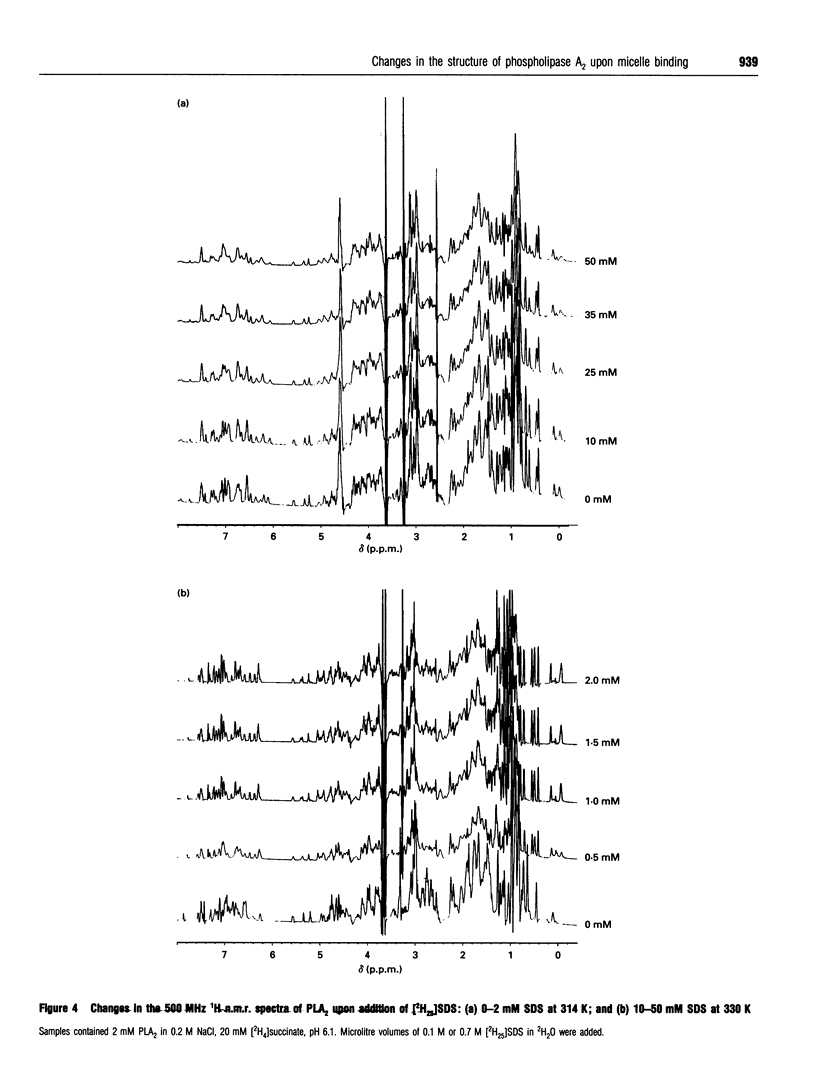
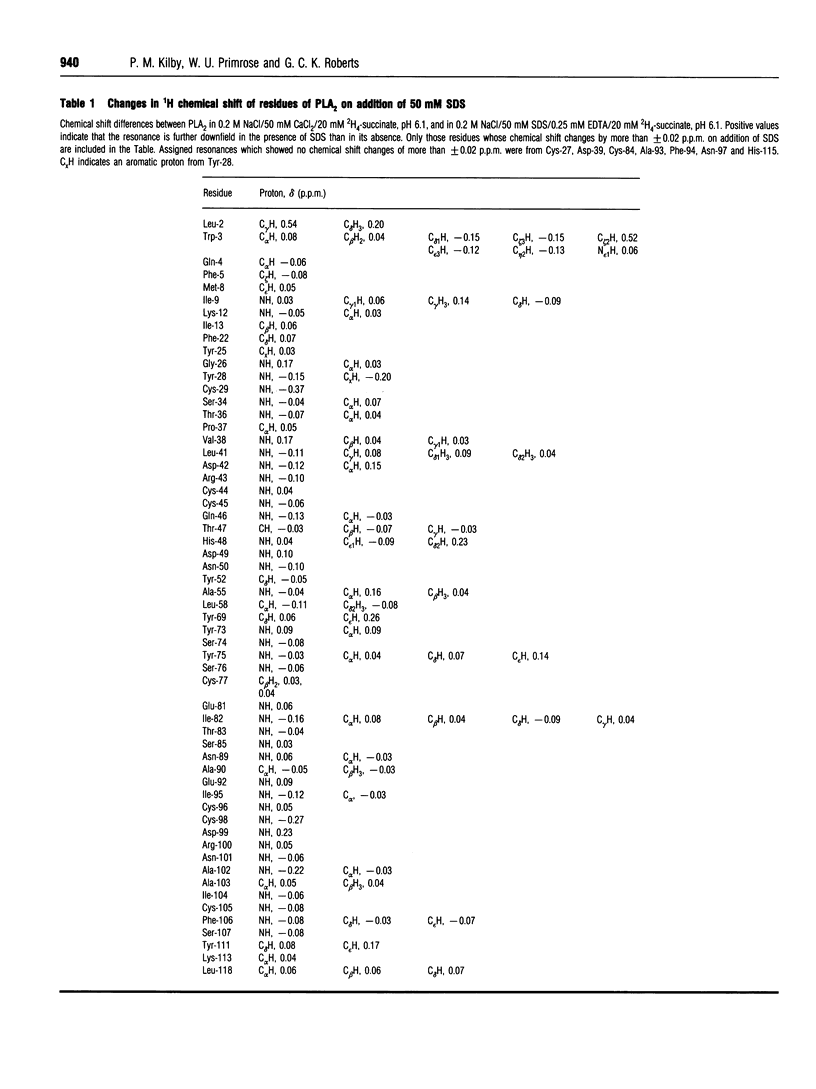
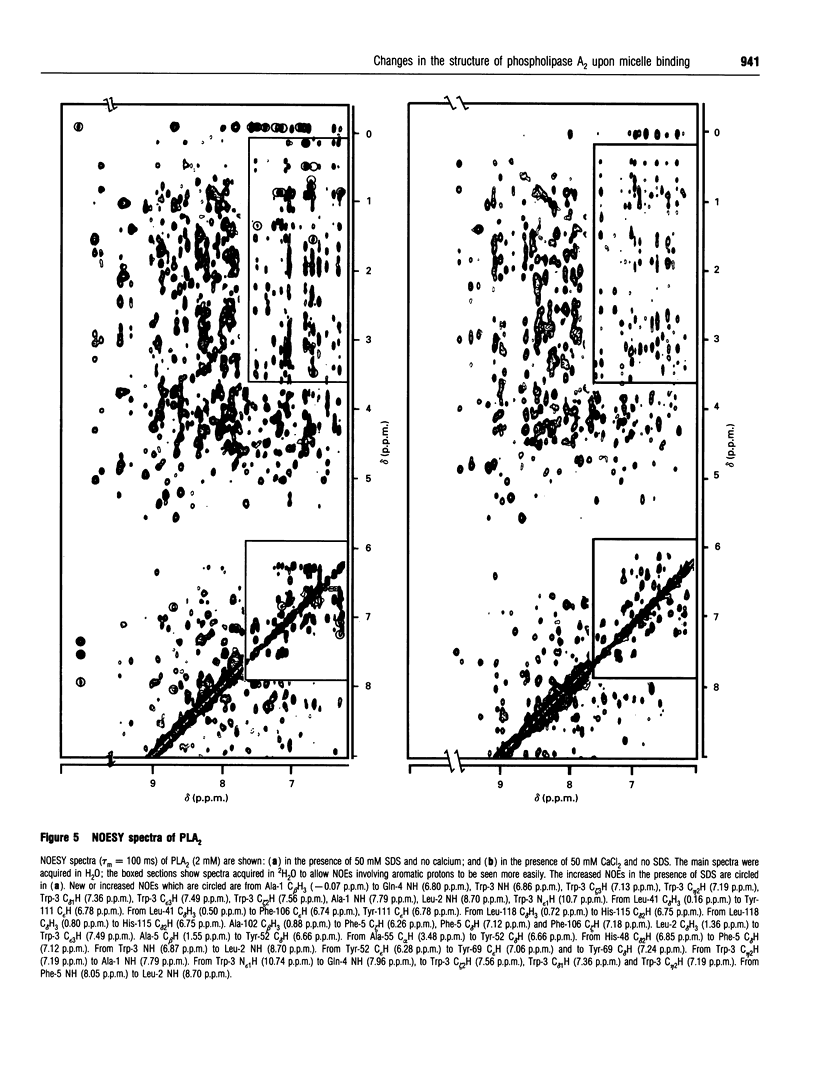
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) is a calcium-dependent enzyme which hydrolyses the 2-acyl ester bond of phospholipids. The extracellular PLA2s are activated by as much as 10000-fold on binding to micelles or vesicles of substrate, possibly due to a conformational change induced in the enzyme. We have studied the complex of bovine pancreatic PLA2 with micelles of SDS by ultracentrifugation, equilibrium dialysis, microcalorimetry, fluorescence and n.m.r. spectroscopy. Ultracentrifugation and equilibrium dialysis measurements showed that on average 1.28 (+/- 0.17) PLA2 molecules and 26.4 (+/- 3.1) SDS molecules are involved in the complex and that there is a rapid equilibrium between micellar species containing one or more enzyme monomers. The estimated heat of formation of the complex, measured calorimetrically as the heat released when PLA2 was injected into excess 10 mM SDS, was 162.3 +/- 1.5) kJ/mol [38.8 (+/- 0.35) kcal/mol] of PLA2 added. The fluorescence of the single tryptophan at position 3 in the N-terminal helix of the protein increases when PLA2 binds to SDS micelles, indicating that this part of the protein is in a more hydrophobic environment in the complex. The structural changes in PLA2 on addition of [2H25]SDS were monitored using n.m.r. spectroscopy. The overall structure of the protein is unchanged, but changes in nuclear Overhauser effects (NOEs) were observed for residues in the N-terminal helix, at the active site region and in a lysine-rich region near the C-terminus. The NOE changes at the N-terminus indicate that this portion of the protein molecule adopts a more ordered, helical conformation when bound to a micelle. We suggest that these conformational changes could be the mechanism by which the enzyme becomes activated in the presence of aggregated substrate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achari A., Scott D., Barlow P., Vidal J. C., Otwinowski Z., Brunie S., Sigler P. B. Facing up to membranes: structure/function relationships in phospholipases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:441–452. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion C., Connolly S., Gensmantel N. P., Hallam C., Jackson C. G., Primrose W. U., Roberts G. C., Robinson D. H., Slaich P. K. Design and synthesis of some substrate analogue inhibitors of phospholipase A2 and investigations by NMR and molecular modeling into the binding interactions in the enzyme-inhibitor complex. J Med Chem. 1992 Aug 7;35(16):2939–2951. doi: 10.1021/jm00094a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. The control of free arachidonic acid levels. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):365–366. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Musser J. H., McGregor H. Phospholipase A2: function and pharmacological regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 1;36(15):2429–2436. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90512-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker N., Peters A. R., Slotboom A. J., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Dijkman R., de Haas G. Two-dimensional 1H-NMR studies of phospholipase-A2-inhibitor complexes bound to a micellar lipid-water interface. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):601–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra B. W., Kalk K. H., Hol W. G., Drenth J. Structure of bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at 1.7A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):97–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Primrose W. U., Roberts G. C., Dekker N., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Slotboom A. J. 1H NMR studies of bovine and porcine phospholipase A2: assignment of aromatic resonances and evidence for a conformational equilibrium in solution. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5939–5946. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Egmond M. R., Verheij H. M., Apitz-Castro R., Dijkman R., De Haas G. H. Interaction of phospholipase A2 and phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90345-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Maliwal B. P. Spectroscopic properties of the states of pig pancreatic phospholipase A2 at interfaces and their possible molecular origin. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 9;32(44):11838–11846. doi: 10.1021/bi00095a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Ranadive G., Yu B. Z., Verheij H. M. Interfacial catalysis by phospholipase A2: monomeric enzyme is fully catalytically active at the bilayer interface. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7330–7340. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers O. P., Vincent M., Brochon J. C., Verheij H. M., de Haas G. H., Gallay J. Insight into the conformational dynamics of specific regions of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2 from a time-resolved fluorescence study of a genetically inserted single tryptophan residue. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 10;30(36):8771–8785. doi: 10.1021/bi00100a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers O. P., Vincent M., Brochon J. C., Verheij H. M., de Haas G. H., Gallay J. Insight into the conformational dynamics of specific regions of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2 from a time-resolved fluorescence study of a genetically inserted single tryptophan residue. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 10;30(36):8771–8785. doi: 10.1021/bi00100a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. R., Dekker N., van den Berg L., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H. Conformational changes in phospholipase A2 upon binding to micellar interfaces in the absence and presence of competitive inhibitors. A 1H and 15N NMR study. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):10024–10030. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. R., Dekker N., van den Berg L., Boelens R., Kaptein R., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H. Conformational changes in phospholipase A2 upon binding to micellar interfaces in the absence and presence of competitive inhibitors. A 1H and 15N NMR study. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):10024–10030. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. R., Dekker N., van den Berg L., Boelens R., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H., Kaptein R. NMR studies of interactions between inhibitors and porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2. Biochimie. 1992 Sep-Oct;74(9-10):859–866. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90069-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renetseder R., Brunie S., Dijkstra B. W., Drenth J., Sigler P. B. A comparison of the crystal structures of phospholipase A2 from bovine pancreas and Crotalus atrox venom. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11627–11634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Determination of molecular weight of the protein moiety in protein-detergent complexes without direct knowledge of detergent binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4467–4470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., White S. P., Otwinowski Z., Yuan W., Gelb M. H., Sigler P. B. Interfacial catalysis: the mechanism of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1541–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2274785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaich P. K., Primrose W. U., Robinson D. H., Wharton C. W., White A. J., Drabble K., Roberts G. C. The binding of amide substrate analogues to phospholipase A2. Studies by 13C-nuclear-magnetic-resonance and infrared spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):167–173. doi: 10.1042/bj2880167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H. Specific transformations at the N-terminal region of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5394–5399. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunnissen M. M., Ab E., Kalk K. H., Drenth J., Dijkstra B. W., Kuipers O. P., Dijkman R., de Haas G. H., Verheij H. M. X-ray structure of phospholipase A2 complexed with a substrate-derived inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):689–691. doi: 10.1038/347689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij H. M., Slotboom A. J., de Haas G. H. Structure and function of phospholipase A2. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;91:91–203. doi: 10.1007/3-540-10961-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volwerk J. J., Pieterson W. A., de Haas G. H. Histidine at the active site of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 26;13(7):1446–1454. doi: 10.1021/bi00704a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P., Marion D., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure in the solution conformation of the proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):341–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas G. H., Postema N. M., Nieuwenhuizen W., van Deenen L. L. Purification and properties of phospholipase A from porcine pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 24;159(1):103–117. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


