Abstract
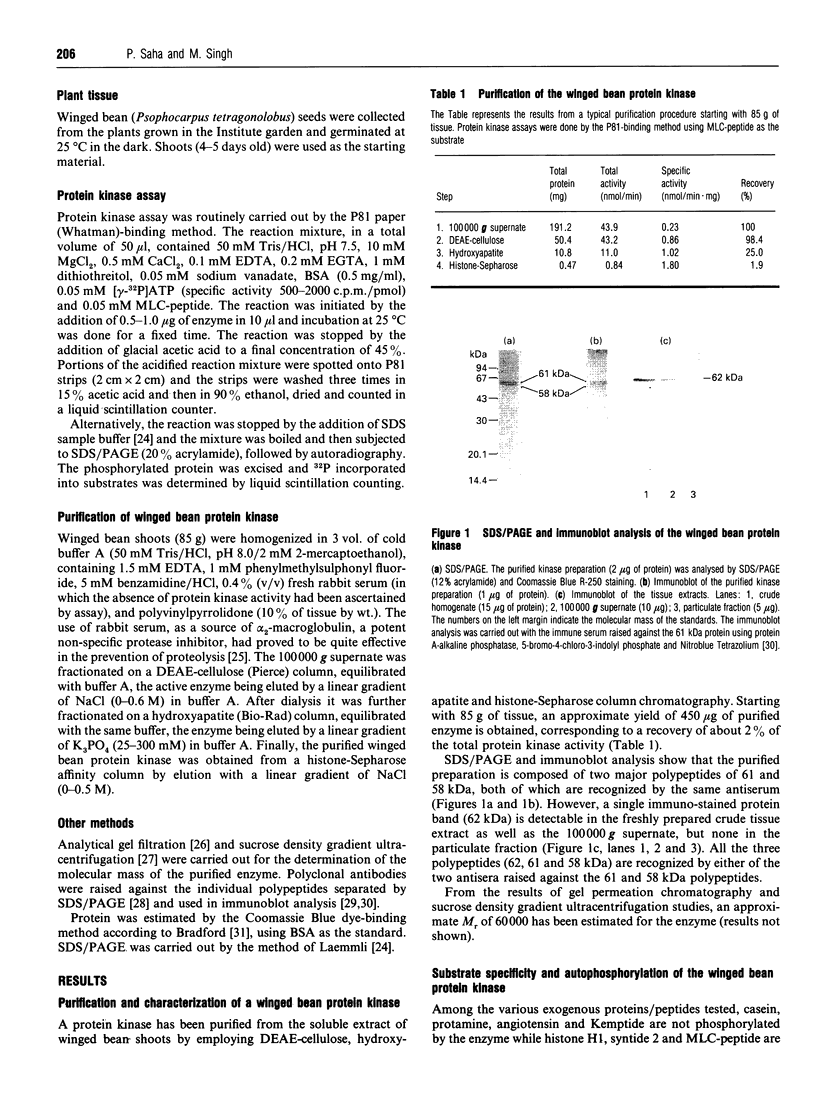
A soluble protein kinase purified from winged bean (Psophocarpus tetragonolobus) shoots, has been assessed as a monomeric enzyme with an approximate M(r) of 60,000 in spite of the presence of two polypeptides of 61 and 58 kDa determined by SDS/PAGE. Immunoblot analyses using either of the two antisera raised individually against the polypeptides, detect both of them in purified preparations and a single larger polypeptide (62 kDa) in freshly prepared tissue homogenates, clearly indicating the likelihood of the doublet being formed from the larger one by proteolysis. Histone H1, syntide 2 and a synthetic myosin light chain-related peptide (MLC-peptide) have been identified as exogenous substrates of the enzyme. Complete Ca(2+)-dependence for substrate phosphorylation, a drastic inhibition of the reaction by a calmodulin (CaM) antagonist which can be partially reversed by a heterologous CaM and direct 45Ca(2+)-binding on blot, form compelling evidence in favour of a CaM-like domain of the enzyme. Both the polypeptides of the purified enzyme undergo intramolecular autophosphorylation on serine residue(s). Unlike the substrate phosphorylation reaction, autophosphorylation is Ca(2+)-independent and is not inhibited by the CaM antagonist. Down-regulation of substrate phosphorylation by auto-phosphorylation, and stimulation of the autophosphorylation by histone H1 and MLC-peptide, are novel regulatory features of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF
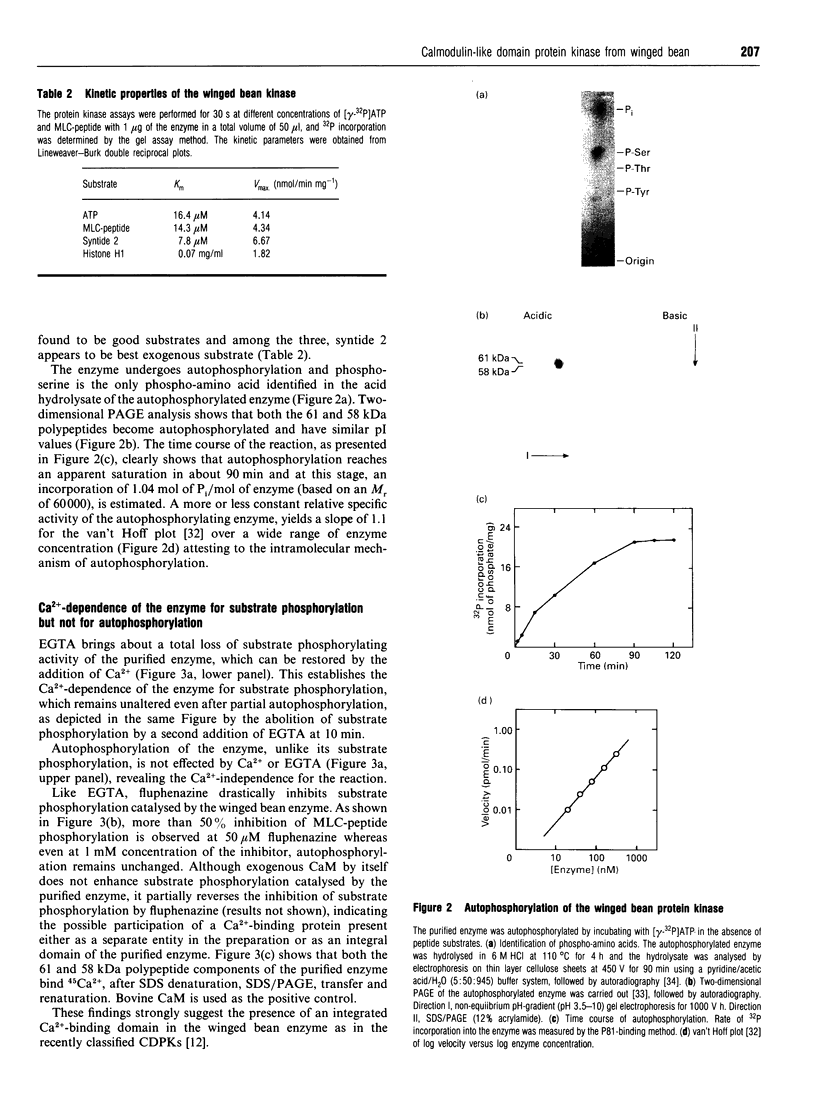

Images in this article
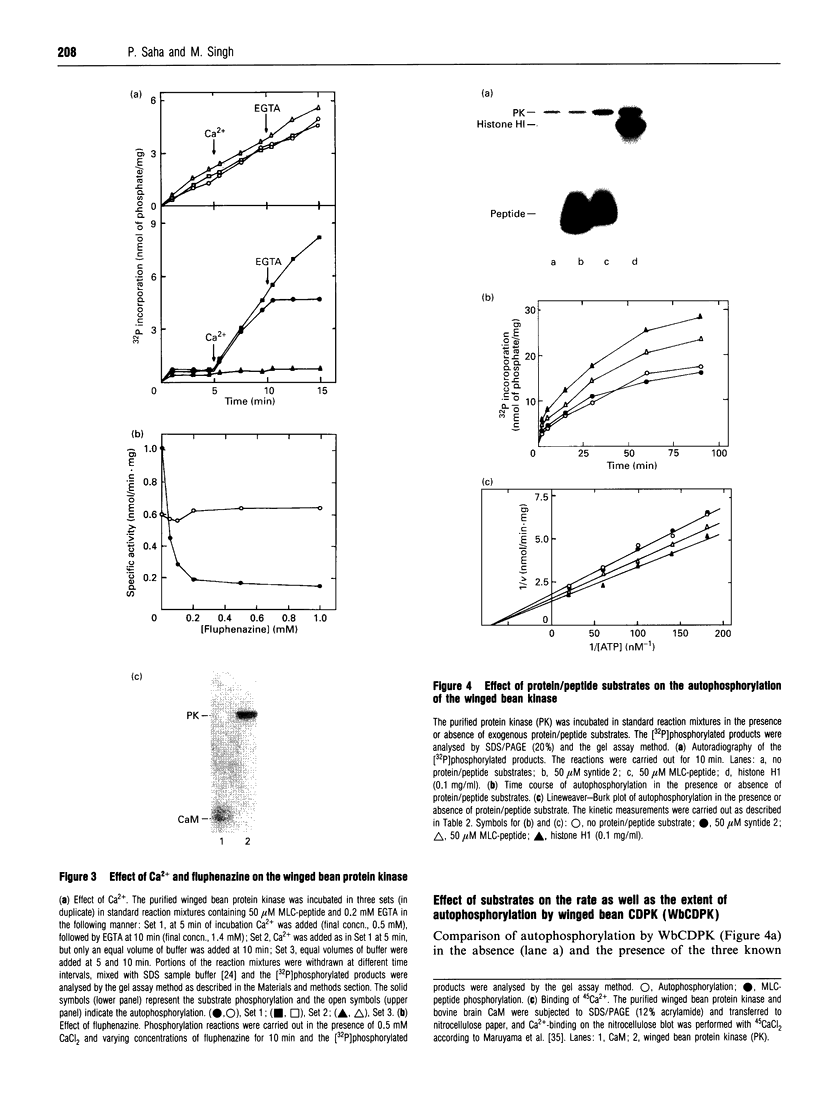
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackshear P. J., Nairn A. C., Kuo J. F. Protein kinases 1988: a current perspective. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2957–2969. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.2972578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
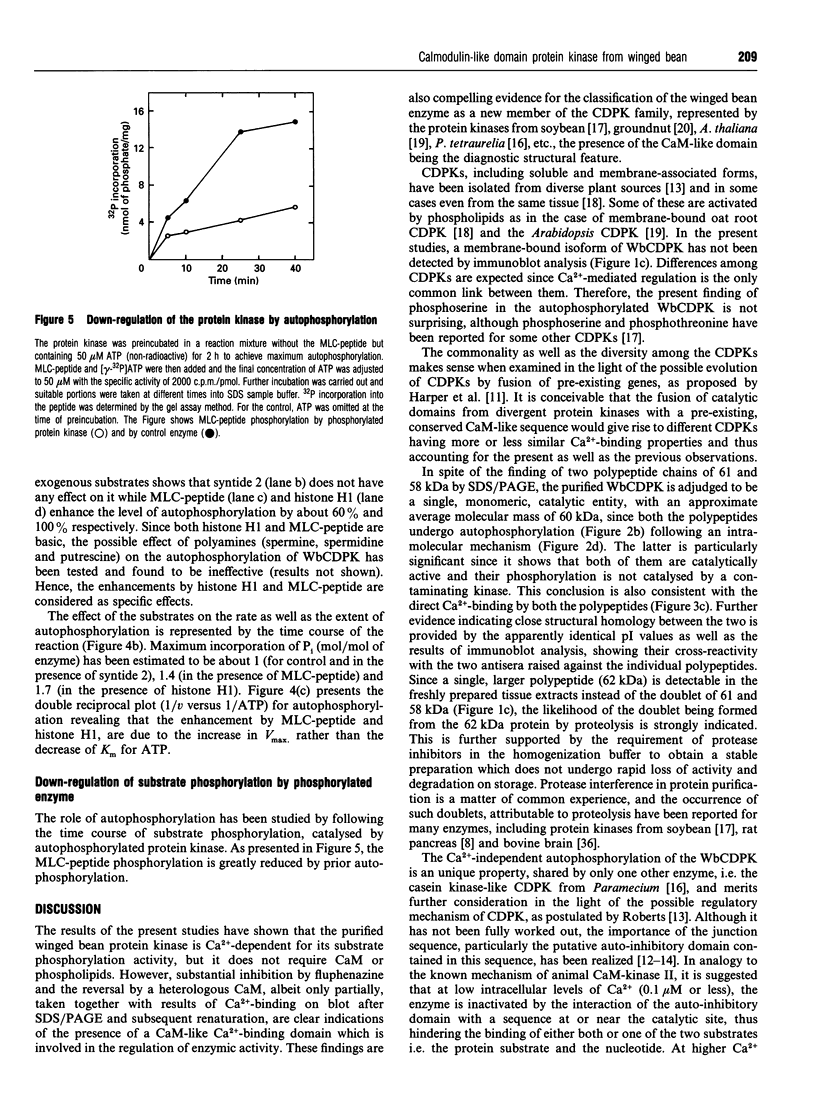
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta M. Characterization of a calcium-dependent protein kinase from Arachis hypogea (groundnut) seeds. Plant Physiol. 1994 Mar;104(3):961–969. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen R. E., Nelson D. L. A novel Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from Paramecium tetraurelia. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4602–4609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Binder B. M., Sussman M. R. Calcium and lipid regulation of an Arabidopsis protein kinase expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3282–3290. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Sussman M. R., Schaller G. E., Putnam-Evans C., Charbonneau H., Harmon A. C. A calcium-dependent protein kinase with a regulatory domain similar to calmodulin. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):951–954. doi: 10.1126/science.1852075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Sarre T. F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):329–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2910329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Schulman H. Mechanism of autophosphorylation of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6427–6433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Srere P. A. Identification of ATP citrate lyase as a phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1691–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H. Protein phosphorylation in plants: enzymes, substrates and regulators. Trends Genet. 1993 Jul;9(7):228–230. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90075-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald O. B., Merrill B. M., Bland M. M., Taylor L. C., Sahyoun N. Site and consequences of the autophosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type "Gr". J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10054–10059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Brady M., Palfrey H. C., Nairn A. C. Purification and characterization of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III from rabbit reticulocytes and rat pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13422–13433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7273–7281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planas-Silva M. D., Means A. R. Expression of a constitutive form of calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II leads to arrest of the cell cycle in G2. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):507–517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam-Evans C. L., Harmon A. C., Cormier M. J. Purification and characterization of a novel calcium-dependent protein kinase from soybean. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2488–2495. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. M. Protein kinases with calmodulin-like domains: novel targets of calcium signals in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller G. E., Harmon A. C., Sussman M. R. Characterization of a calcium- and lipid-dependent protein kinase associated with the plasma membrane of oat. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1721–1727. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H. The multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Son M., Gundersen R. E., Nelson D. L. A second member of the novel Ca(2+)-dependent protein kinase family from Paramecium tetraurelia. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5940–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Miron T., Kohn J. Affinity chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:3–55. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]