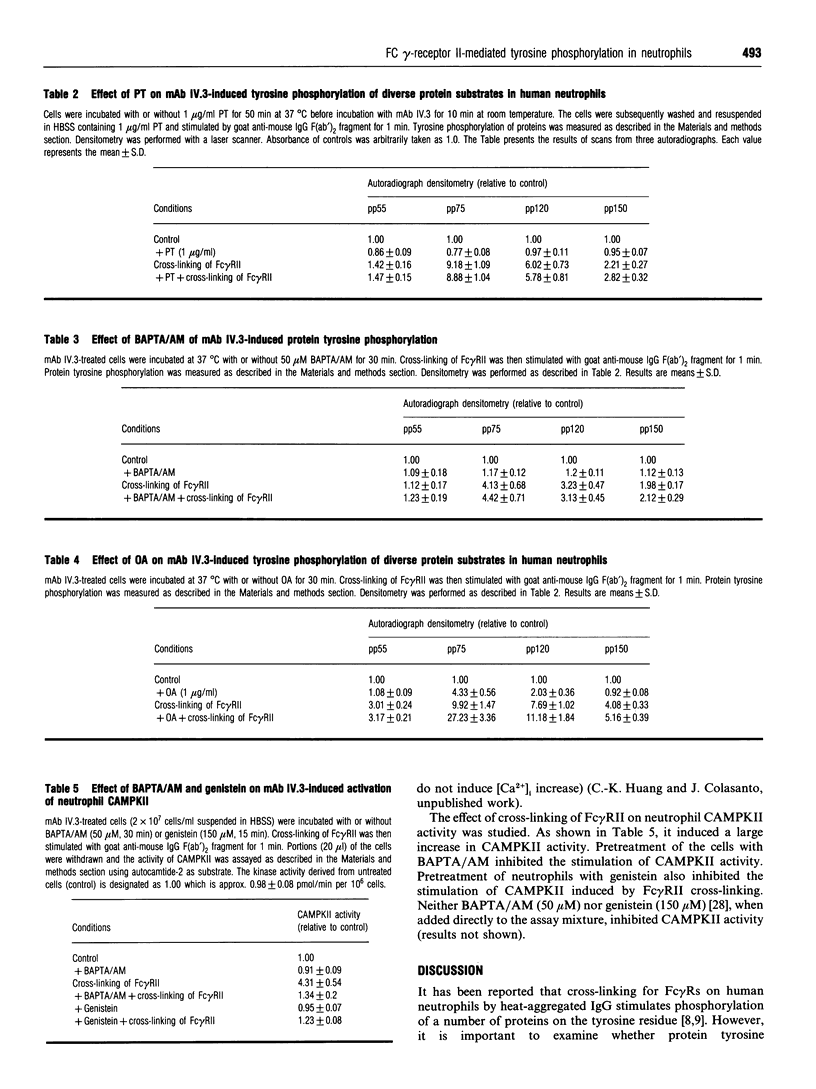
Abstract
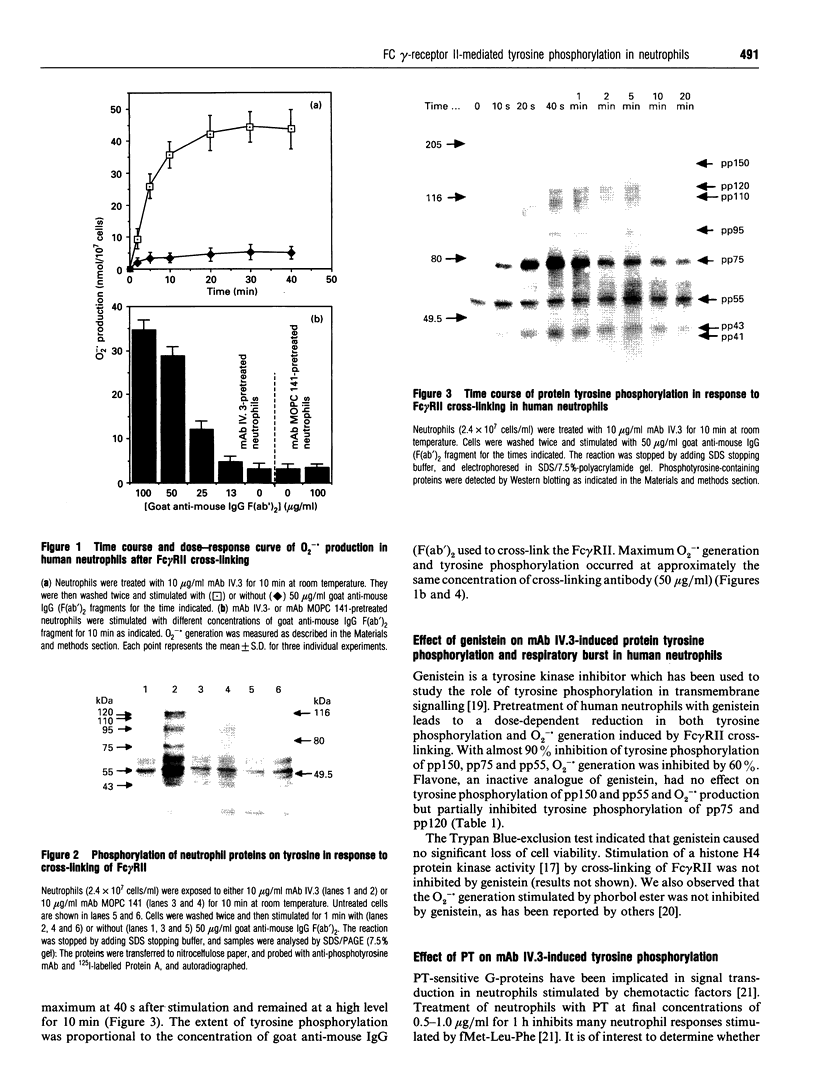
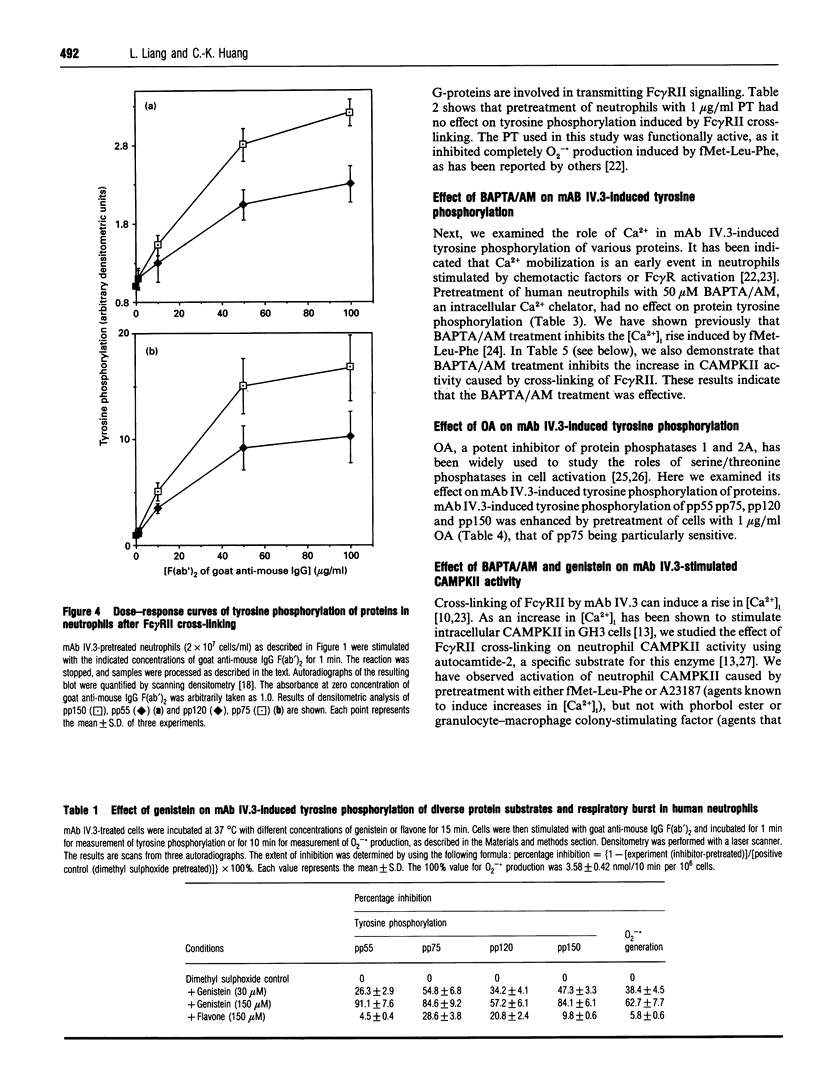
Neutrophils express several receptors for the Fc region of IgG molecules. Specific cross-linking of the type II receptor (Fc gamma RII) can be achieved by treating neutrophils with the Fab fragment of a specific monoclonal antibody IV.3 against the receptor followed by goat anti-mouse IgG F(ab')2 fragment. Such treatment initiates a number of neutrophil responses including the release of O2-. and increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation. The increase in tyrosine phosphorylation is rapid and transient and correlates with O2-. release. Both responses are inhibited by pretreatment of neutrophils with a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, genistein. The increase in protein tyrosine phosphorylation is not inhibited by pretreatment of neutrophils with pertussis toxin or an intracellular Ca2+ chelator, but is enhanced by a phosphoprotein phosphatase inhibitor, okadaic acid. The activity of a neutrophil Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMPKII) is also stimulated by cross-linking Fc gamma RII. The increase in CAMPKII activity is inhibited by pretreatment with either genistein or Ca2+ chelator. The results suggest that the increase in protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced by cross-linking of Fc gamma RII requires neither pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-proteins nor a rise in intracellular Ca2+ but can be regulated by protein phosphatases. Furthermore, protein tyrosine phosphorylation may be an early signal functionally linked to Fc gamma RII-mediated signal transduction leading to CAMPKII activation and O2-. release in human neutrophils.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal A., Salem P., Robbins K. C. Involvement of p72syk, a protein-tyrosine kinase, in Fc gamma receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15900–15905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Ogawara H. Use and specificity of genistein as inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:362–370. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01032-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Kermode J. C., Naccache P. H., Yassin R., Marsh M. L., Munoz J. J., Sha'afi R. I. The inhibition of neutrophil granule enzyme secretion and chemotaxis by pertussis toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1641–1646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou M., Gutkind J. S., Robbins K. C., Siraganian R. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation coupled to IgE receptor-mediated signal transduction and histamine release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5327–5330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. A., Farrell C. A., Merenda J. M., Conklyn M. J., Showell H. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation is an early signaling event common to Fc receptor crosslinking in human neutrophils and rat basophilic leukemia cells (RBL-2H3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):192–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91967-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockett-Torabi E., Fantone J. C. Soluble and insoluble immune complexes activate human neutrophil NADPH oxidase by distinct Fc gamma receptor-specific mechanisms. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3026–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bianca V., Grzeskowiak M., Dusi S., Rossi F. Transmembrane signaling pathways involved in phagocytosis and associated activation of NADPH oxidase mediated by Fc gamma Rs in human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Apr;53(4):427–438. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R. C., Whitaker M., Heyworth P. G., Segal A. W. Okadaic acid produces changes in phosphorylation and translocation of proteins and in intracellular calcium in human neutrophils. Relationship with the activation of the NADPH oxidase by different stimuli. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):687–692. doi: 10.1042/bj2860687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Colasanto J. M., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. Direct stimulation by tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein (MAP) kinase activity by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):211–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2910211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Chang P., Silverstein S. C. Tyrosine phosphorylation is required for Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):529–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada F., Aoki M., Akiyama T., Toyoshima K. Association of immunoglobulin G Fc receptor II with Src-like protein-tyrosine kinase Fgr in neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6305–6309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Laramee G. F. Stimulation of a histone H4 protein kinase in Triton X-100 lysates of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils pretreated with chemotactic factors. Effect of fMet-Leu-Phe and partial characterization of the protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13144–13151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Laramee G. R., Casnellie J. E. Chemotactic factor induced tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane associated proteins in rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):794–801. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Laramee G. R., Yamazaki M., Sha'afi R. I. Stimulation of a histone H4 protein kinase in Triton X-100 lysates of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils pretreated with chemotactic factors: lack of requirements of calcium mobilization and protein kinase C activation. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Dec;44(4):221–228. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240440404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Indik Z., Brass L. F., Hoxie J. A., Schreiber A. D., Brugge J. S. Activation of Fc gamma RII induces tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple proteins including Fc gamma RII. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5467–5473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Travis S. M., Schulman H. Activation of multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in GH3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1484–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreienbühl P., Keller H., Niggli V. Protein phosphatase inhibitors okadaic acid and calyculin A alter cell shape and F-actin distribution and inhibit stimulus-dependent increases in cytoskeletal actin of human neutrophils. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki T., Higashi H., Hosoi S., Hata D., Sugie K., Mayumi M., Mikawa H. Tyrosine phosphorylation and its possible role in superoxide production by human neutrophils stimulated with FMLP and IgG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):789–796. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90552-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Shin H. S., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 induced by cross-linking of the high-affinity or low-affinity Fc receptor for IgG in U937 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D. J., Takai A., Leto T. L., Grinstein S. Modulation of neutrophil activation by okadaic acid, a protein phosphatase inhibitor. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):C39–C49. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.1.C39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo L. A., Curnutte J. T. Kinetic microplate assay for superoxide production by neutrophils and other phagocytic cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:567–575. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86151-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen H. M., Rose J. K., Mellman I. Fc receptor isoforms exhibit distinct abilities for coated pit localization as a result of cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90846-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell T. J., Kandel E. R., Grant S. G. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus is blocked by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):558–560. doi: 10.1038/353558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odin J. A., Edberg J. C., Painter C. J., Kimberly R. P., Unkeless J. C. Regulation of phagocytosis and [Ca2+]i flux by distinct regions of an Fc receptor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1785–1788. doi: 10.1126/science.1837175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Min H. K., Rhee S. G. Inhibition of CD3-linked phospholipase C by phorbol ester and by cAMP is associated with decreased phosphotyrosine and increased phosphoserine contents of PLC-gamma 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1496–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Marth J. D., Ziegler S. F., Garvin A. M., Pawar S., Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M. Specialized protein tyrosine kinase proto-oncogenes in hematopoietic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb;948(3):245–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin B. M., Yocum S. A., Mittler R. S., Kiener P. A. Stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation and calcium mobilization by Fc gamma receptor cross-linking. Regulation by the phosphotyrosine phosphatase CD45. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):605–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., Brown E. J. Signal transduction by neutrophil immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Dissociation of intracytoplasmic calcium concentration rise from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5265–5271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi T., Klostergaard J., Akimaru K., Edashige K., Sato E. F., Utsumi K. Modulation of TNF-alpha-priming and stimulation-dependent superoxide generation in human neutrophils by protein kinase inhibitors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Apr;294(1):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90168-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. A., Hagenlocker B. E., Stubbs E. B., Jr, Sandborg R. R., Agranoff B. W., Ward P. A. Signal transduction events and Fc gamma R engagement in human neutrophils stimulated with immune complexes. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Anderson C. L. Biology of human immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 May;49(5):511–524. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.5.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]