Abstract
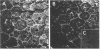
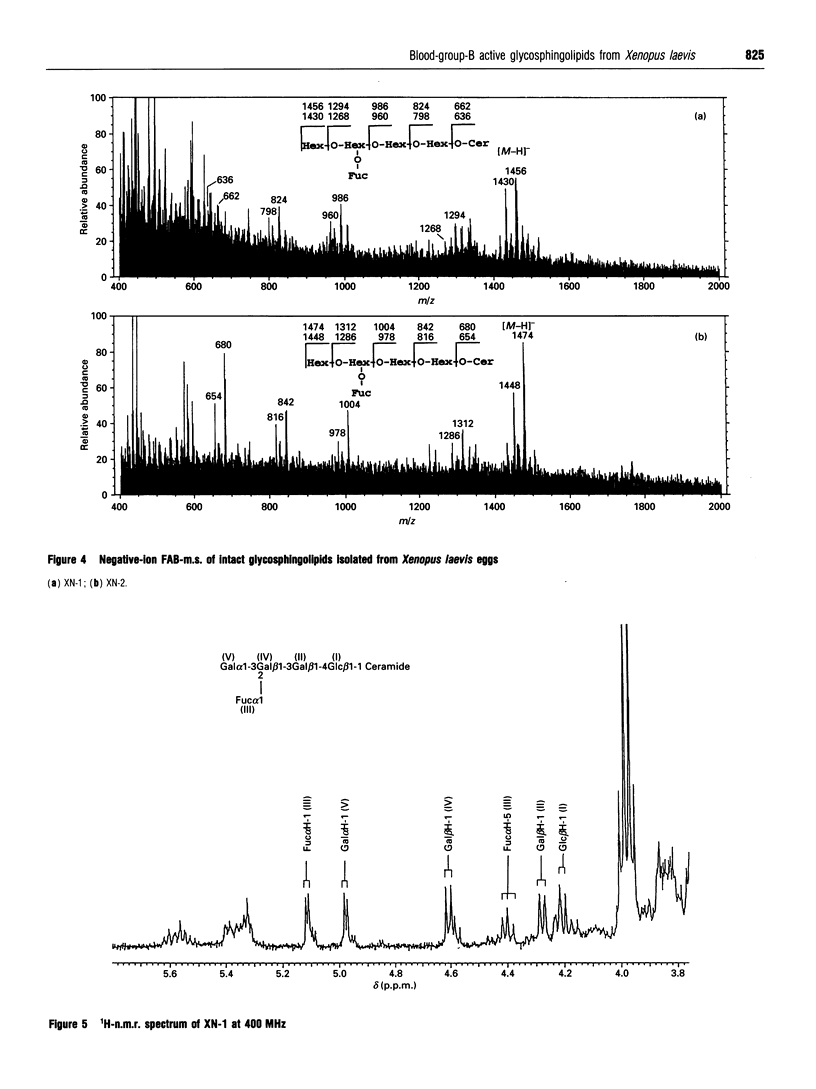
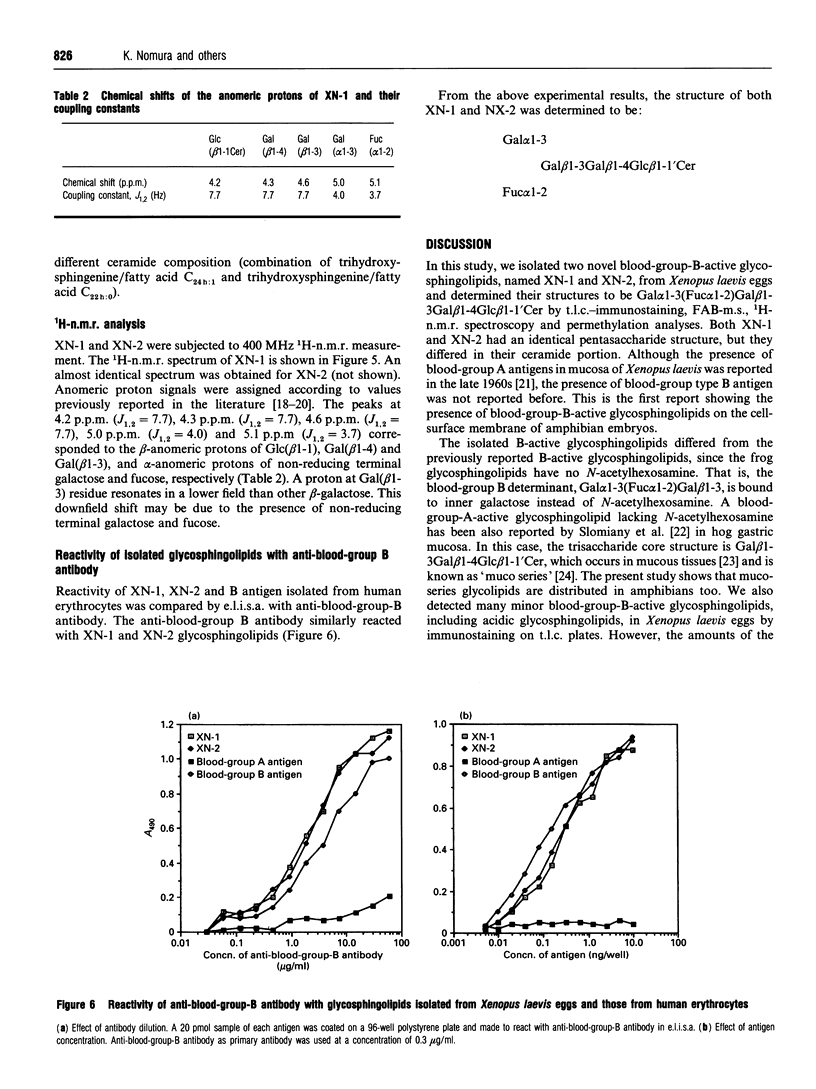
For understanding of the biological function of glycoconjugates during embryogenesis and morphogenesis, Xenopus laevis is considered a very useful animal model. We have found that blood-group-active molecules characteristically were distributed in the cell-cell contact region of Xenopus blastula cells. The chemical nature of blood-group-active glycoconjugates, including glycosphingolipids, is little known. T.l.c.-immunostaining using anti-blood-group-antigen antibodies showed that many species of blood group-B-active glycosphingolipids existed in the neutral glycosphingolipid fraction extracted from Xenopus laevis eggs. Among the B-active glycosphingolipids detected, two major components with the fastest mobility on a t.l.c. plate, tentatively termed XN-1 and XN-2, were isolated, and their chemical structures were characterized by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, immunological anlaysis, fast-atom-bombardment mass spectrometry and 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy. Both XN-1 and XN-2 had an identical pentaoligosaccharide structure, but differed in their ceramide moiety. The chemical structure is: [table: see text]. This is a novel type of pentaglycosylceramide with blood-group B activity, in that it lacks N-acetylhexosamine in its core carbohydrate structure. In this paper, a possible involvement of the blood-group antigen in the cell-adhesion process of Xenopus embryonic cells is discussed.
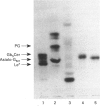
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando S., Chang N. C., Yu R. K. High-performance thin-layer chromatography and densitometric determination of brain ganglioside compositions of several species. Anal Biochem. 1978 Sep;89(2):437–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando S., Yu R. K., Scarsdale J. N., Kusunoki S., Prestegard J. H. High resolution proton NMR studies of gangliosides. Structure of two types of GD3 lactones and their reactivity with monoclonal antibody R24. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3478–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angres B., Müller A. H., Kellermann J., Hausen P. Differential expression of two cadherins in Xenopus laevis. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):829–844. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti T., Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. The gas chromatographic properties of biologically important N-acetylglucosamine derivatives, monosaccharides, disaccharides, trisaccharides, tetrasaccharides and pentasaccharides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggens I., Fenderson B., Toyokuni T., Dean B., Stroud M., Hakomori S. Specific interaction between Lex and Lex determinants. A possible basis for cell recognition in preimplantation embryos and in embryonal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9476–9484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS C., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 4. The determination of mannose in hen's-egg albumin by radioisotope dilution. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:335–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0830335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Demonstration by monoclonal antibodies that carbohydrate structures of glycoproteins and glycolipids are onco-developmental antigens. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):53–57. doi: 10.1038/314053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenderson B. A., Zehavi U., Hakomori S. A multivalent lacto-N-fucopentaose III-lysyllysine conjugate decompacts preimplantation mouse embryos, while the free oligosaccharide is ineffective. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1591–1596. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasa S., Mitsuyama T., Makita A. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance of neutral and acidic glycosphingolipids. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):174–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooi H. C., Feizi T., Kapadia A., Knowles B. B., Solter D., Evans M. J. Stage-specific embryonic antigen involves alpha 1 goes to 3 fucosylated type 2 blood group chains. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):156–158. doi: 10.1038/292156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Glycosphingolipids in cellular interaction, differentiation, and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:733–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg F., Wildermuth V., Wedlich D. Expression of XBcad, a novel cadherin, during oogenesis and early development of Xenopus. Mech Dev. 1991 Aug;35(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidari K., Itonori S., Sanai Y., Ohashi M., Kasama T., Nagai Y. Isolation and characterization of a monosialosylgangliopentaosyl ceramide from Xenopus laevis oocyte. J Biochem. 1991 Sep;110(3):412–416. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Fukui Y., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirabayashi Y., Matsumoto M., Naiki M. Sensitive enzyme-immunostaining and densitometric determination on thin-layer chromatography of N-glycolylneuraminic acid-containing glycosphingolipids, Hanganutziu-Deicher antigens. J Biochem. 1984 May;95(5):1517–1520. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Hirabayashi Y., Fukui Y., Naiki M., Matsumoto M., Ueda S., Kato S. Characterization of N-glycolylneuraminic acid-containing gangliosides as tumor-associated Hanganutziu-Deicher antigen in human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3796–3802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Ikuta K., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirabayashi Y., Matsumoto M., Naiki M. Characterization of N-glycolyneuraminic acid-containing glycosphingolipids from a Marek's disease lymphoma-derived chicken cell line, MSB1, as tumor-associated heterophile Hanganutziu-Deicher antigens. J Biochem. 1984 Mar;95(3):785–794. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Hamaoka A., Matsumoto M., Matsubara T., Tagawa M., Wakabayashi S., Taniguchi M. Syngeneic monoclonal antibody against melanoma antigen with interspecies cross-reactivity recognizes GM3, a prominent ganglioside of B16 melanoma. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13328–13333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Lander A. D. Contact and adhesive specificities in the associations, migrations, and targeting of cells and axons. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90472-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. A., Jr, Prestegard J. H., Demou P. C., Yu R. K. High-resolution proton NMR studies of gangliosides. 1. Use of homonuclear two-dimensional spin-echo J-correlated spectroscopy for determination of residue composition and anomeric configurations. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2676–2687. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher B. A., Sweeley C. C. Glycosphingolipids: structure, biological source, and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:236–251. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Nilsson B., Brockhaus M., Zopf D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H., Ginsburg V. A monoclonal antibody-defined antigen associated with gastrointestinal cancer is a ganglioside containing sialylated lacto-N-fucopentaose II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14365–14369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander G. K., Levery S. B., Hakomori S., Holmes E. H. Isolation and characterization of the major acidic glycosphingolipids from the liver of the English sole (Parophrys vetulus). Presence of a novel ganglioside with a Forssman antigen determinant. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3103–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Okada T. S., Takeichi M. The calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion system regulates inner cell mass formation and cell surface polarization in early mouse development. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Slomiany A. Branched blood group A-active fucolipids of hog gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 25;486(3):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Slomiany A., Horowitz M. I. Blood group A active ceramide hexasaccharide lacking N-acetylglucosamine isolated from hog stomach mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 29;326(2):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Kobata A. Synthesis and mass fragmentographic analysis of partially O-methylated 2-N-methylglucosamines. J Biochem. 1975 Oct;78(4):679–686. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. P., Brown D., Heasman J., Cook G. M., Evans J., Vickers L., Wylie C. C. Involvement of a neutral glycolipid in differential cell adhesion in the Xenopus blastula. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3845–3855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. J., Hakomori S. I. A sphingolipid having a novel type of ceramide and lacto-N-fucopentaose 3. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1192–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]