Abstract
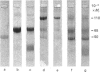
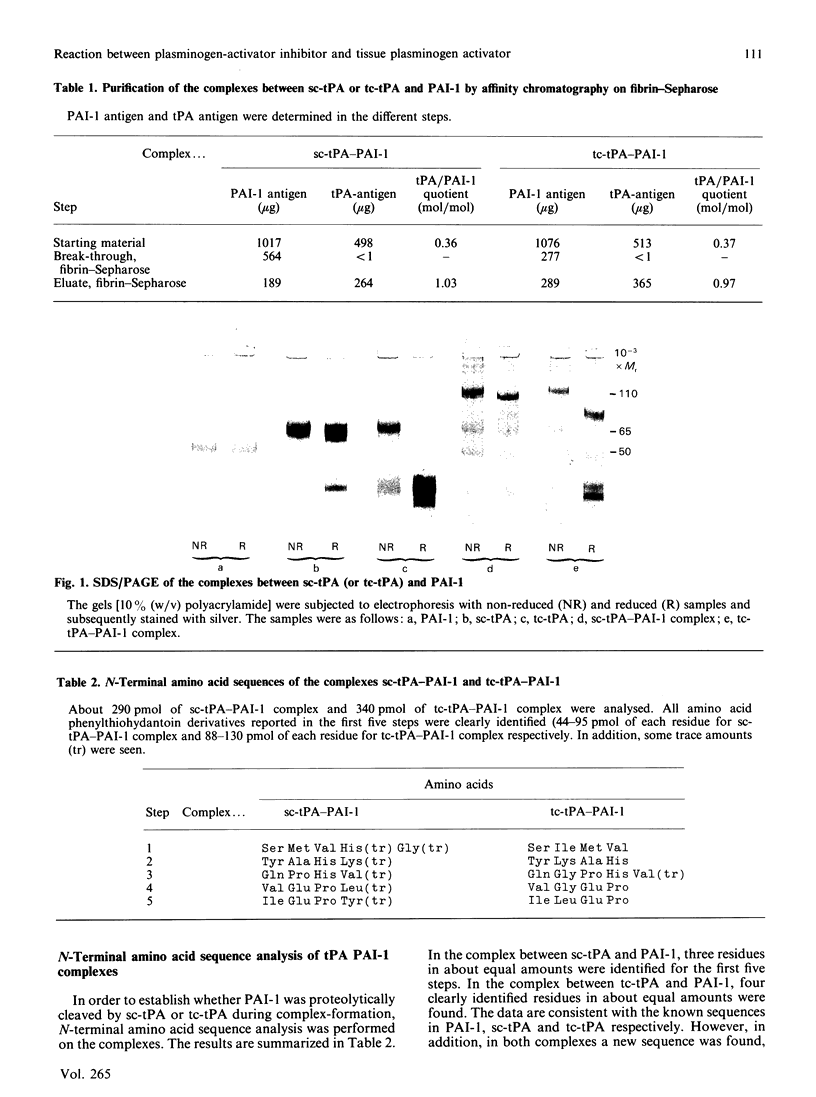
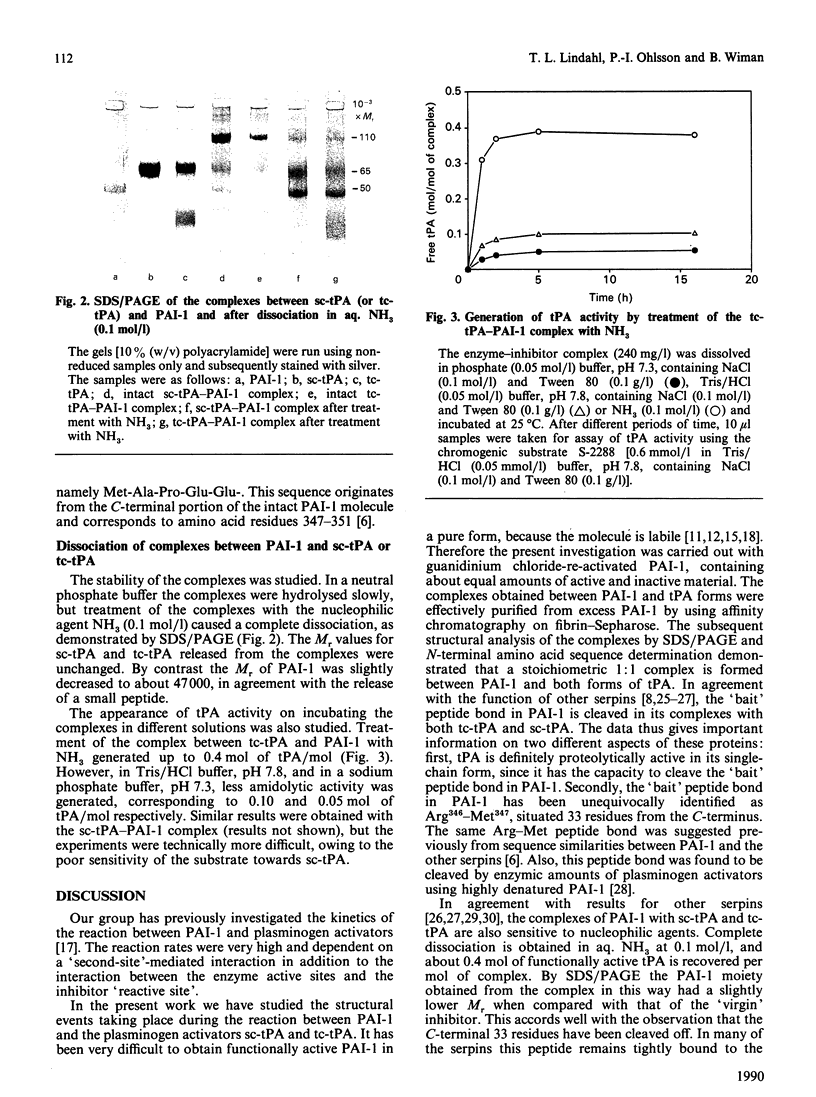
The structural events taking place during the reaction between PAI-1 (plasminogen-activator inhibitor 1) and the plasminogen activators sc-tPA (single-chain tissue plasminogen activator) and tc-tPA (two-chain tissue plasminogen activator) were studied. Complexes were formed by mixing sc-tPA or tc-tPA with PAI-1 in slight excess (on an activity basis). The complexes were purified from excess PAI-1 by affinity chromatography on fibrin-Sepharose. Examination of the purified complexes by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis (SDS/PAGE) and N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis demonstrated that a stoichiometric 1:1 complex is formed between PAI-1 and both forms of tPA. Data obtained from both complexes revealed the amino acid sequences of the parent molecules and, in addition, a new sequence: Met-Ala-Pro-Glu-Glu-. This sequence is found in the C-terminal portion of the intact PAI-1 molecule and thus locates the reactive centre of PAI-1 to Arg346-Met347. The proteolytic activity of sc-tPA is demonstrated by its capacity to cleave the 'bait' peptide bond in PAI-1. The complexes were inactive and dissociated slowly at physiological pH and ionic strength, but rapidly in aq. NH3 (0.1 mol/l). Amidolytic tPA activity was generated on dissociation of the complexes, corresponding to 0.4 mol of tPA/mol of complex. SDS/PAGE of the dissociated complexes indicated a small decrease in the molecular mass of PAI-1, in agreement with proteolytic cleavage of the 'bait' peptide bond during complex-formation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Riccio A., Welinder K. G., Douglas R., Sartorio R., Nielsen L. S., Oppenheimer C., Blasi F., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1: reactive center and amino-terminal heterogeneity determined by protein and cDNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Skriver K., Nielsen E., Thøgersen H. C., Wiman B., Donaldson V. H., Eddy R. L., Marrinan J., Radziejewska E., Huber R. Human C1 inhibitor: primary structure, cDNA cloning, and chromosomal localization. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4292–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewska J., Rånby M., Wiman B. Kinetics of the inhibition of plasminogen activators by the plasminogen-activator inhibitor. Evidence for 'second-site' interactions. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):327–332. doi: 10.1042/bj2510327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewska J., Wiman B. Determination of tissue plasminogen activator and its "fast" inhibitor in plasma. Clin Chem. 1986 Mar;32(3):482–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., Wiman B., de Faire U., Blombäck M. Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1557–1563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Pannell R. N., Travis J. The molecular stoichiometry of trypsin inhibition by human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):584–589. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90586-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Bachmann F. Studies on the release of a plasminogen activator inhibitor by human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Ransijn A., Bachmann F. Demonstration of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activators in human plasma. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Quantitation and properties of the active and latent plasminogen activator inhibitors in cultures of human endothelial cells. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1309–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Holmes W. E., van Hoef B., Wiman B., Rodriguez H., Collen D. Amino-acid sequence of human alpha 2-antiplasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):565–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Wiman B. Purification of high and low molecular weight plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 from fibrosarcoma cell-line HT 1080 conditioned medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 23;994(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Sjöholm I., Wiman B. Structural and circular-dichroism studies on the interaction between human C1-esterase inhibitor and C1s. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):617–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2130617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Wiman B. On the structure of the stable complex between plasmin and alpha-2-antiplasmin. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Sawdey M., Lawrence D., Millan J. L., Loskutoff D. J. Cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for the human beta-migrating endothelial-cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6776–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G. Evidence for the formation of an ester between thrombin and heparin cofactor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek H., Veerman H., Lambers H., Diergaarde P., Verweij C. L., van Zonneveld A. J., van Mourik J. A. Endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI): a new member of the Serpin gene family. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2539–2544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl G., Källström M., Bergsdorf N., Wallén P., Jörnvall H. Tissue plasminogen activator: peptide analyses confirm an indirectly derived amino acid sequence, identify the active site serine residue, establish glycosylation sites, and localize variant differences. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3701–3707. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., van Hinsbergh V. W., Jansen B. G. The active and the inactive plasminogen activator inhibitor from human endothelial cell conditioned medium are immunologically and functionally related to each other. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 4;883(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdén G., Hamsten A., Wiman B. Comparison of plasminogen activator inhibitor activity and antigen in plasma samples. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Nov 16;169(2-3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner O. F., Vetterlein M., Binder B. R. Purification of an active plasminogen activator inhibitor immunologically related to the endothelial type plasminogen activator inhibitor from the conditioned media of a human melanoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14474–14481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Chmielewska J., Rånby M. Inactivation of tissue plasminogen activator in plasma. Demonstration of a complex with a new rapid inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3644–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the mechanism of the reaction between human alpha 2-antiplasmin and plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9291–9297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]