Abstract
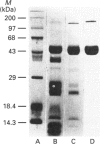
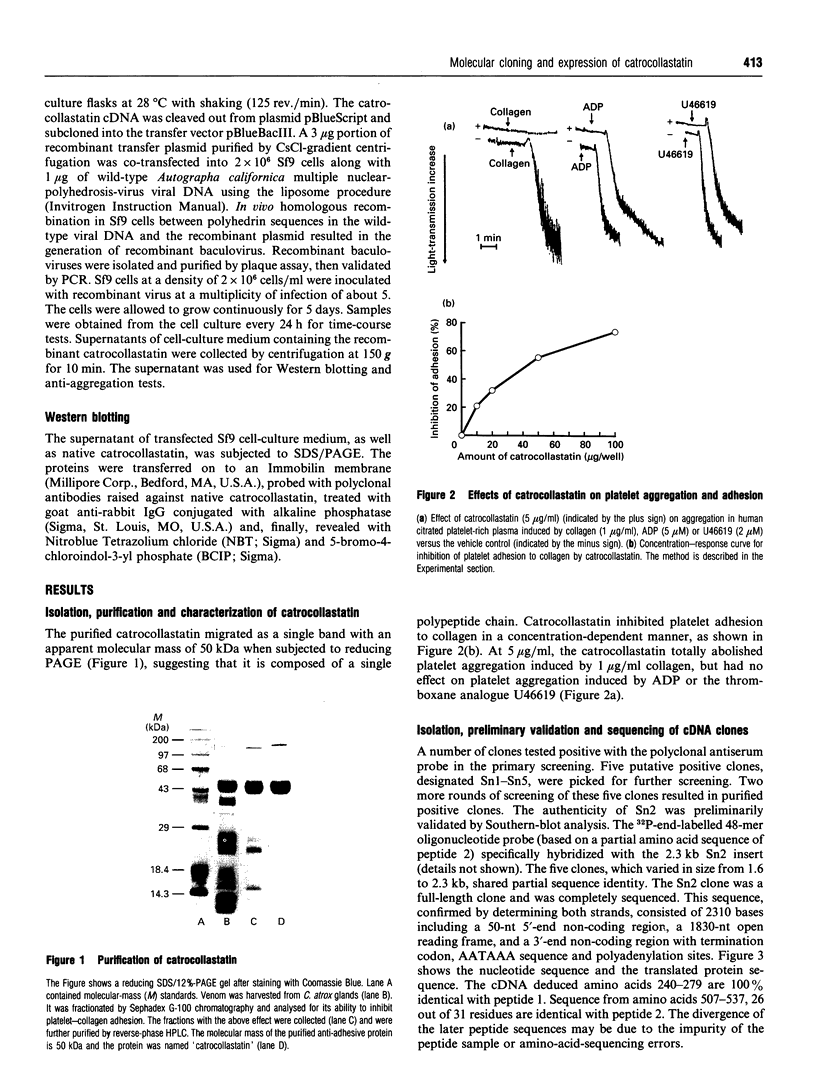
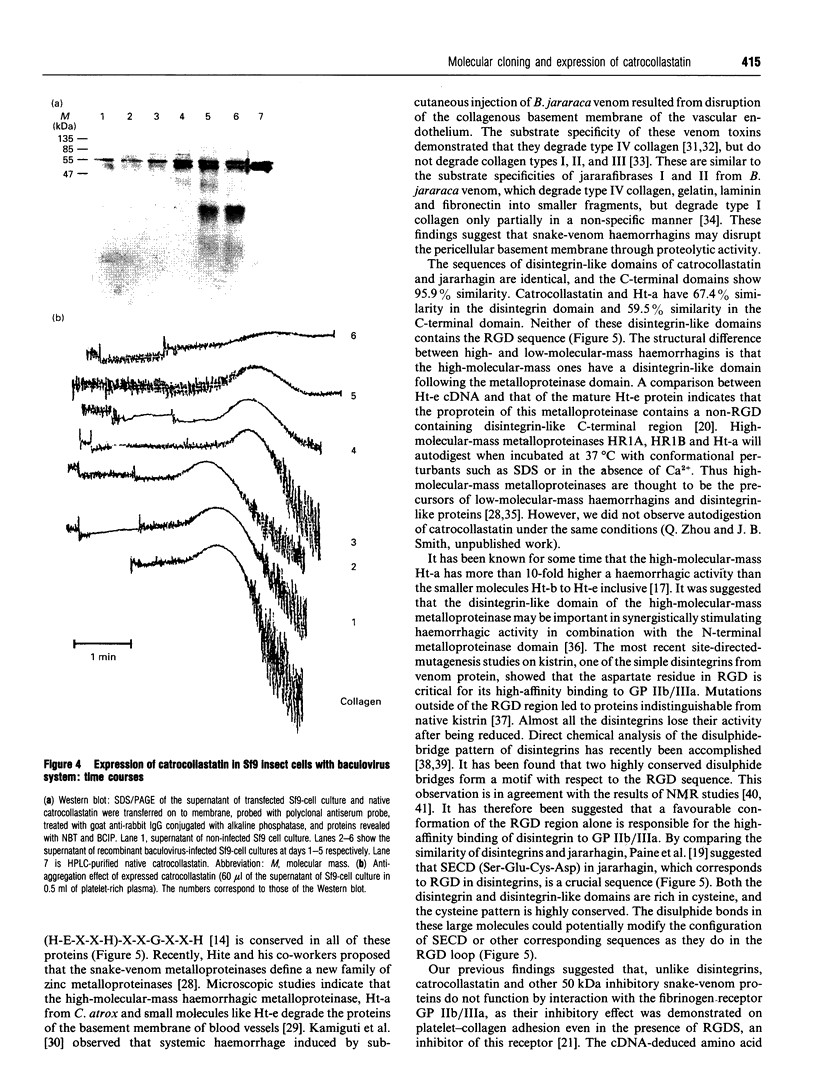
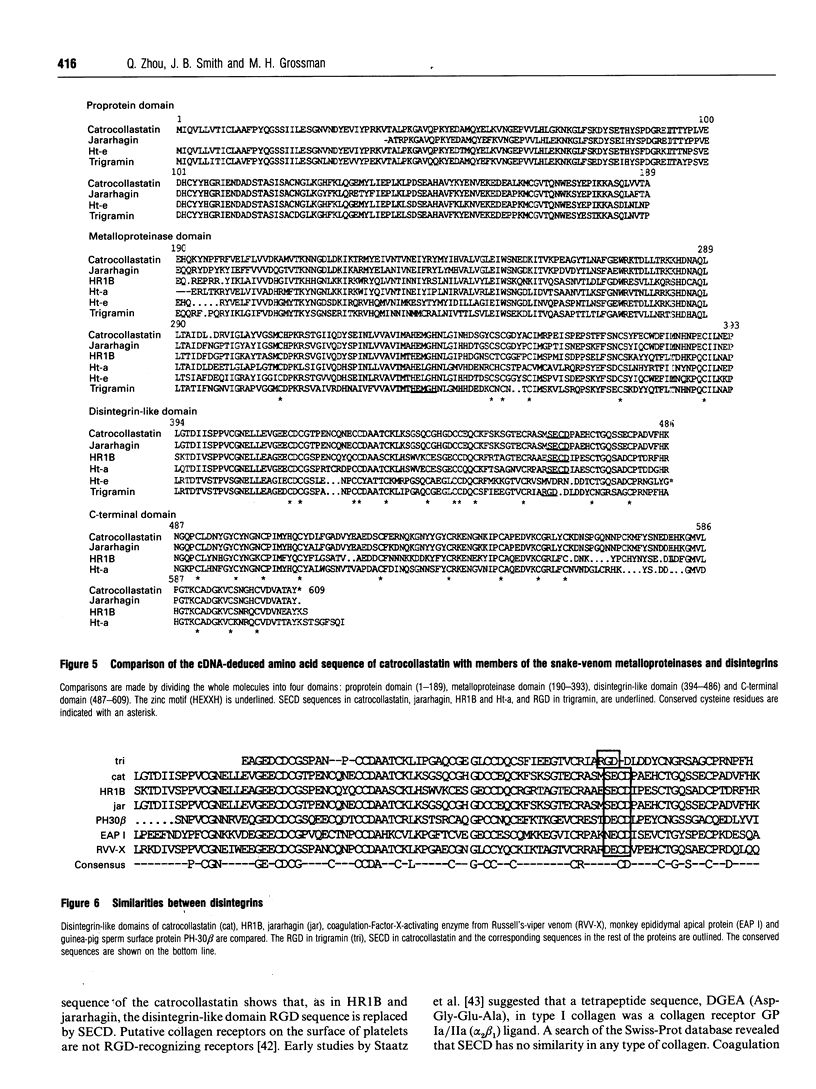
A 50 kDa protein that inhibits platelet adhesion to collagen has been isolated from snake venom of Crotalus atrox (western diamondback rattlesnake) and has been named 'catrocollastatin'. The cDNA cloning of catrocollastatin has been accomplished. A full-length cDNA of 2310 bp with an open reading frame between nucleotides 51 and 1880 was obtained. The deduced amino acid sequence consists of 609 amino acids. The cDNA-predicted amino acid sequence is highly similar to that of haemorrhagic metalloproteinase jararhagin from Bothrops jararaca venom, HR1B from Trimeresurus flavoviridis, Ht-e from C. atrox and trigramin from T. gramineus. Like jararhagin and HR1B, catrocollastatin is a multidomain molecule composed of an N-terminal domain, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain and a cysteine-rich C-terminal domain. In the disintegrin-like domain, the frequently seen RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) sequence is replaced by SECD (Ser-Glu-Cys-Asp). This cDNA was expressed in Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) (Sf9) insect cells using a baculovirus expression system. Like native catrocollastatin, the expressed protein is capable of selectively blocking collagen-induced platelet aggregation. This is the first full-length clone of a high-molecular-mass haemorrhagin to be expressed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler M., Lazarus R. A., Dennis M. S., Wagner G. Solution structure of kistrin, a potent platelet aggregation inhibitor and GP IIb-IIIa antagonist. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):445–448. doi: 10.1126/science.1862345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baramova E. N., Shannon J. D., Bjarnason J. B., Fox J. W. Degradation of extracellular matrix proteins by hemorrhagic metalloproteinases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 15;275(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baramova E. N., Shannon J. D., Fox J. W., Bjarnason J. B. Proteolytic digestion of non-collagenous basement membrane proteins by the hemorrhagic metalloproteinase Ht-e from Crotalus atrox venom. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(4-6):763–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason J. B., Tu A. T. Hemorrhagic toxins from Western diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) venom: isolation and characterization of five toxins and the role of zinc in hemorrhagic toxin e. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3395–3404. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel C. P., Wolfsberg T. G., Turck C. W., Myles D. G., Primakoff P., White J. M. A potential fusion peptide and an integrin ligand domain in a protein active in sperm-egg fusion. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):248–252. doi: 10.1038/356248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., Schäfer W., Soszka T., Lu W. Q., Cook J. J., Jameson B. A., Niewiarowski S. Identification of the disulfide bond pattern in albolabrin, an RGD-containing peptide from the venom of Trimeresurus albolabris: significance for the expression of platelet aggregation inhibitory activity. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5225–5229. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., Wang Y., Mann K., Schäfer W., Niewiarowski S., Stewart G. J. The disulfide bridge pattern of snake venom disintegrins, flavoridin and echistatin. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 14;309(3):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80797-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid (RGD): a cell adhesion motif. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jul;16(7):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90096-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. S., Carter P., Lazarus R. A. Binding interactions of kistrin with platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa: analysis by site-directed mutagenesis. Proteins. 1993 Mar;15(3):312–321. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. S., Henzel W. J., Pitti R. M., Lipari M. T., Napier M. A., Deisher T. A., Bunting S., Lazarus R. A. Platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa protein antagonists from snake venoms: evidence for a family of platelet-aggregation inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2471–2475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan Z. R., Gould R. J., Jacobs J. W., Friedman P. A., Polokoff M. A. Echistatin. A potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from the venom of the viper, Echis carinatus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19827–19832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Polokoff M. A., Friedman P. A., Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Cook J. J., Niewiarowski S. Disintegrins: a family of integrin inhibitory proteins from viper venoms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1990 Nov;195(2):168–171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-195-43129b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hite L. A., Fox J. W., Bjarnason J. B. A new family of proteinases is defined by several snake venom metalloproteinases. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1992 Jul;373(7):381–385. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hite L. A., Jia L. G., Bjarnason J. B., Fox J. W. cDNA sequences for four snake venom metalloproteinases: structure, classification, and their relationship to mammalian reproductive proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Jan;308(1):182–191. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Kirby E. P., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin: primary structure and its inhibition of von Willebrand factor binding to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on human platelets. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):661–666. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Liu C. Z., Ouyang C. H., Teng C. M. Halysin, an antiplatelet Arg-Gly-Asp-containing snake venom peptide, as fibrinogen receptor antagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 22;42(6):1209–1219. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiguti A. S., Theakston R. D., Desmond H., Hutton R. A. Systemic haemorrhage in rats induced by a haemorrhagic fraction from Bothrops jararaca venom. Toxicon. 1991;29(9):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Evans H. J. Structural domains in venom proteins: evidence that metalloproteinases and nonenzymatic platelet aggregation inhibitors (disintegrins) from snake venoms are derived by proteolysis from a common precursor. Toxicon. 1992 Mar;30(3):265–293. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90869-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Sugiki M., Yoshida E., Shimaya K., Mihara H. Broad substrate specificity of snake venom fibrinolytic enzymes: possible role in haemorrhage. Toxicon. 1992 Nov;30(11):1387–1397. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J., Stocker K. Effects of snake venoms on hemostasis. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1991;21(3):171–182. doi: 10.3109/10408449109089878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. J., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. The origin of matrix metalloproteinases and their familial relationships. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):4–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80895-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeper M. P., Jacobson M. A. Sequence of a cDNA encoding the platelet aggregation inhibitor trigramin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4255–4255. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. J., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Huffman W. F., Poste G., Samanen J. Development of GPIIb/IIIa antagonists as antithrombotic drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Nov;13(11):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ownby C. L., Bjarnason J., Tu A. T. Hemorrhagic toxins from rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) venom. Pathogenesis of hemorrhage induced by three purified toxins. Am J Pathol. 1978 Oct;93(1):201–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine M. J., Desmond H. P., Theakston R. D., Crampton J. M. Purification, cloning, and molecular characterization of a high molecular weight hemorrhagic metalloprotease, jararhagin, from Bothrops jararaca venom. Insights into the disintegrin gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22869–22876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A. C., Jones R., Barker P. J., Hall L. A mammalian epididymal protein with remarkable sequence similarity to snake venom haemorrhagic peptides. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):671–675. doi: 10.1042/bj2860671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle H., Marsh N. Nomenclature of exogenous hemostatic factors. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Aug 1;66(2):264–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudek V., Atkinson R. A., Pelton J. T. Three-dimensional structure of echistatin, the smallest active RGD protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7369–7372. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage B., Marzec U. M., Chao B. H., Harker L. A., Maraganore J. M., Ruggeri Z. M. Binding of the snake venom-derived proteins applaggin and echistatin to the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid recognition site(s) on platelet glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex inhibits receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11766–11772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Naughton M. A., Teng W., Rose J. W., Phillips D. R., Nannizzi L., Arfsten A., Campbell A. M., Charo I. F. Design of potent and specific integrin antagonists. Peptide antagonists with high specificity for glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1066–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Rose J. W., Hsu M. A., Phillips D. R., Fried V. A., Campbell A. M., Nannizzi L., Charo I. F. Barbourin. A GPIIb-IIIa-specific integrin antagonist from the venom of Sistrurus m. barbouri. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9359–9362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. D., Baramova E. N., Bjarnason J. B., Fox J. W. Amino acid sequence of a Crotalus atrox venom metalloproteinase which cleaves type IV collagen and gelatin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11575–11583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Dangelmaier C., Selak M. Identification of 50 kDa snake venom proteins which specifically inhibit platelet adhesion to collagen. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80615-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staatz W. D., Fok K. F., Zutter M. M., Adams S. P., Rodriguez B. A., Santoro S. A. Identification of a tetrapeptide recognition sequence for the alpha 2 beta 1 integrin in collagen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7363–7367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya H., Arakawa M., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Omori-Satoh T. Primary structure of H2-proteinase, a non-hemorrhagic metalloproteinase, isolated from the venom of the habu snake, Trimeresurus flavoviridis. J Biochem. 1989 Jul;106(1):151–157. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya H., Nishida S., Miyata T., Kawada S., Saisaka Y., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Coagulation factor X activating enzyme from Russell's viper venom (RVV-X). A novel metalloproteinase with disintegrin (platelet aggregation inhibitor)-like and C-type lectin-like domains. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14109–14117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya H., Oda K., Miyata T., Omori-Satoh T., Iwanaga S. The complete amino acid sequence of the high molecular mass hemorrhagic protein HR1B isolated from the venom of Trimeresurus flavoviridis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16068–16073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya H., Oda K., Onikura A., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Nikai T., Sugihara H., Omori-Satoh T. The structure and function relationships of hemorrhagic factors isolated from the venoms of Trimeresurus flavoviridis and Crotalus ruber ruber. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1990 Dec;43(6):252–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya H., Onikura A., Nikai T., Sugihara H., Iwanaga S. Primary structure of a hemorrhagic metalloproteinase, HT-2, isolated from the venom of Crotalus ruber ruber. J Biochem. 1990 Nov;108(5):711–719. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]