Abstract
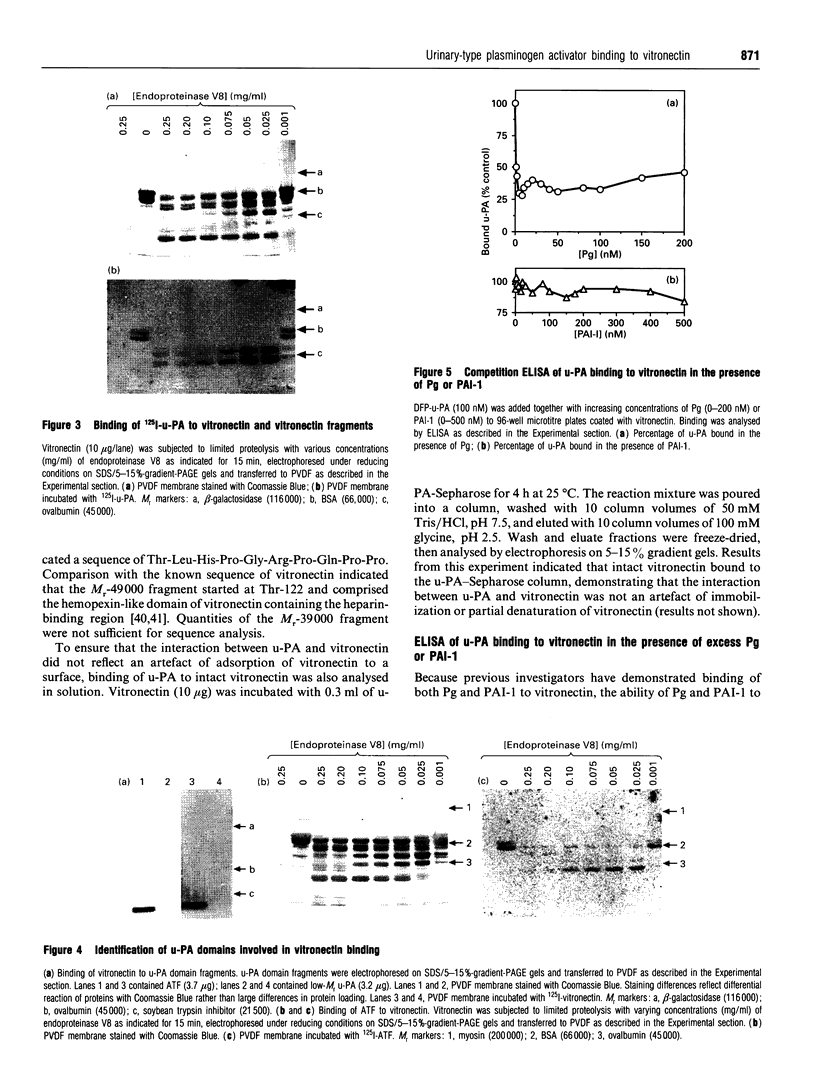
The present paper described interactions of urinary-type plasminogen activator (u-PA) with isolated protein components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) using kinetic and ligand-blotting analyses, as well as adhesion studies with u-PA-saturated U937 monocytic cells. Kinetic analyses showed that fibronectin and laminin were moderately effective at decreasing activation of plasminogen by u-PA (3-4-fold decrease in kcat/Km), while activation was stimulated slightly by collagen types I and IV (2-4-fold increase in kcat/Km). Ligand-blotting experiments using intact immobilized ECM proteins demonstrated that u-PA binds predominantly to vitronectin. This was supported by ELISA studies, which showed concentration dependent, saturable, reversible binding of u-PA to vitronectin (Kd,app. of 97 nM). Limited proteolysis of vitronectin followed by ligand-blotting analysis demonstrated u-PA binding to a specific vitronectin fragment (M(r) 49,000), and binding was shown to occur through the N-terminal fragment of u-PA. N-terminal sequence analysis indicated that this binding fragment of vitronectin originates with Thr-122 and comprises the hemopexin domain, including the heparin-binding region of the vitronectin molecule. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type I did not compete with u-PA for binding to vitronectin, suggesting both molecules may co-localize on vitronectin. In contrast, binding of u-PA to vitronectin was significantly inhibited by plasminogen, suggesting these molecules share a common binding site on vitronectin. In addition to in vitro studies, experiments were performed to assess the contribution of direct binding of u-PA to vitronectin on the adhesive behaviour of U937 cells. Binding of u-PA-saturated U937 cells to vitronectin was inhibited 66% by excess vitronectin, suggesting that direct binding of u-PA to vitronectin is the mechanism by which u-PA-dependent adhesion of U937 cells to vitronectin is mediated.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrendt N., Ploug M., Rønne E., Høyer-Hansen G., Danø K. Cellular receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator: protein structure. Methods Enzymol. 1993;223:207–222. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)23047-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt N., Rønne E., Ploug M., Petri T., Løber D., Nielsen L. S., Schleuning W. D., Blasi F., Appella E., Danø K. The human receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence and glycosylation variants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6453–6460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Podack E. R. Characterization of human S protein, an inhibitor of the membrane attack complex of complement. Demonstration of a free reactive thiol group. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2368–2374. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Behrendt N., Danø K. Plasminogen activation by receptor-bound urokinase. A kinetic study with both cell-associated and isolated receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12752–12758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Wun T. C., Behrendt N., Rønne E., Danø K. Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9904–9908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Robbins K. C. In vitro biosynthesis of plasminogen in a cell-free system directed by mRNA fractions isolated from monkey liver. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):190–196. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith R. F. Isolation and properties of a plasminogen activator derived from canine vascular tissue. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6788–6795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen B. S., Silverstein R. L., Leung L. L., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Binding of plasminogen to extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10765–10771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooistra T., Sprengers E. D., van Hinsbergh V. W. Rapid inactivation of the plasminogen-activator inhibitor upon secretion from cultured human endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):497–503. doi: 10.1042/bj2390497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost C., Stüber W., Ehrlich H. J., Pannekoek H., Preissner K. T. Mapping of binding sites for heparin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and plasminogen to vitronectin's heparin-binding region reveals a novel vitronectin-dependent feedback mechanism for the control of plasmin formation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12098–12105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimuro J., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of a protein from bovine plasma that binds to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and prevents its interaction with extracellular matrix. Evidence that the protein is vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):936–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuizen W., Verheijen J. H., Vermond A., Chang G. T. Plasminogen activation by tissue activator is accelerated in the presence of fibrin(ogen) cyanogen bromide fragment FCB-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 22;755(3):531–533. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novokhatny V., Medved L., Mazar A., Marcotte P., Henkin J., Ingham K. Domain structure and interactions of recombinant urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3878–3885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A. R., Chapman H. A., Jr An autocrine role for urokinase in phorbol ester-mediated differentiation of myeloid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI115070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Jenne D. Structure of vitronectin and its biological role in haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):123–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T. Specific binding of plasminogen to vitronectin. Evidence for a modulatory role of vitronectin on fibrin(ogen)-induced plasmin formation by tissue plasminogen activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):966–971. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91123-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Saksela O., Salonen E. M., Andreasen P., Nielsen L., Danø K., Vaheri A. Distinct localizations of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type 1 inhibitor under cultured human fibroblasts and sarcoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1085–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich R., Thompson E. W., Iwamoto Y., Martin G. R., Deason J. R., Fuller G. C., Miskin R. Effects of inhibitors of plasminogen activator, serine proteinases, and collagenase IV on the invasion of basement membranes by metastatic cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3307–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M. Studies on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by tissue plasminogen activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 24;704(3):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Saksela O., Vartio T., Vaheri A., Nielsen L. S., Zeuthen J. Plasminogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator bind to immobilized fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12302–12307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Pöllänen J., Stephens R., Andreasen P., Mayer M., Danø K., Gailit J., Ruoslahti E. Interaction of plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) with vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6339–6343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Ciambrone G., Wagner N. V., Binder B. R., Loskutoff D. J. The somatomedin B domain of vitronectin. Structural requirements for the binding and stabilization of active type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2659–2666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Loskutoff D. J. Evidence that type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor binds to the somatomedin B domain of vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2824–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Loskutoff D. J. Kinetic analysis of the interaction between type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and vitronectin and evidence that the bovine inhibitor binds to a thrombin-derived amino-terminal fragment of bovine vitronectin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 30;1078(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90087-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Wagner N. N., Loskutoff D. J. Serum-derived vitronectin influences the pericellular distribution of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1283–1291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L., Pannell R., Gurewich V., Harpel P. C. Thrombospondin forms complexes with single-chain and two-chain forms of urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11289–11294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack M. S., Moser T. L., Pizzo S. V. Binding of human plasminogen to basement-membrane (type IV) collagen. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):103–108. doi: 10.1042/bj2840103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack M. S., Pizzo S. V. Modulation of tissue plasminogen activator-catalyzed plasminogen activation by synthetic peptides derived from the amino-terminal heparin binding domain of fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18924–18928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack S., Gonzalez-Gronow M., Pizzo S. V. Regulation of plasminogen activation by components of the extracellular matrix. Biochemistry. 1990 May 22;29(20):4966–4970. doi: 10.1021/bi00472a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Aumailley M., Timpl R., Reisberg T., Tapiovaara H., Myöhänen H., Murphy-Ullrich J., Vaheri A. Urokinase binding to laminin-nidogen. Structural requirements and interactions with heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;207(3):937–942. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Bokman A. M., Myöhänen H. T., Reisberg T., Tapiovaara H., Pedersen N., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Llinás M., Vaheri A. Heparin binding to the urokinase kringle domain. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7572–7579. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Oldberg A., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Complete amino acid sequence of human vitronectin deduced from cDNA. Similarity of cell attachment sites in vitronectin and fibronectin. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2519–2524. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03965.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terato K., Nagai Y., Kawanishi K., Yamamoto S. A rapid assay method of collagenase activity using 14C-labeled soluble collagen as substrate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 11;445(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasini B. R., Mosher D. F. Vitronectin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1991;10:269–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz D. A., Chapman H. A. Reversible cellular adhesion to vitronectin linked to urokinase receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14746–14750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz D. A., Sailor L. Z., Chapman H. A. Cytokines induce urokinase-dependent adhesion of human myeloid cells. A regulatory role for plasminogen activator inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1541–1552. doi: 10.1172/JCI116360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohl R. C., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Kinetics of activation of human plasminogen by different activator species at pH 7.4 and 37 degrees C. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]