Abstract
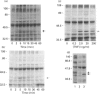
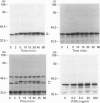
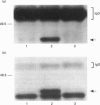
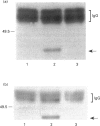
The present study was undertaken to determine the identities and characteristics of proteins with molecular masses between 40 and 44 kDa whose tyrosine phosphorylation increases in human neutrophils following stimulation of these cells with tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Immunoblotting results demonstrate that addition of GM-CSF to human neutrophils increases the tyrosine phosphorylation of two proteins with molecular masses of 42 and 44 kDa. However, the addition of TNF-alpha to neutrophils induces a time- and dose-dependent increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of a 40 kDa protein. Immunoprecipitation using specific mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) isoform antibodies and an antibody which recognizes phosphotyrosine-containing proteins demonstrated that the 42 and 44 kDa proteins are isoforms of MAPKs. Utilizing an in situ gel kinase activity assay, GM-CSF increases the kinase activity of the 42 and 44 kDa proteins. Moreover, using immunoprecipitated p42 and p44 MAPK isoforms in this gel assay revealed activity associated with the p42 and p44 MAPK isoforms. Using the same in situ assay, TNF-alpha induces an increase in kinase activity of a 40-42 kDa protein. However, the 40 kDa protein whose phosphorylation on tyrosine residues increased in human neutrophils following stimulation with TNF-alpha is not a member of the known MAPK family, demonstrating the divergences in pathways utilized by GM-CSF and TNF-alpha. This 40 kDa protein may be related to the recently identified protein that becomes phosphorylated on tyrosine residues upon stimulation of the human epidermal carcinoma cell line KB by interleukin-1. In these cells the p40 protein is part of a protein kinase cascade which results in the phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein, hsp27.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos-González R., Glenney J. R., Jr Temperature-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in epidermal growth factor-stimulated human fibroblasts. Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):663–673. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao T. S., Byron K. L., Lee K. M., Villereal M., Rosner M. R. Activation of MAP kinases by calcium-dependent and calcium-independent pathways. Stimulation by thapsigargin and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19876–19883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey S., Eguinoa A., Puyana-Theall K., Bolen J. B., Cantley L., Mollinedo F., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T., Stephens L. R. Granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor stimulates both association and activation of phosphoinositide 3OH-kinase and src-related tyrosine kinase(s) in human myeloid derived cells. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2681–2690. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNichilo M. O., Stewart A. G., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is a stimulant of platelet-activating factor and superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4896–4902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J. F., Billing P., Williams R., Gasson J. C. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines prime human neutrophils for enhanced arachidonic acid release and leukotriene B4 synthesis. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4315–4322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freshney N. W., Rawlinson L., Guesdon F., Jones E., Cowley S., Hsuan J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin-1 activates a novel protein kinase cascade that results in the phosphorylation of Hsp27. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1039–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuortes M., Jin W. W., Nathan C. Adhesion-dependent protein tyrosine phosphorylation in neutrophils treated with tumor necrosis factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):777–784. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Colasanto J. M., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. Direct stimulation by tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein (MAP) kinase activity by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):211–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2910211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Gomez-Cambronero T. M., Waterman W. H., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Yamazaki M., Metwally F., Molski T. F., Bonak V. A., Huang C. K., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22159–22163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanazono Y., Chiba S., Sasaki K., Mano H., Miyajima A., Arai K., Yazaki Y., Hirai H. c-fps/fes protein-tyrosine kinase is implicated in a signaling pathway triggered by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1641–1646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayadev S., Linardic C. M., Hannun Y. A. Identification of arachidonic acid as a mediator of sphingomyelin hydrolysis in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5757–5763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. A sensitive method for detection of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Druker B., Cannistra S. A., Furukawa Y., Torimoto Y., Griffin J. D. Signal transduction of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 receptors involves tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of cytoplasmic proteins. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):706–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Tsao H., Cobb M. H., Greene L. A. NGF and other growth factors induce an association between ERK1 and the NGF receptor, gp140prototrk. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1053–1065. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90065-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., DiPersio J. F., Caon A. C., Ho P., Naccache P. H. Involvement of tyrosine kinases in the activation of human peripheral blood neutrophils by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1842–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Hendrie P. C., Mantel C., Wood K., Ashman L. K., Broxmeyer H. E. Comparative analysis of signaling pathways between mast cell growth factor (c-kit ligand) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in a human factor-dependent myeloid cell line involves phosphorylation of Raf-1, GTPase-activating protein and mitogen-activated protein kinase. Exp Hematol. 1991 Dec;19(11):1110–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Gotoh Y. The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90019-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Chen R. H., Blenis J., Forsman J. p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase and p90 ribosomal S6 kinase are selectively phosphorylated and activated during thrombin-induced platelet activation and aggregation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):463–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. MAP kinases: charting the regulatory pathways. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.1382311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Golde D. W., Daeipour M., Nel A. E. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activates microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase in neutrophils via a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3350–3354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport A. P., Abboud C. N., DiPersio J. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): receptor biology, signal transduction, and neutrophil activation. Blood Rev. 1992 Mar;6(1):43–57. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(92)90007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M. Cell biology. A signal chain of events. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):534–535. doi: 10.1038/360534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lint J., Agostinis P., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W., Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates multiple serine/threonine protein kinases in Swiss 3T3 and L929 cells. Implication of casein kinase-2 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases in the tumor necrosis factor signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25916–25921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietor I., Schwenger P., Li W., Schlessinger J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18994–18999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Lee T. H. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7313–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R., Sanghera J., Wu F., Carbonaro-Hall D., Campbell D. L., Warburton D., Pelech S., Hall F. Identification of a human epidermal growth factor receptor-associated protein kinase as a new member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase family. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18213–18217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo A., Kitagawa S., Azuma E., Natori Y., Togawa A., Saito M., Takaku F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and intracellular alkalinization are early events in human neutrophils stimulated by tumor necrosis factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Feb 13;1156(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(93)90136-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]