Abstract
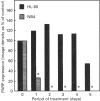
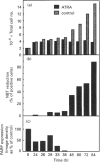
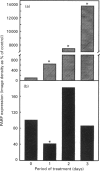
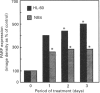
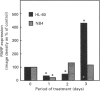
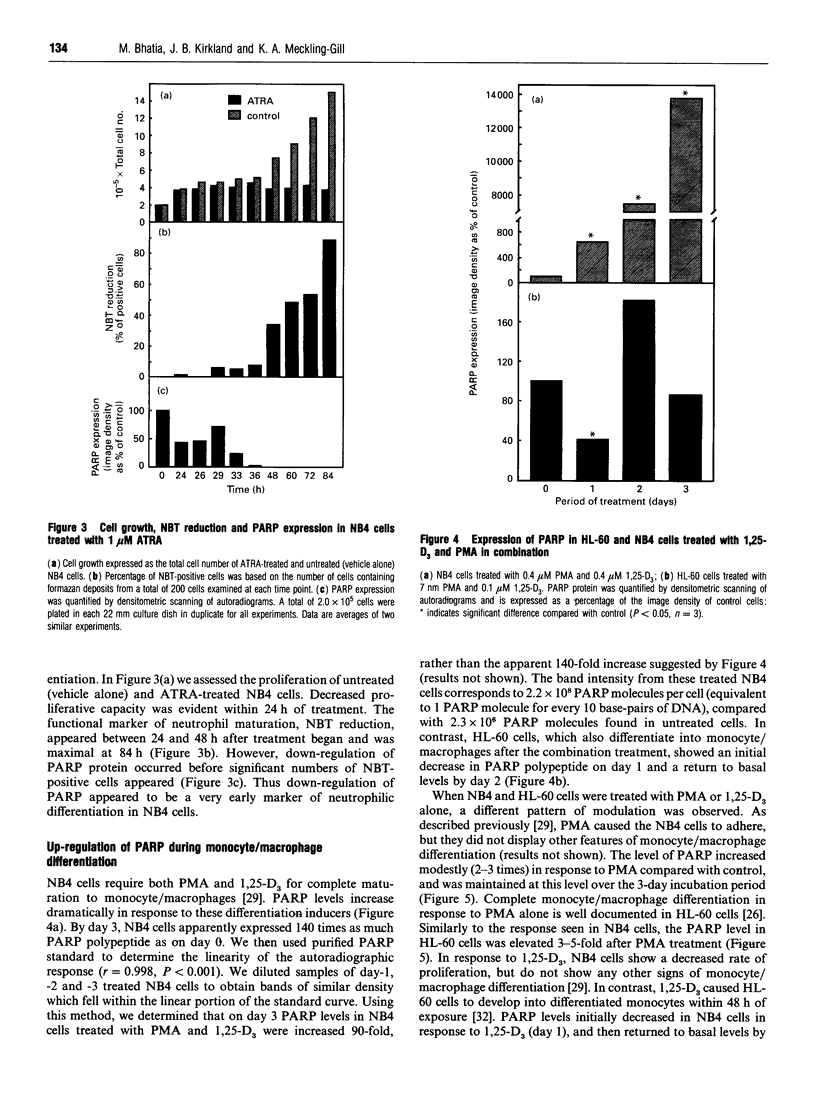
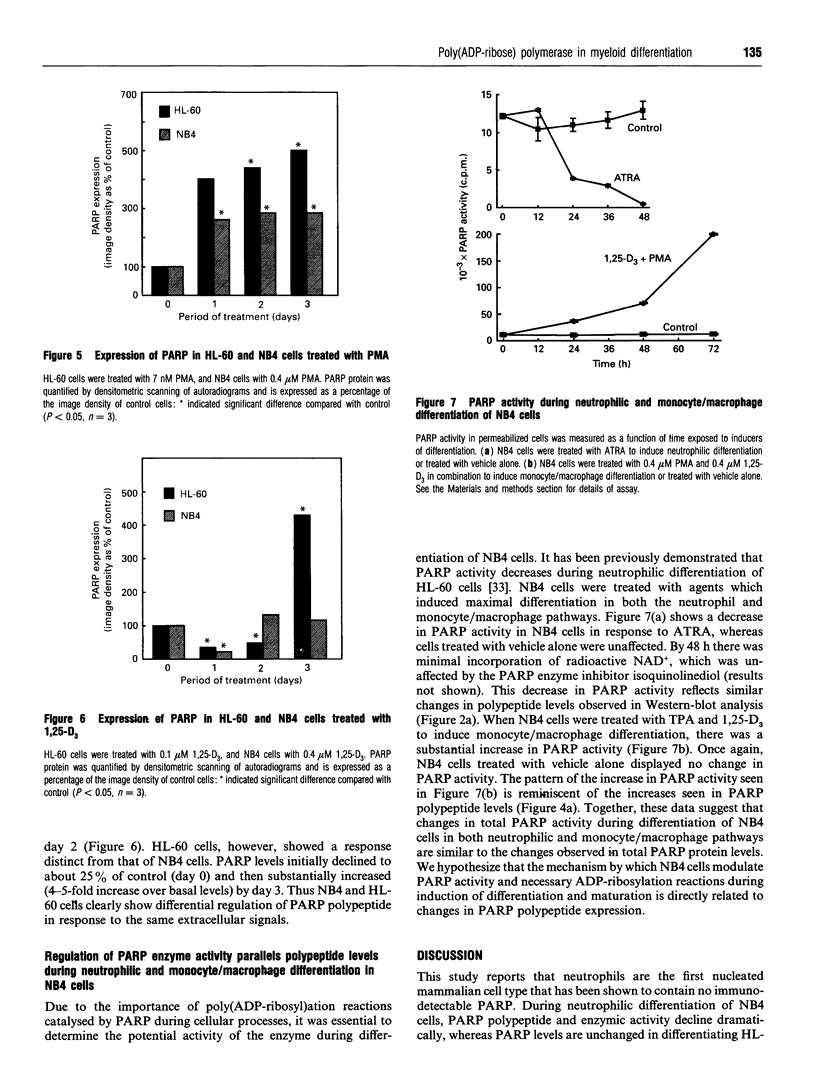
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is a nuclear enzyme which has been shown to play a role in the differentiation of haematopoietic cells. We report here that neutrophils are the first nucleated mammalian cell type demonstrated to be devoid of immunoreactive PARP. Both NB4 acute promyelocytic leukaemia and HL-60 (acute myelocytic leukaemia) cells were differentiated into non-malignant neutrophils with all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA). Western blot analysis demonstrated that ATRA had no effect on PARP expression in HL-60 cells. However, PARP was completely down-regulated in NB4 cells within 36 h of treatment initiation. This decrease in PARP polypeptide coincided with growth arrest and preceded the appearance of neutrophilic differentiation features. NB4 cells require a combination of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-D3) and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) to differentiate completely into monocyte/macrophages, whereas HL-60 cells can be made to differentiate by combined or single agents. PARP expression was up-regulated 90-fold when NB4 cells were treated with PMA and 1,25-D3 together, and this increase accompanied expression of the monocyte/macrophage phenotype. Only modest changes in PARP expression were observed when each agent was used alone in NB4 cells or when HL-60 cells were differentiated along the monocyte/macrophage pathway. In addition, PARP activity was modulated in a pattern similar to protein levels when NB4 cells were induced to differentiate along the neutrophilic and monocyte/macrophage pathways. This suggests that the activity of PARP may be controlled through regulation of protein levels during NB4 cell differentiation. We conclude that PARP levels are dramatically modulated during monocyte/macrophage and neutrophilic differentiation. On the basis of the tremendous changes in PARP polypeptide and total activity during myeloid differentiation, we propose that modulation of PARP gene expression is required for cellular maturation in both lineages.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berton G., Sorio C., Laudanna C., Menegazzi M., Carcereri De Prati A., Suzuki H. Activation of human monocyte-derived macrophages by interferon gamma is accompanied by increase of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 10;1091(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90228-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia K., Pommier Y., Giri C., Fornace A. J., Imaizumi M., Breitman T. R., Cherney B. W., Smulson M. E. Expression of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase gene following natural and induced DNA strand breakage and effect of hyperexpression on DNA repair. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jan;11(1):123–128. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia M., Kirkland J. B., Meckling-Gill K. A. M-CSF and 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3 synergize with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate to induce macrophage differentiation in acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cells. Leukemia. 1994 Oct;8(10):1744–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabert M. G., Kopp P. C., Bischoff P. L., Mandel P. Cell culture of tumors alters endogenous poly(ADPR)polymerase expression and activity. Int J Cancer. 1993 Mar 12;53(5):837–842. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damji N., Khoo K. E., Booker L., Browman G. P. Influence of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor 3-aminobenzamide on macrophage and granulocyte differentiation of HL-60 cells. Am J Hematol. 1986 Jan;21(1):67–78. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830210109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisuzaki K., Casley W. L., Griffiths A., Wheaton L. Temporal mapping of the differentiation pathway of the murine erythroleukemia cell. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 15;51(6):1668–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh F., Meldrum R., Shall S. Transient formation of DNA strand breaks during the induced differentiation of a human promyelocytic leukaemic cell line, HL-60. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3493–3502. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farzaneh F., Zalin R., Brill D., Shall S. DNA strand breaks and ADP-ribosyl transferase activation during cell differentiation. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):362–366. doi: 10.1038/300362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro A. M., Olivera B. M. Poly(ADP-ribosylation) of DNA topoisomerase I from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):547–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. E., Gray D. A., Berney J. J., Wing M. A., Guimaraes J. E., Hoffbrand A. V. Role of ADP-ribosyl transferase in differentiation of human granulocyte-macrophage progenitors to the macrophage lineage. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):1055–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. E., Ho A. D., Gray D. A., Berney J. J., Wing M. A., Yaxley J. J., Ma D. D., Hoffbrand A. V. DNA strand breakage and ADP-ribosyl transferase mediated DNA ligation during stimulation of human bone marrow cells by granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating activity. Leuk Res. 1984;8(3):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradwohl G., Ménissier de Murcia J. M., Molinete M., Simonin F., Koken M., Hoeijmakers J. H., de Murcia G. The second zinc-finger domain of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase determines specificity for single-stranded breaks in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2990–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube K., Küpper J. H., Bürkle A. Direct stimulation of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase in permeabilized cells by double-stranded DNA oligomers. Anal Biochem. 1991 Mar 2;193(2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90015-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone A. P., Williams G. T. Role of DNA breaks and ADP-ribosyl transferase activity in eukaryotic differentiation demonstrated in human lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):368–370. doi: 10.1038/300368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai M., Miwa M., Kondo T., Tanaka Y., Nakayasu M., Sugimura T. Involvement of poly (ADP-ribose) metabolism in induction of differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):404–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91448-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Desnoyers S., Ottaviano Y., Davidson N. E., Poirier G. G. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: an early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 1;53(17):3976–3985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan Z., Francis G. E. Contrasting patterns of DNA strand breakage and ADP-ribosylation-dependent DNA ligation during granulocyte and monocyte differentiation. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1114–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsten E., Bauer P. I., Kun E. Cellular regulation of ADP-ribosylation of proteins. IV. Conversion of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity to NAD-glycohydrolase during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of HL60 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 May;194(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90122-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Amatruda T., Ikekawa N., Kobayashi Y., DeLuca H. F. Induction of macrophage differentiation of human normal and leukemic myeloid stem cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its fluorinated analogues. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5624–5628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanotte M., Martin-Thouvenin V., Najman S., Balerini P., Valensi F., Berger R. NB4, a maturation inducible cell line with t(15;17) marker isolated from a human acute promyelocytic leukemia (M3). Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):1080–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautier D., Lagueux J., Thibodeau J., Ménard L., Poirier G. G. Molecular and biochemical features of poly (ADP-ribose) metabolism. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 May 26;122(2):171–193. doi: 10.1007/BF01076101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Regulation of normal differentiation in mouse and human myeloid leukemic cells by phorbol esters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5158–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis G., Althaus F. R. Uncoupling of DNA excision repair and nucleosomal unfolding in poly(ADP-ribose)-depleted mammalian cells. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jul;11(7):1237–1239. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.7.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazen A., Menissier-de Murcia J., Molinete M., Simonin F., Gradwohl G., Poirier G., de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase: a novel finger protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4689–4698. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menegazzi M., Carcereri de Prati A., Miwa M., Suzuki H., Libonati M. Regulation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase gene expression in mitogen-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biochem Int. 1992 Feb;26(1):69–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menegazzi M., Suzuki H., Carcereri de Prati A., Tommasi M., Miwa M., Gandini G., Gerosa F. Increase of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase mRNA levels during TPA-induced differentiation of human lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80327-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinete M., Vermeulen W., Bürkle A., Ménissier-de Murcia J., Küpper J. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., de Murcia G. Overproduction of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase DNA-binding domain blocks alkylation-induced DNA repair synthesis in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2109–2117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Gajate C., Tugores A., Flores I., Naranjo J. R. Differences in expression of transcription factor AP-1 in human promyelocytic HL-60 cells during differentiation towards macrophages versus granulocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):137–144. doi: 10.1042/bj2940137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka K., Tanaka K., Nokuo T., Ishizawa M., Ono T. Erythroid differentiation and poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in Friend leukemia cells. Gan. 1979 Feb;70(1):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménissier-de Murcia J., Molinete M., Gradwohl G., Simonin F., de Murcia G. Zinc-binding domain of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase participates in the recognition of single strand breaks on DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosseri C., Coppola S., Ghibelli L. Possible involvement of poly(ADP-ribosyl) polymerase in triggering stress-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Jun;212(2):367–373. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Ueda K., Hayaishi O., Ikai K., Niwa O. Induction of murine teratocarcinoma cell differentiation by suppression of poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. M., Glasser L., Tischler M. E., Wyckoff D., Cromey D., Fiederlein R., Bohnert O. Programmed cell death of the normal human neutrophil: an in vitro model of senescence. Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Jul 1;28(4):327–344. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070280408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry S. S., Kun E. Molecular interactions between DNA, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, and histones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1505–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher W., Friend C. Breakage of DNA and alterations in folded genomes by inducers of differentiation in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):841–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simbulan C. M., Suzuki M., Izuta S., Sakurai T., Savoysky E., Kojima K., Miyahara K., Shizuta Y., Yoshida S. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase stimulates DNA polymerase alpha by physical association. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Uchida K., Shima H., Sato T., Okamoto T., Kimura T., Miwa M. Molecular cloning of cDNA for human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and expression of its gene during HL-60 cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90543-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Yamauchi K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Harada N., Tanaka H., Takahashi S., Yamamoto H., Fujimoto S. Depression in gene expression for poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase during the interferon-gamma-induced activation process of murine macrophage tumor cells. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):571–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanuma S., Kanai Y. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of chromosomal proteins in the HeLa S3 cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6565–6570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada M., Nudel U., Fibach E., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Changes in DNA associated with induction of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):835–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoda T., Kurashige T., Yamamoto H., Fujimoto S., Taniguchi T. Fluctuation of gene expression for poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase during hemin-induced erythroid differentiation of human leukemia K562 cells and its reversion process. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]