Abstract
Plasmodium falciparum is an intracellular parasite of human erythrocytes. Parasite development is accompanied by an increase of the phospholipid content of the infected erythrocyte, but it results in a selective decrease of sphingomyelin. We have studied sphingomyelin biosynthesis in infected erythrocytes using as substrate a synthetic radiolabelled ceramide precursor, truncated in both hydrophobic chains. Lysates of infected, unlike those of non-infected, erythrocytes contained sphingomyelin synthase activity, which therefore is of parasite origin. The enzyme activity was associated with a membrane fraction. In contrast to mammalian cells, the parasite did not synthesize detectable levels of glycosphingolipids. In intact infected erythrocytes the ceramide precursor was converted into a correspondingly truncated soluble sphingomyelin which was released into the medium at 37 degrees C. Release of truncated sphingomyelin was inhibited by low temperature (15 degrees C) but not by the fungal metabolite brefeldin A which, however, arrests protein export from the parasite. While membranes of mammalian cells, including the plasma membrane of non-infected erythrocytes, are impermeable to truncated sphingomyelin, the membrane of infected erythrocytes allowed passage of the molecule in both directions. The results obtained with the unicellular eukaryote used here as an experimental model are discussed in comparison with sphingomyelin synthesis and transport in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF

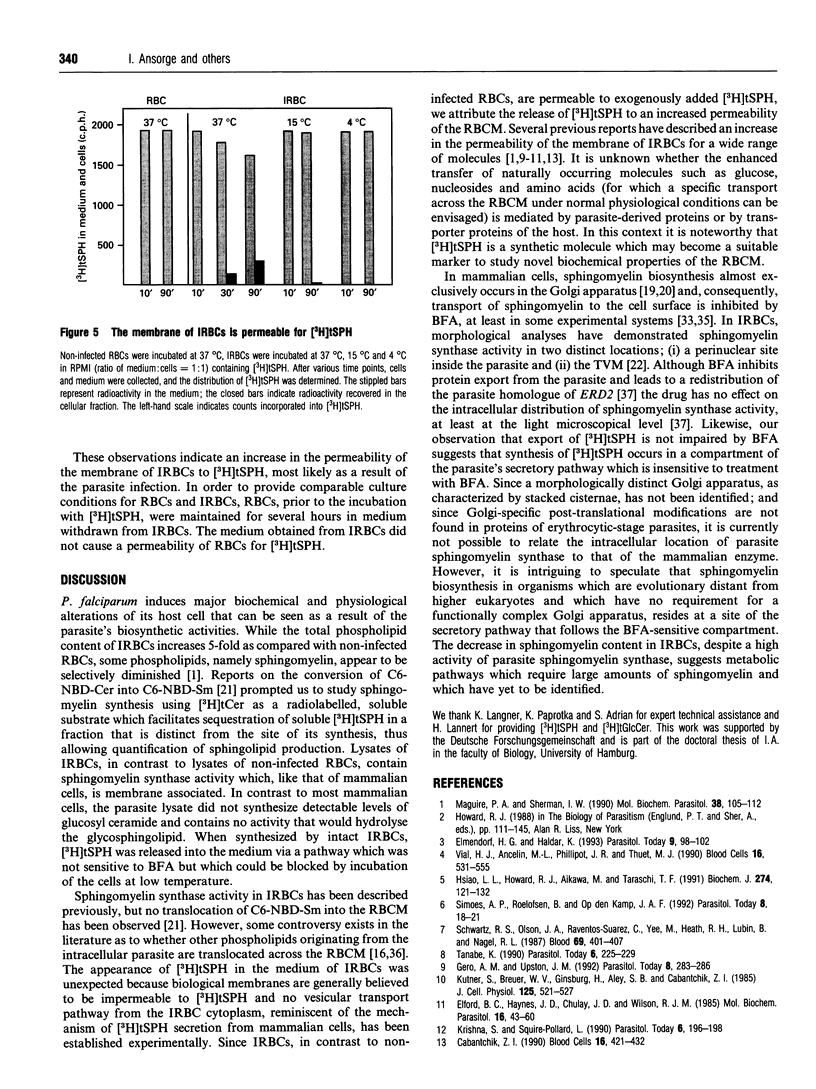

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M. Morphological changes in erythrocytes induced by malarial parasites. Biol Cell. 1988;64(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(88)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W. Vesicle-mediated transport of membrane and proteins in malaria-infected erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):379–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benting J., Mattei D., Lingelbach K. Brefeldin A inhibits transport of the glycophorin-binding protein from Plasmodium falciparum into the host erythrocyte. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 15;300(Pt 3):821–826. doi: 10.1042/bj3000821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüning A., Karrenbauer A., Schnabel E., Wieland F. T. Brefeldin A-induced increase of sphingomyelin synthesis. Assay for the action of the antibiotic in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5052–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I. Properties of permeation pathways induced in the human red cell membrane by malaria parasites. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Ferguson D. J. Secretory processes in Plasmodium. Parasitol Today. 1993 Mar;9(3):80–81. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90205-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Haynes J. D., Chulay J. D., Wilson R. J. Selective stage-specific changes in the permeability to small hydrophilic solutes of human erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jun;16(1):43–60. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Identification and localization of ERD2 in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: separation from sites of sphingomyelin synthesis and implications for organization of the Golgi. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4763–4773. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Plasmodium falciparum exports the Golgi marker sphingomyelin synthase into a tubovesicular network in the cytoplasm of mature erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):449–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Secretory transport in Plasmodium. Parasitol Today. 1993 Mar;9(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Stieger B., Hubbard A. L., Pagano R. E. Sphingomyelin synthesis in rat liver occurs predominantly at the cis and medial cisternae of the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8650–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gero A. M., Upston J. M. Altered membrane permeability: a new approach to malaria chemotherapy. Parasitol Today. 1992 Aug;8(8):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90147-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther K., Tümmler M., Arnold H. H., Ridley R., Goman M., Scaife J. G., Lingelbach K. An exported protein of Plasmodium falciparum is synthesized as an integral membrane protein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 May;46(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90208-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Uyetake L., Ghori N., Elmendorf H. G., Li W. L. The accumulation and metabolism of a fluorescent ceramide derivative in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90137-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Uyetake L. The movement of fluorescent endocytic tracers in Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):161–177. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90253-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao L. L., Howard R. J., Aikawa M., Taraschi T. F. Modification of host cell membrane lipid composition by the intra-erythrocytic human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):121–132. doi: 10.1042/bj2740121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeckel D., Karrenbauer A., Birk R., Schmidt R. R., Wieland F. Sphingomyelin is synthesized in the cis Golgi. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80659-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeckel D., Karrenbauer A., Burger K. N., van Meer G., Wieland F. Glucosylceramide is synthesized at the cytosolic surface of various Golgi subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):259–267. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallen K. J., Quinn P., Allan D. Effects of brefeldin A on sphingomyelin transport and lipid synthesis in BHK21 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):307–312. doi: 10.1042/bj2890307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrenbauer A., Jeckel D., Just W., Birk R., Schmidt R. R., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. The rate of bulk flow from the Golgi to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90159-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna S., Squire-Pollard L. Calcium metabolism in malaria-infected erythrocytes. Parasitol Today. 1990 Jun;6(6):196–198. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutner S., Breuer W. V., Ginsburg H., Aley S. B., Cabantchik Z. I. Characterization of permeation pathways in the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes infected with early stages of Plasmodium falciparum: association with parasite development. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):521–527. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingelbach K. R. Plasmodium falciparum: a molecular view of protein transport from the parasite into the host erythrocyte. Exp Parasitol. 1993 May;76(3):318–327. doi: 10.1006/expr.1993.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky N. G., Pagano R. E. Sphingolipid metabolism in cultured fibroblasts: microscopic and biochemical studies employing a fluorescent ceramide analogue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire P. A., Sherman I. W. Phospholipid composition, cholesterol content and cholesterol exchange in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jan 1;38(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90210-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasvol G., Wilson R. J., Smalley M. E., Brown J. Separation of viable schizont-infected red cells of Plasmodium falciparum from human blood. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1978 Feb;72(1):87–88. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1978.11719283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Olson J. A., Raventos-Suarez C., Yee M., Heath R. H., Lubin B., Nagel R. L. Altered plasma membrane phospholipid organization in Plasmodium falciparum-infected human erythrocytes. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao Y. J., Vance J. E. Sphingomyelin transport to the cell surface occurs independently of protein secretion in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26085–26092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui W. A., Kan S. C., Kramer K., Richmond-Crum S. M. In vitro production and partial purification of Plasmodium falciparum antigen. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):75–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simões A. P., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid compartmentalization in erythrocytes parasitized by Plasmodium spp. Parasitol Today. 1992 Jan;8(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90305-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K. Glucose transport in malaria infected erythrocytes. Parasitol Today. 1990 Jul;6(7):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90199-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Ancelin M. L., Philippot J. R., Thuet M. J. Biosynthesis and dynamics of lipids in Plasmodium-infected mature mammalian erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):531–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]