Abstract
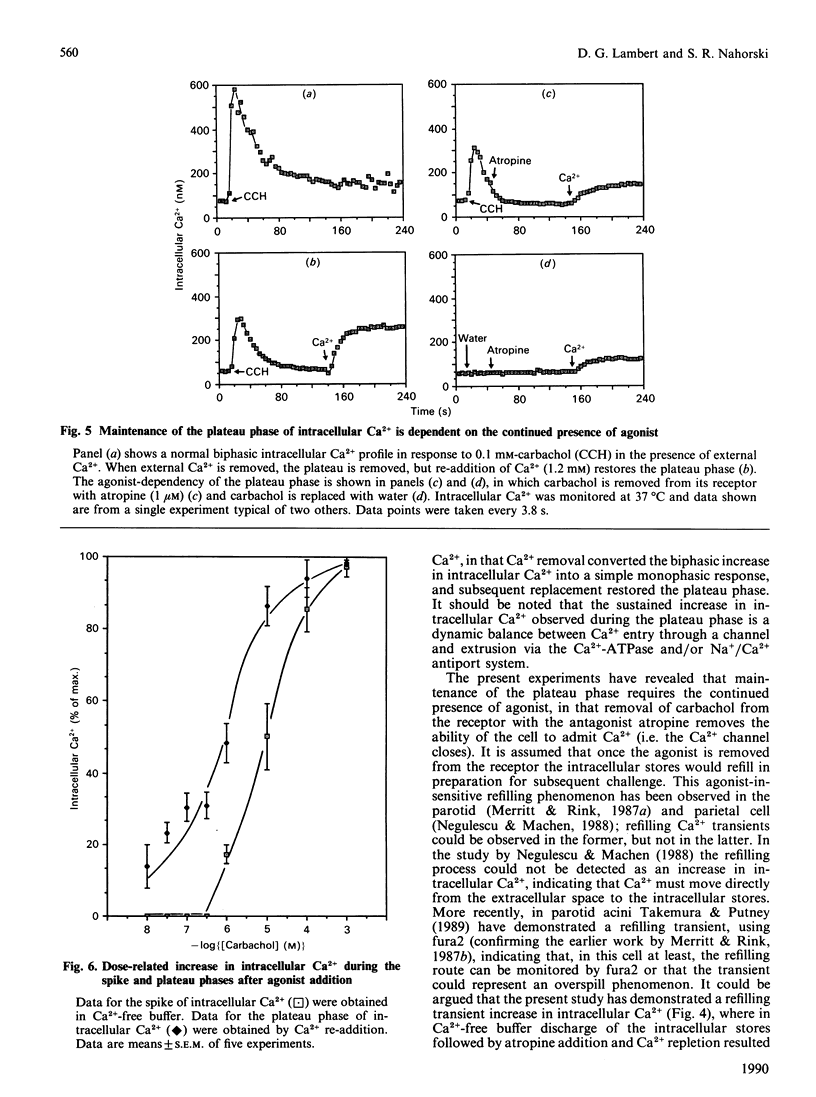
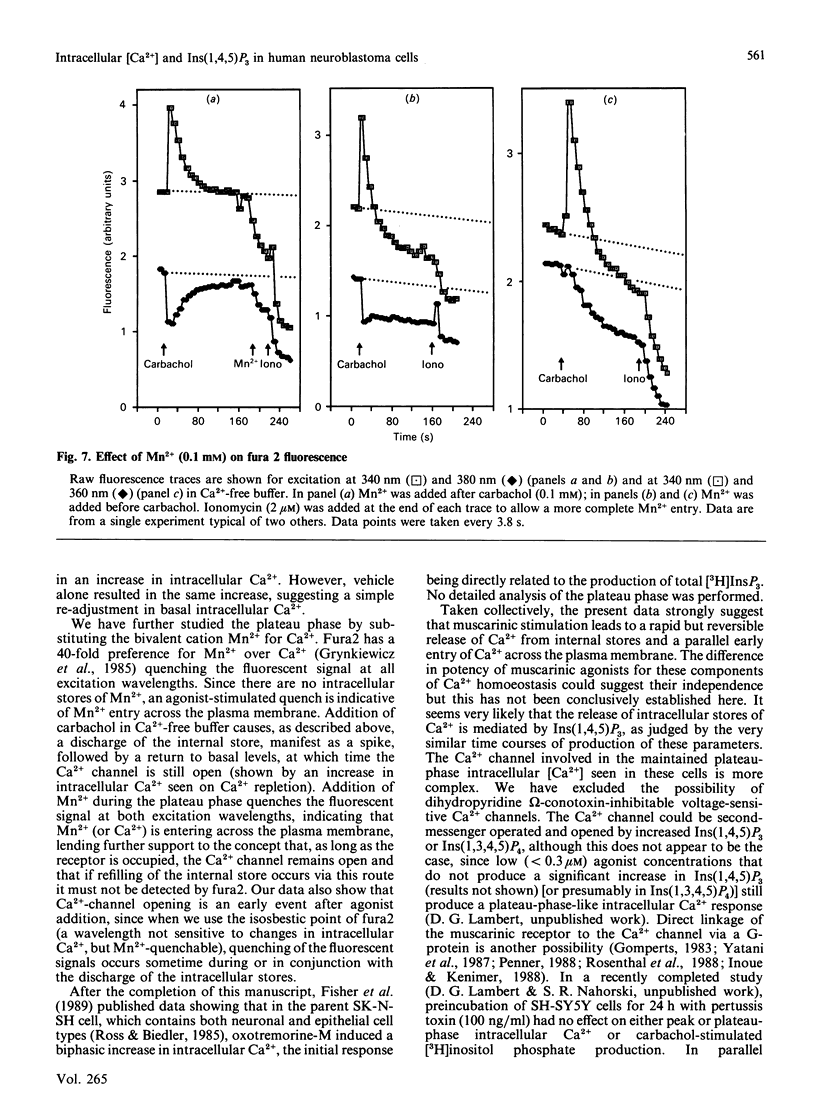
This study reports increased intracellular Ca2+ and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [Ins(1,4,5)P3] in response to muscarinic-cholinergic stimulation of human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells. Carbachol stimulation leads to a rapid increase in intracellular Ca2+ and Ins(1,4,5)P3 mass, both reaching a peak at around 10 s and then declining to a new maintained phase significantly above basal. Dose-response analysis of peak and plateau phases of intracellular Ca2+ shows different agonist potencies for both phases, carbachol being more potent for the plateau phase. The plateau-phase intracellular Ca2+ was dependent on extracellular Ca2+, which is admitted to the cell through a non-voltage-sensitive Ni2(+)-blockable Ca2+ channel. Using a Mn2+ quench protocol, we have shown that Ca2+ entry occurs early during the discharge of the internal stores. The plateau phase (Ca2(+)-channel opening) is dependent on the continued presence of agonist, since addition of atropine closes the Ca2+ channel and intracellular Ca2+ declines rapidly back to basal. We also failed to detect a refilling transient when we added back Ca2+ after intracellular Ca2+ had reached a peak and then declined in Ca2(+)-free conditions. These data strongly suggest that muscarinic stimulation of SH-SY5Y cells leads to a rapid release of Ca2+ from an Ins(1,4,5)P3-sensitive internal store and a parallel early entry of Ca2+ across the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerman K. E. Depolarization of human neuroblastoma cells as a result of muscarinic receptor-induced rise in cytosolic Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Calcium transport and buffering in neurons. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Challiss R. A., Barnes P. J., Nahorski S. R. Mass changes of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in trachealis muscle following agonist stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Calcium-mediated neurotoxicity: relationship to specific channel types and role in ischemic damage. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):465–469. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P. H., Rink T. J. Fluorescence and bioluminescence measurement of cytoplasmic free calcium. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):313–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2480313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Pandiella A., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Generation of inositol phosphates, cytosolic Ca2+, and ionic fluxes in PC12 cells treated with bradykinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17350–17359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Domask L. M., Roland R. M. Muscarinic receptor regulation of cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations in human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells: Ca2+ requirements for phospholipase C activation. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;35(2):195–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T., Okano Y., Nozawa Y. Bradykinin-induced generation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in fibroblasts and neuroblastoma cells: effect of pertussis toxin, extracellular calcium, and down-regulation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1429–1435. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D. Involvement of guanine nucleotide-binding protein in the gating of Ca2+ by receptors. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):64–66. doi: 10.1038/306064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Merritt J. E. Evidence that agonists stimulate bivalent-cation influx into human endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):179–184. doi: 10.1042/bj2550179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Agonists stimulate divalent cation channels in the plasma membrane of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80703-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkilä J. E., Scott I. G., Suominen L. A., Akerman K. E. Differentiation-associated decrease in muscarinic receptor sensitivity in human neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jan;130(1):157–162. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Kenimer J. G. Muscarinic stimulation of calcium influx and norepinephrine release in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8157–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M., Pollock W. K., Smith P. M., Wreggett K. A. Inositol phosphates: proliferation, metabolism and function. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):281–298. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Hallam T. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Receptor coupled events in bradykinin action: rapid production of inositol phosphates and regulation of cytosolic free Ca2+ in a neural cell line. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):49–54. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kater S. B., Mattson M. P., Cohan C., Connor J. Calcium regulation of the neuronal growth cone. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Ghataorre A. S., Nahorski S. R. Muscarinic receptor binding characteristics of a human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH and its clones SH-SY5Y and SH-EP1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 8;165(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90771-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Milani D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Pathways of Ca2+ influx at the plasma membrane: voltage-, receptor-, and second messenger-operated channels. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Aug;171(2):271–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J. Platelets and parotid acinar cells have different mechanisms for agonist-stimulated divalent cation entry. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6161–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17362–17369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. The effects of substance P and carbachol on inositol tris- and tetrakisphosphate formation and cytosolic free calcium in rat parotid acinar cells. A correlation between inositol phosphate levels and calcium entry. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14912–14916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R. Inositol polyphosphates and neuronal calcium homeostasis. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):444–448. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Potter B. V. Molecular recognition of inositol polyphosphates by intracellular receptors and metabolic enzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negulescu P. A., Machen T. E. Release and reloading of intracellular Ca stores after cholinergic stimulation of the parietal cell. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):C498–C504. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.4.C498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Matthews G., Neher E. Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):499–504. doi: 10.1038/334499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R. Multiple signaling pathways control stimulus-secretion coupling in rat peritoneal mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9856–9860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Van De Walle C. M. The relationship between muscarinic receptor binding and ion movements in rat parotid cells. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:521–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Hescheler J., Trautwein W., Schultz G. Control of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels by G protein-coupled receptors. FASEB J. 1988 Sep;2(12):2784–2790. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.12.2457531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. A., Biedler J. L. Presence and regulation of tyrosinase activity in human neuroblastoma cell variants in vitro. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1628–1632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Augustine G. J. Calcium ions, active zones and synaptic transmitter release. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Capacitative calcium entry in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):409–412. doi: 10.1042/bj2580409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


