Abstract
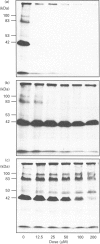
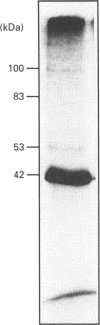
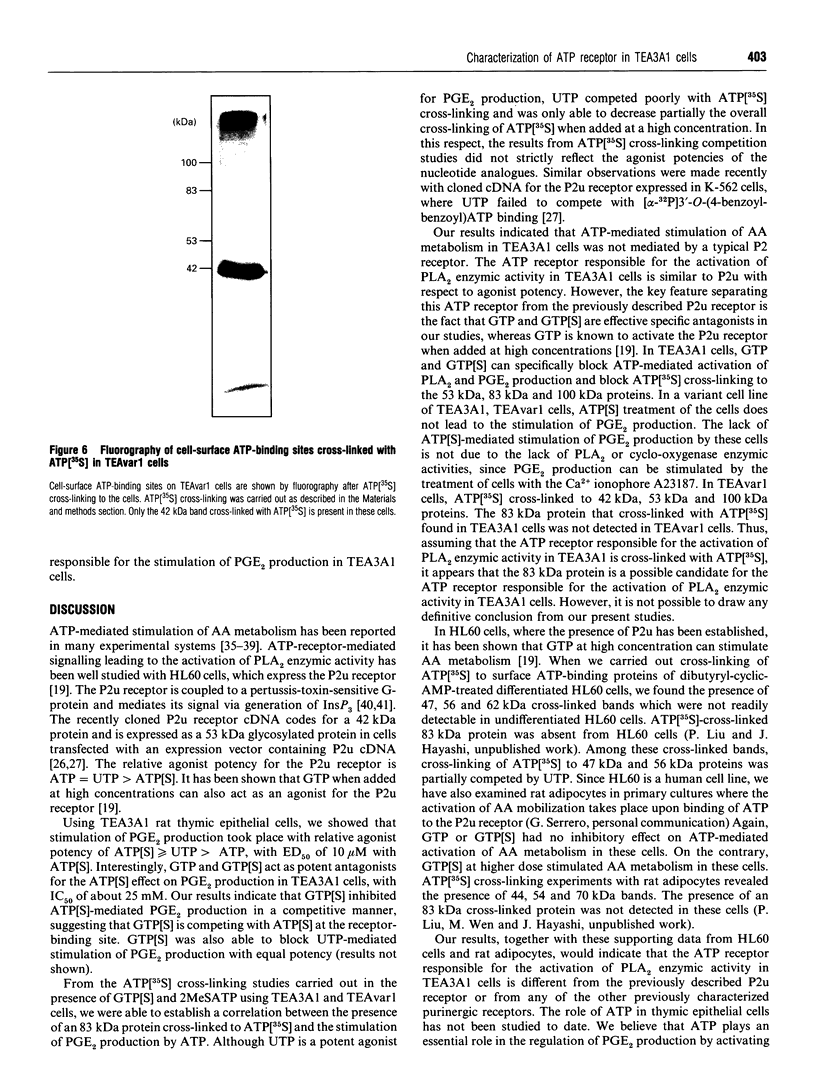
In TEA3A1 rat thymic epithelial cells, ATP stimulates prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production through activation of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymic activity. The stimulation of PGE2 production tested with other nucleotides indicated the agonist potency of adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (ATP[S]) > or = UTP > ATP, with ED50 of about 10 microM for ATP[S]. In TEA3A1 cells, cross-linking studies with ATP[35S] revealed the presence of four cell-surface cross-linked bands of 42 kDa, 53 kDa, 83 kDa and 100 kDa in Triton X-100 extracts of TEA3A1 cells by fluorography. Guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate specifically blocked the cross-linking of ATP[35S] to the 53 kDa, 83 kDa and 100 kDa ATP-binding proteins, and inhibited the ATP[S]-mediated stimulation of PGE2 production with an ED50 of about 25 microM. On the other hand, 2-methylthioadenosine triphosphate (2MeSATP) blocked ATP[35S] cross-linking to the 42 kDa protein, but had no effect on ATP[S]-mediated stimulation of PGE2 production. In a variant cell line, TEAvarl, derived from TEA3A1 cells that lost their response to ATP in the activation of PLA2, the presence of 83 kDa ATP-binding protein was not detected. Results from our study suggest that ATP activates PLA2 enzymic activity in TEA3A1 cells by binding to an atypical ATP receptor that has not been described previously.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Burnstock G. Species differences in characteristics and distribution of [3H] alpha,beta-methylene ATP binding sites in urinary bladder and urethra of rat, guinea-pig and rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 May 27;216(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90209-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Simon J., Burnstock G., Barnard E. A. Solubilization and molecular size determination of the P2x purinoceptor from rat vas deferens. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17581–17587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E., Kirby M. L. Dependence of thymus development on derivatives of the neural crest. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):498–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6606851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Cooper C. L., Harden T. K. [32P]3'-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyl ATP as a photoaffinity label for a phospholipase C-coupled P2Y-purinergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13515–13520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruner G., Murphy S. Purinergic P2Y receptors on astrocytes are directly coupled to phospholipase A2. Glia. 1993 Mar;7(3):219–224. doi: 10.1002/glia.440070305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Neural nomenclature. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):282–283. doi: 10.1038/229282d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvano S. E., Mark D. A., Good R. A., Fernandes G. Age-related changes in lymphoid tissue content of prostaglandins in (NZB X NZW)F1 and CBA/H mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):113–116. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Welte K., Mertelsmann R., Dupont B. Prostaglandin E2 acts at two distinct pathways of T lymphocyte activation: inhibition of interleukin 2 production and down-regulation of transferrin receptor expression. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1172–1179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. The receptors for ATP and fMetLeuPhe are independently coupled to phospholipases C and A2 via G-protein(s). Relationship between phospholipase C and A2 activation and exocytosis in HL60 cells and human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):715–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2630715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristalli G., Mills D. C. Identification of a receptor for ADP on blood platelets by photoaffinity labelling. Biochem J. 1993 May 1;291(Pt 3):875–881. doi: 10.1042/bj2910875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., Cowen D. S., Meuller L. M. Activation of inositol phospholipid breakdown in HL60 cells by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Evidence for mediation by both pertussis toxin-sensitive and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18108–18117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R. Signal transduction by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;4(4):295–300. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb L., Lustig K. D., Sullivan D. M., Turner J. T., Weisman G. A. Functional expression and photoaffinity labeling of a cloned P2U purinergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10449–10453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Derkach V., Surprenant A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):503–505. doi: 10.1038/357503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Humes J. L. The role of arachidonic acid metabolism in the activities of interleukin 1 and 2. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1153–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Williams H. L., Axelrod J. A transduction pathway associated with receptors coupled to the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein Gi that amplifies ATP-mediated arachidonic acid release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6477–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg E. J., Feuerstein G., Shohami E., Pollard H. B. Adenosine triphosphate stimulates inositol phospholipid metabolism and prostacyclin formation in adrenal medullary endothelial cells by means of P2-purinergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5630–5634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen V., Legros J. J., Franchimont P., Baudrihaye M., Defresne M. P., Boniver J. The neuroendocrine thymus: coexistence of oxytocin and neurophysin in the human thymus. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):508–511. doi: 10.1126/science.3961493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Wang D. J., Huang N. N., Heppel L. A. Activation of early events of the mitogenic response by a P2Y purinoceptor with covalently bound 3'-O-(4-benzoyl)-benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Ceuppens J. Regulation of the immune response by prostaglandins. J Clin Immunol. 1983 Oct;3(4):295–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00915791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Bray M. A., Morley J. Control of lymphokine secretion by prostaglandins. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):401–402. doi: 10.1038/262401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayari Y., Kukulansky T., Globerson A. Regulation of thymocyte proliferative response by macrophage-derived prostaglandin E2 and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jan;15(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. S., Sun L., Wen M., Hayashi J. Stimulation of prostaglandin production in rat thymic epithelial cells by protein kinase C mediated activation of phospholipase A2. Biochem Int. 1992 Aug;27(5):931–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Wen M., Hayashi J. Cross-linking of [35S]ATP gamma S to cell surface ATP binding sites. Anal Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;212(2):565–566. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Wen M., Hayashi J. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein stimulates arachidonic acid metabolism in TEA3A1 thymic epithelial cells by stimulating release and inhibiting incorporation of arachidonic acid. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1993 Nov;31(4):613–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Wen M., Sun L., Hayashi J. Activation of phospholipase A2 and stimulation of prostaglandin E2 production by transforming growth factor-alpha in rat thymic epithelial cells requires influx of calcium. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 1;293(Pt 1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2930109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Shiau A. K., Brake A. J., Julius D. Expression cloning of an ATP receptor from mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Sato K., Nazarea M., Sho K., Kondo Y. A permissive role of pertussis toxin substrate G-protein in P2-purinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover and arachidonate release in FRTL-5 thyroid cells. Cooperative mechanism of signal transduction systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13029–13037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiernik M., Homo-Delarche F. Thymic reticulum in mice. III. Phagocytic cells of the thymic reticulum in culture secrete both prostaglandin E2 and interleukin 1 which regulate thymocyte proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):689–692. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piltch A., Naylor P., Hayashi J. A cloned rat thymic epithelial cell line established from serum-free selective culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;24(4):289–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02628829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Piltch A. S., Liu P. S., Johnson L. A., Hayashi J. Thymocytes stimulate metabolism of arachidonic acid in rat thymic epithelial cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Nov;131(1):86–97. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90236-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trams E. G. Evidence for ATP action on the cell surface. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):480–482. doi: 10.1038/252480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth C. D., Johnson R. G., Jr ATP compartmentation in neuroendocrine secretory vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:353–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Kristensen F., Bettens F., deWeck A. L. Lymphokine regulation of activated (G1) lymphocytes. I. Prostaglandin E2-induced inhibition of interleukin 2 production. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1770–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. E., Simon J., Krishek B. J., Bateson A. N., Smart T. G., King B. F., Burnstock G., Barnard E. A. Cloning and functional expression of a brain G-protein-coupled ATP receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81397-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum J., Goldschneider I., Greiner D., Zurier R. Developmental abnormalities of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase positive bone marrow cells and thymocytes in New Zealand mice: effects of prostaglandin E1. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):272–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing M., Thévenod F., Mattera R. Dual regulation of arachidonic acid release by P2U purinergic receptors in dibutyryl cyclic AMP-differentiated HL60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6602–6610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B. Prostaglandins, immune responses, and murine lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):804–809. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Shawaf A. A., Kendall M. D., Cowen T. Identification of neural profiles containing vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, acetylcholinesterase and catecholamines in the rat thymus. J Anat. 1991 Feb;174:131–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]