Abstract
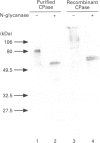
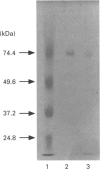
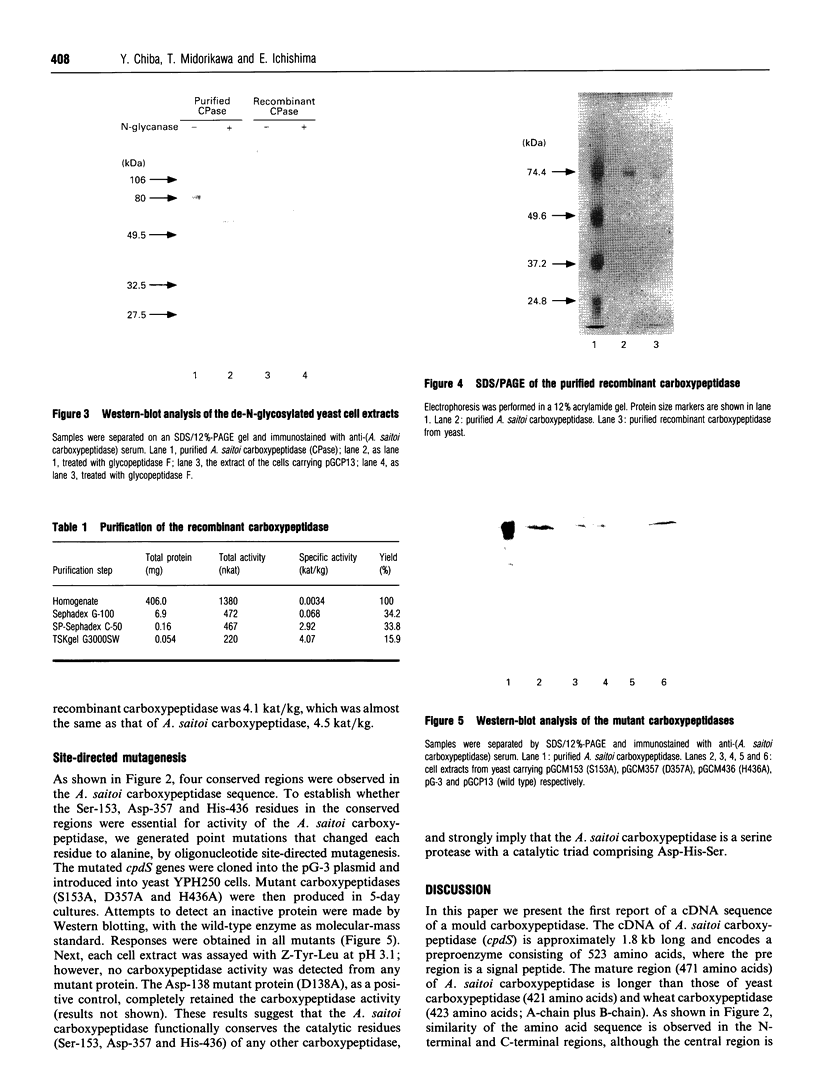
Carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus saitoi removes acidic, neutral and basic amino acids as well as proline from the C-terminal position at pH 2-5. cpdS, a cDNA encoding A. saitoi carboxypeptidase, was cloned and expressed. Analysis of the 1816-nucleotide sequence revealed a single open reading frame coding for 523 amino acids. When A. saitoi carboxypeptidase cDNA was expressed in yeast cells, carboxypeptidase activity was detected in the cell extract and was immunostained with a 72 kDa protein with polyclonal anti-(A. saitoi carboxypeptidase) serum. The recombinant enzyme treated with glycopeptidase F migrated with an apparent molecular mass of 60 kDa on SDS/PAGE, which was the same as that of the de-N-glycosylated carboxypeptidase from A. saitoi. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cpdS indicated that Ser-153, Asp-357 and His-436 residues were essential for the enzymic catalysis. It can be concluded that A. saitoi carboxypeptidase has a catalytic triad comprising Asp-His-Ser and is a member of serine carboxypeptidase family (EC 3.4.16.1).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai T., Ichishima E. Mode of action on proteins of acid carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus saitoi. J Biochem. 1974 Oct;76(4):765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. E. Isolation, characterization, and properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mnn mutants with nonconditional protein glycosylation defects. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:440–470. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85038-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech L. M., Breddam K. Inactivation of carboxypeptidase Y by mutational removal of the putative essential histidyl residue. Carlsberg Res Commun. 1989;54(5):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF02904470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba Y., Nieda Y., Nakajima T., Ichishima E. Unique enzymatic properties of alpha-amylase-III from suspension-cultured rice cells. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 Mar;55(3):901–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba Y., Yamagata Y., Iijima S., Nakajima T., Ichishima E. The carbohydrate moiety of the acid carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus saitoi. Curr Microbiol. 1993 Nov;27(5):281–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01575993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba Y., Yamagata Y., Nakajima T., Ichishima E. A new high-mannose type N-linked oligosaccharide from Aspergillus carboxypeptidase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1992 Aug;56(8):1371–1372. doi: 10.1271/bbb.56.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U. Effects of pH on carboxypeptidase-Y-catalyzed hydrolysis and aminolysis reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 15;220(1):149–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. L., Nelson R., Silver M. S. The effect of pH on the rates of hydrolysis of three acylated dipeptides by pepsin. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Jan 17;90(2):479–486. doi: 10.1021/ja01004a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowska A., Dignard D., Henning D., Thomas D. Y., Bussey H. Yeast KEX1 gene encodes a putative protease with a carboxypeptidase B-like function involved in killer toxin and alpha-factor precursor processing. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R., Moore S., Stein W. H. Serine at the active center of yeast carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8366–8369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichishima E., Arai T. Specificity and mode of action of acid carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus saitoi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 15;293(2):444–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichishima E. Purification and characterization of a new type of acid carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):274–288. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90985-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichishima E., Sonoki S., Hirai K., Torii Y., Yokoyama S. Comparative study on enzymatic properties of acid carboxypeptidase of molds of the genus Aspergillus. J Biochem. 1972 Oct;72(4):1045–1048. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao D. I., Remington S. J. Structure of wheat serine carboxypeptidase II at 3.5-A resolution. A new class of serine proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6528–6531. doi: 10.2210/pdb2sc2/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen U. H., Remington S. J., Breddam K. Site-directed mutagenesis on (serine) carboxypeptidase Y. A hydrogen bond network stabilizes the transition state by interaction with the C-terminal carboxylate group of the substrate. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 18;33(2):508–517. doi: 10.1021/bi00168a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani H., Hiromi K., Satoi S., Oda K., murao S. Studies on the interaction between Streptomyces pepsin inhibitor and several acid proteinases by means of a zinc(II)-dye complex as a probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 24;391(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Vectors for constitutive and inducible gene expression in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:389–398. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shintani T., Ichishima E. Primary structure of aspergillopepsin I deduced from nucleotide sequence of the gene and aspartic acid-76 is an essential active site of the enzyme for trypsinogen activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Feb 16;1204(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls L. A., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: the localization determinant of yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y resides in the propeptide. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida N., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Specific excretion of Serratia marcescens protease through the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.937-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]