Abstract
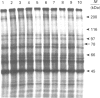
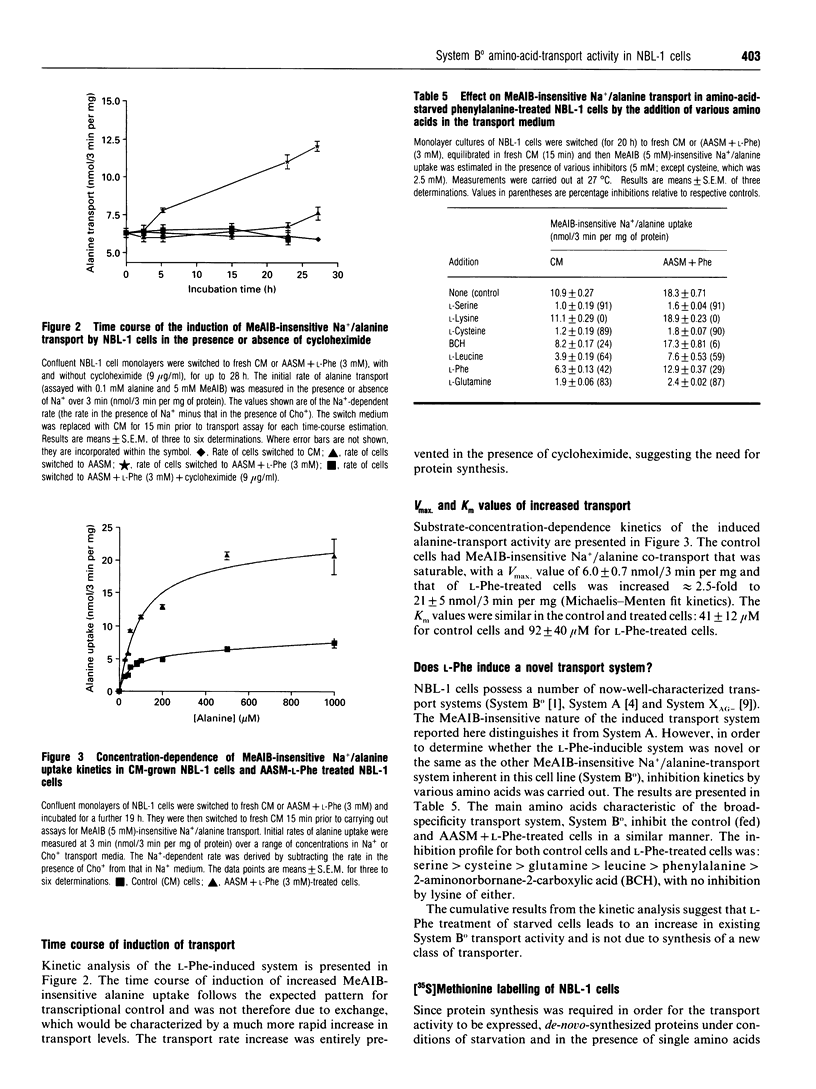
alpha-(Methylamino)isobutyric acid (MeAIB) insensitive Na(+)-dependent alanine transport activity in the bovine kidney cell line NBL-1 was increased upon amino acid starvation (> or = 20% over control levels). When L-phenylalanine (3 mM) was included in the starvation medium the increase was further enhanced (> or = 85% over control levels). In cells grown in control medium the Vmax, for MeAIB-insensitive Na+/alanine co-transport was found to be 6.0 +/- 0.7 nmol/3 min per mg (Km 41 +/- 12 microM) and for L-phenylalanine-treated amino-acid-starved cells the Vmax. was 21 +/- 5 nmol/3 min per mg (Km 92 +/- 40 microM). The increase in Vmax. was prevented by cycloheximide. Substrate specificity analysis identified the L-phenylalanine-induced transport system as System B0. [35S]Methionine labelling of cells during the amino acid starvation/phenylalanine treatments resulted in the differential labelling of a protein of 78 kDa. Northern-blot analysis using a SAAT1-specific probe revealed the presence of a new transcript (3.2 kb) in RNA extracted from cells incubated in amino acid starvation medium with L-phenylalanine included. The present findings suggest a novel means of control for System B0 by the use of physiological stress. It is also proposed that SAAT1 and System-B0 transcripts have considerable sequence similarity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle F. A., McGivan J. D. Reconstitution and identification of the major Na(+)-dependent neutral amino acid-transport protein from bovine renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):95–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2810095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle F. A., McGivan J. D. The bovine renal epithelial cell line NBL-1 expresses a broad specificity Na(+)-dependent neutral amino acid transport system (System Bo) similar to that in bovine renal brush border membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 17;1104(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felipe A., Soler C., McGivan J. D. Amino acid deprivation leads to the emergence of System A activity and the synthesis of a specific membrane glycoprotein in the bovine renal epithelial cell line NBL-1. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):577–582. doi: 10.1042/bj2840577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handlogten M. E., Kilberg M. S. Induction and decay of amino acid transport in the liver. Turnover of transport activity in isolated hepatocytes after stimulation by diabetes or glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3519–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Turk E., Wright E. M. Homology of the human intestinal Na+/glucose and Escherichia coli Na+/proline cotransporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5748–5752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E. Cultured animal cells exposed to amino acid analogues or puromycin rapidly synthesize several polypeptides. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Mar;102(3):407–427. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Hediger M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):467–471. doi: 10.1038/360467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong C. T., Yet S. F., Lever J. E. Cloning and expression of a mammalian Na+/amino acid cotransporter with sequence similarity to Na+/glucose cotransporters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1509–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon H. M., Yamauchi A., Uchida S., Preston A. S., Garcia-Perez A., Burg M. B., Handler J. S. Cloning of the cDNa for a Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter, a hypertonicity stress protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6297–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescale-Matys L., Dyer J., Scott D., Freeman T. C., Wright E. M., Shirazi-Beechey S. P. Regulation of the ovine intestinal Na+/glucose co-transporter (SGLT1) is dissociated from mRNA abundance. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):435–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2910435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch A. M., McGivan J. D. Evidence for a single common Na+-dependent transport system for alanine, glutamine, leucine and phenylalanine in brush-border membrane vesicles from bovine kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 29;899(2):176–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto R. I., Sarge K. D., Abravaya K. Transcriptional regulation of heat shock genes. A paradigm for inducible genomic responses. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):21987–21990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajor A. M., Wright E. M. Cloning and functional expression of a mammalian Na+/nucleoside cotransporter. A member of the SGLT family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3557–3560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petronini P. G., De Angelis E. M., Borghetti A. F., Wheeler K. P. Effect of betaine on HSP70 expression and cell survival during adaptation to osmotic stress. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):553–558. doi: 10.1042/bj2930553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plakidou-Dymock S., McGivan J. D. Regulation of the glutamate transporter by amino acid deprivation and associated effects on the level of EAAC1 mRNA in the renal epithelial cell line NBL-I. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 1;295(Pt 3):749–755. doi: 10.1042/bj2950749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quamme G., Biber J., Murer H. Sodium-phosphate cotransport in OK cells: inhibition by PTH and "adaptation" to low phosphate. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):F967–F973. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.6.F967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell M. A., Kilberg M. S., Oxender D. L. The regulation of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler C., Felipe A., Casado F. J., McGivan J. D., Pastor-Anglada M. Hyperosmolarity leads to an increase in derepressed system A activity in the renal epithelial cell line NBL-1. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):653–658. doi: 10.1042/bj2890653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi A., Uchida S., Preston A. S., Kwon H. M., Handler J. S. Hypertonicity stimulates transcription of gene for Na(+)-myo-inositol cotransporter in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):F20–F23. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.1.F20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]