Abstract
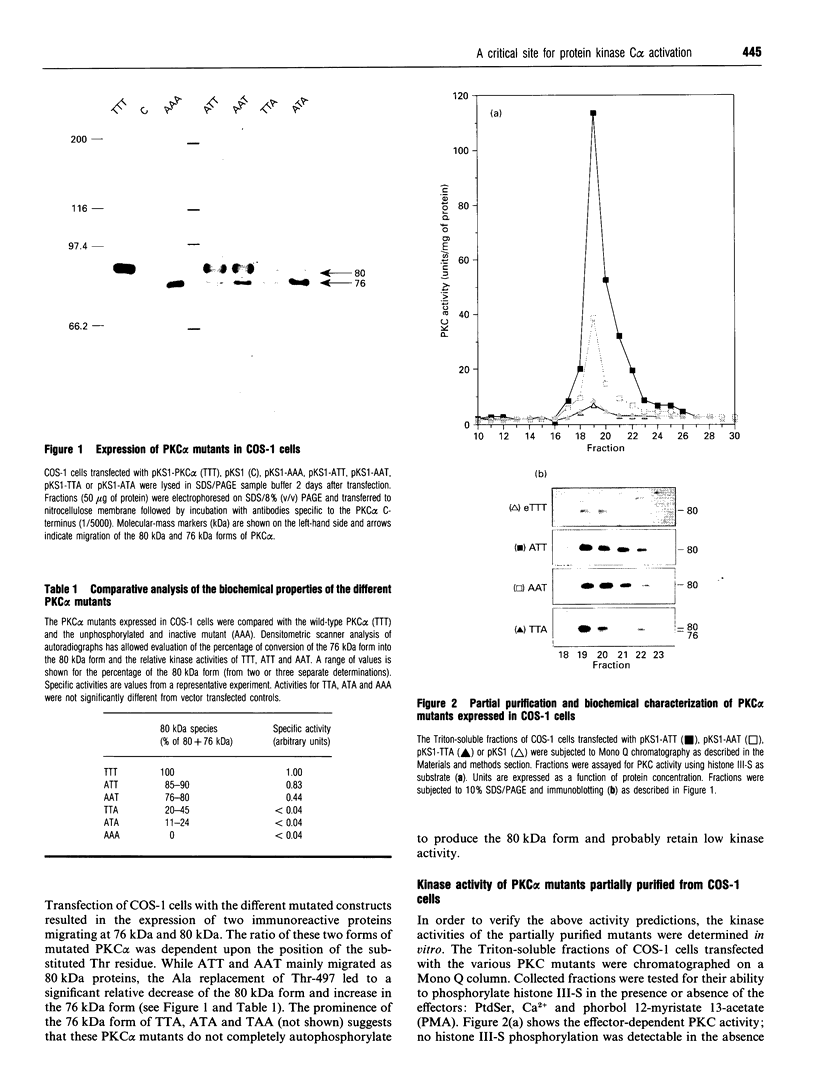
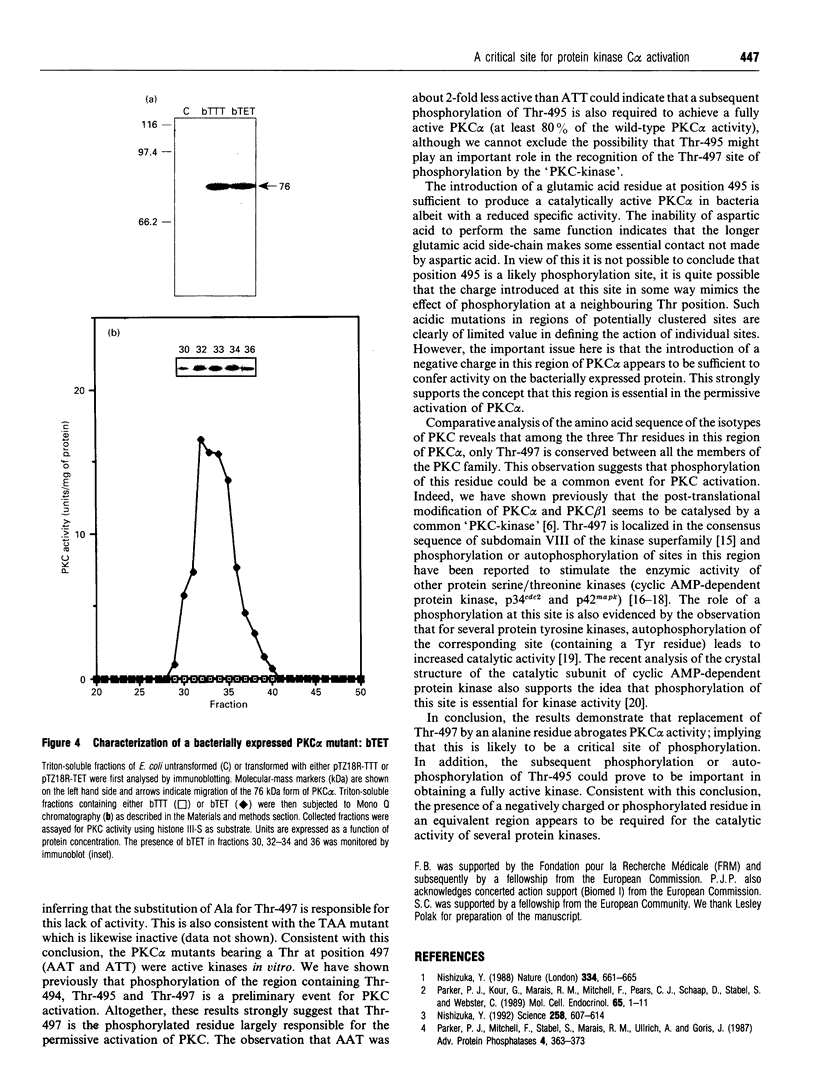
Phosphorylation of the region containing Thr-494, Thr-495 and Thr-497, present in the catalytic domain of protein kinase C alpha (PKC alpha), is a preliminary event necessary for subsequent PKC activation [Cazaubon and Parker (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 17559-17563]. To define the essential residues in this region, various combinations of alanine substitutions for threonine residues 494, 495 and 497 have been tested. These mutations yielded expressed polypeptides of 76 and 80 kDa in ratios that vary from 100% 80 kDa (wild-type kinase, active) to 100% 76 kDa (AAA mutant, inactive) with the hierarchy being wild-type PKC alpha (TTT), ATT, AAT, TTA, ATA, TAA, AAA (the nomenclature indicates the location of alanine residues substituted for Thr-494, Thr-495 and Thr-497 respectively). Only the mutants retaining Thr-497 displayed kinase activity in vitro. The results overall indicate that Thr-497 plays the dominant role in the regulation of PKC alpha activity but that in the wild-type protein, Thr-495 may also be important. Consistent with the need for phosphorylation in this region, an intrinsically active PKC alpha could be produced in bacteria by exchanging Thr-495 for a glutamic acid residue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borner C., Filipuzzi I., Wartmann M., Eppenberger U., Fabbro D. Biosynthesis and posttranslational modifications of protein kinase C in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13902–13909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazaubon S. M., Parker P. J. Identification of the phosphorylated region responsible for the permissive activation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17559–17563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazaubon S., Webster C., Camoin L., Strosberg A. D., Parker P. Effector-dependent conformational changes in protein kinase C gamma through epitope mapping with inhibitory monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):799–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., Parker P. J., McIntyre P. Biochemical properties of rat protein kinase C-eta expressed in COS cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80934-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipuzzi I., Fabbro D., Imber R. Unphosphorylated alpha-PKC exhibits phorbol ester binding but lacks protein kinase activity in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 1993 May;52(1):78–83. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240520111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R. M., Parker P. J. Purification and characterisation of bovine brain protein kinase C isotypes alpha, beta and gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;182(1):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., McKnight G. S. Mutations in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase result in unregulated biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4726–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Kour G., Marais R. M., Mitchell F., Pears C., Schaap D., Stabel S., Webster C. Protein kinase C--a family affair. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;65(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pears C., Stabel S., Cazaubon S., Parker P. J. Studies on the phosphorylation of protein kinase C-alpha. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):515–518. doi: 10.1042/bj2830515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Rothbard J., Parker P. J. A monoclonal antibody recognising the site of limited proteolysis of protein kinase C. Inhibition of down-regulation in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]