Abstract
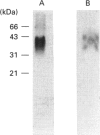
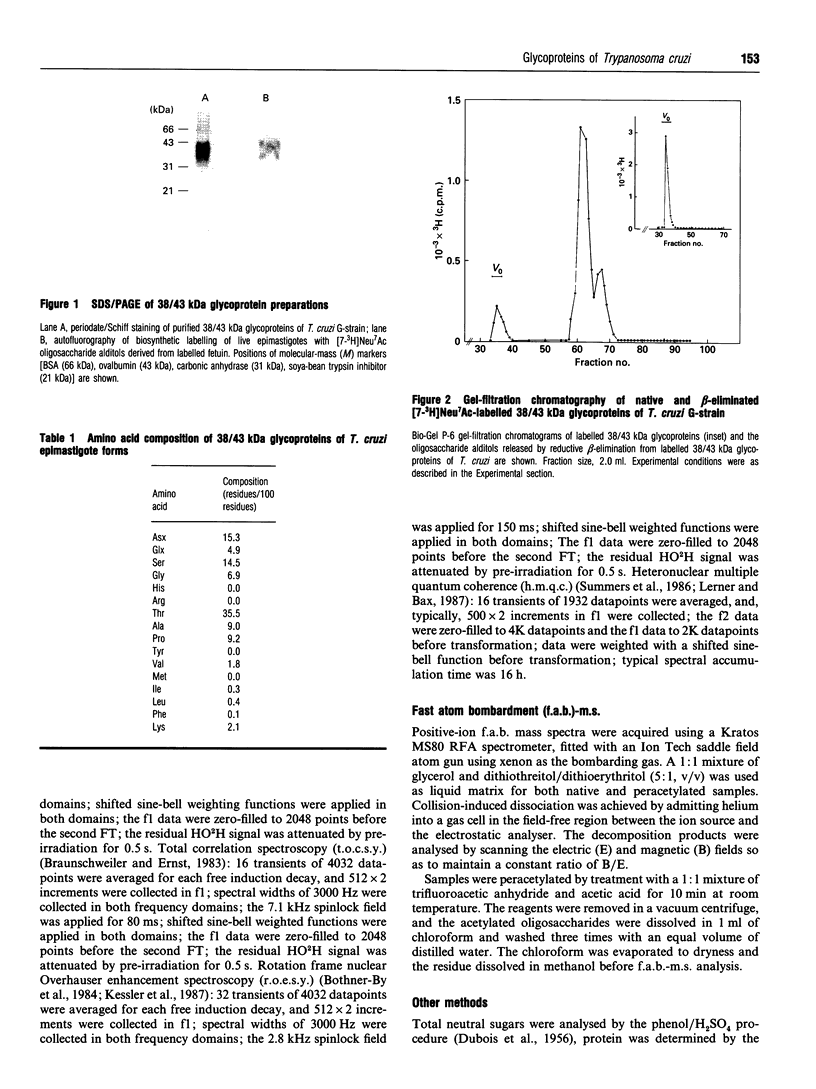
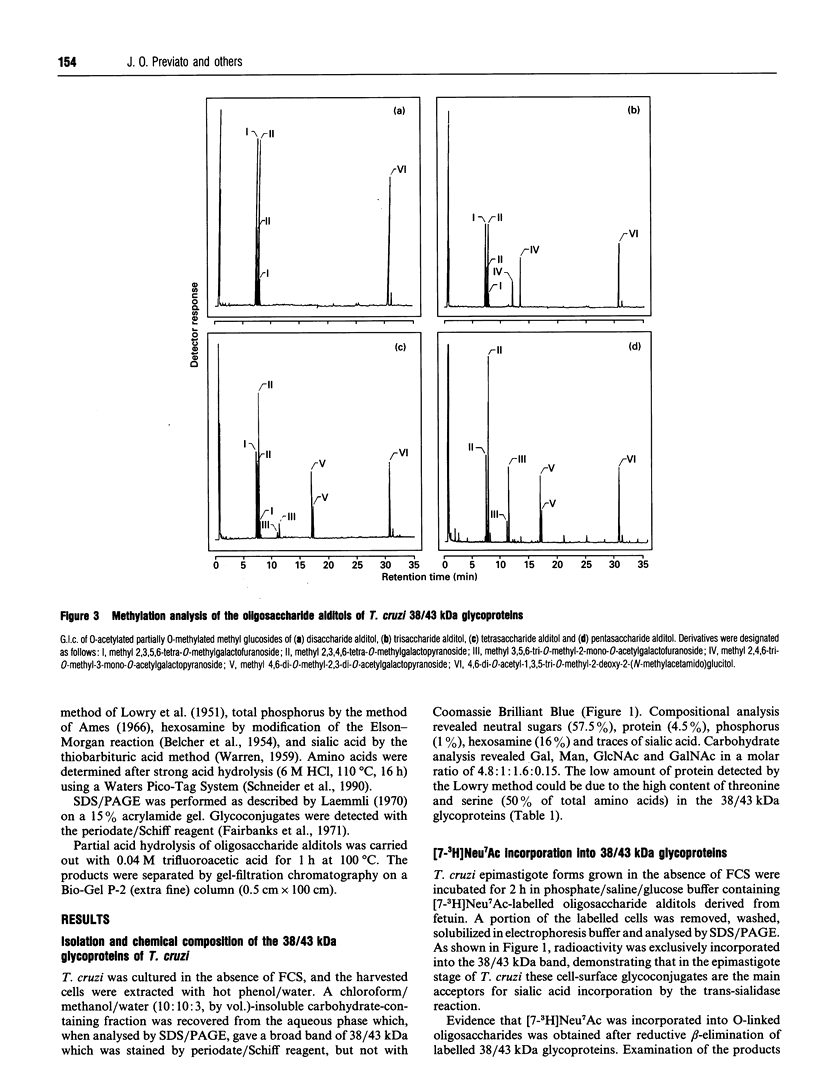
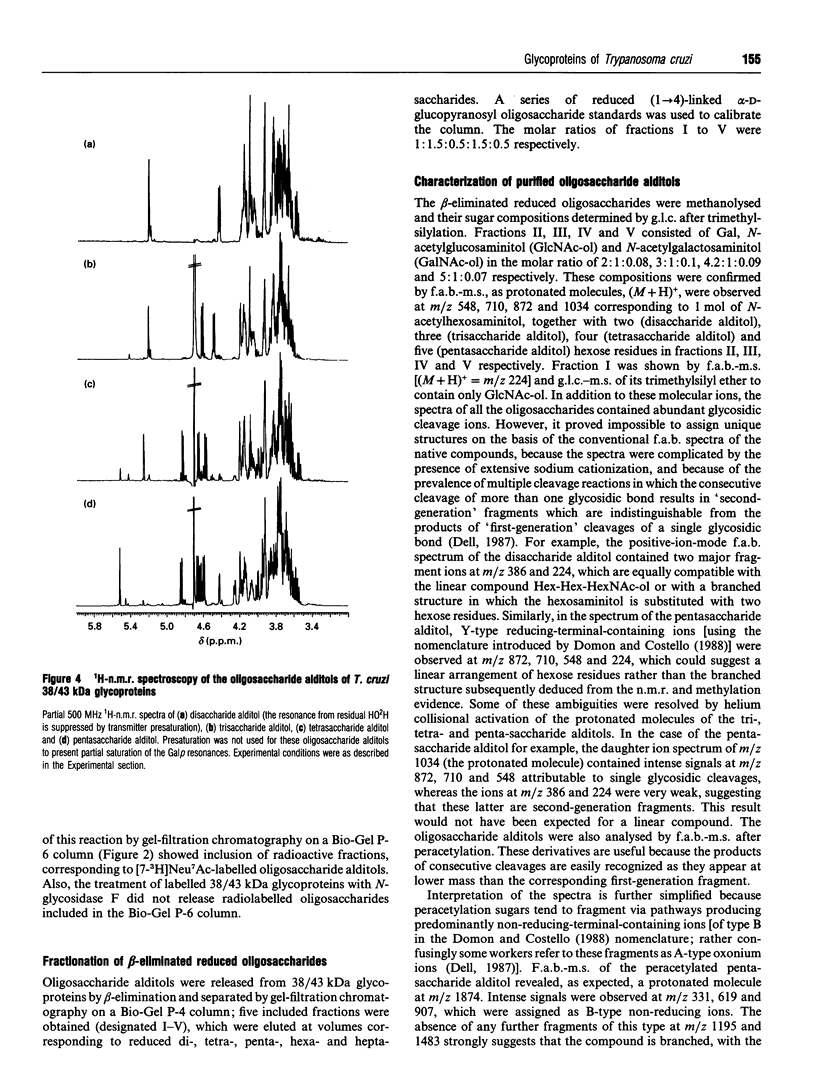
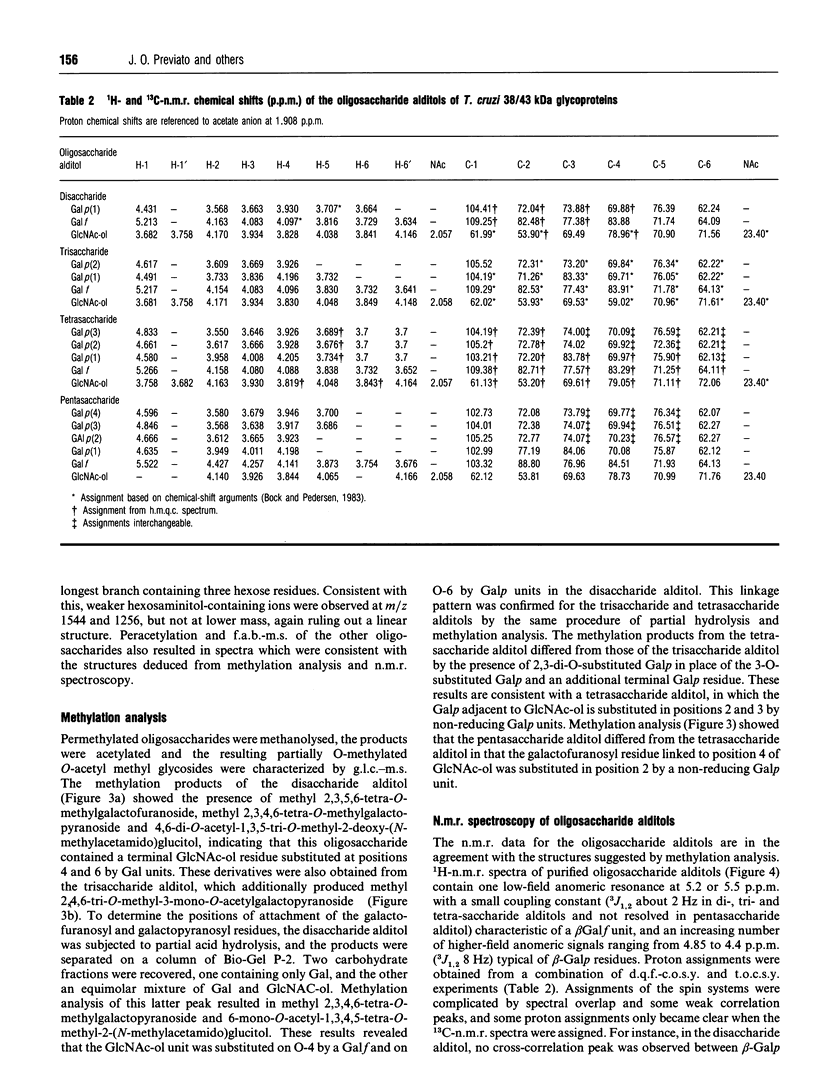
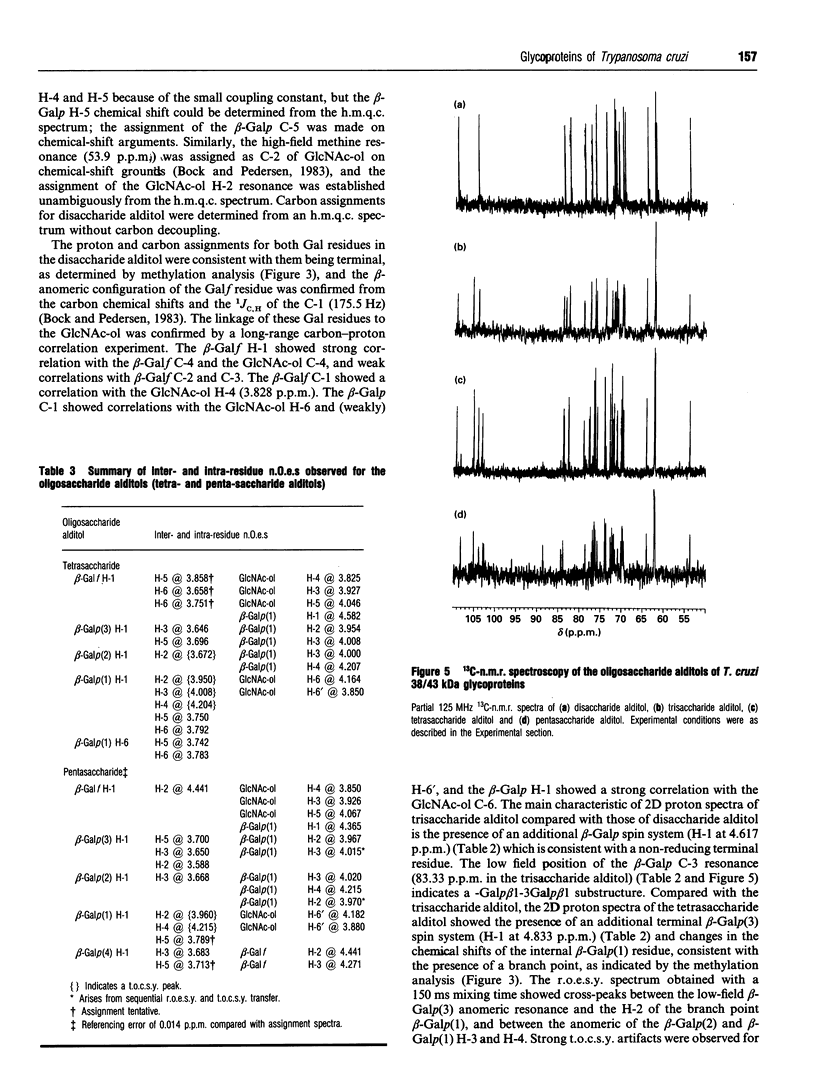
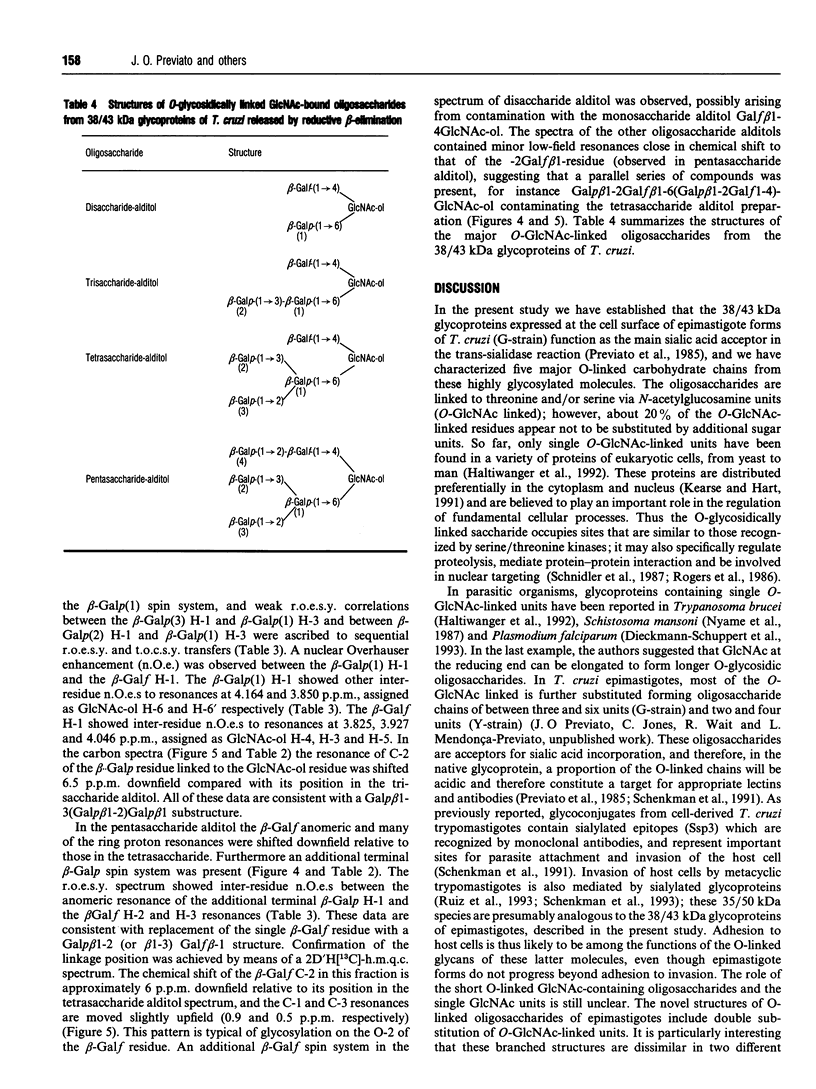
In this report we describe studies on the structures of the O-linked carbohydrate units in cell-surface glycoproteins of epimastigote forms of the G-strain of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mild alkaline reductive degradation of the 38/43 kDa glycoproteins resulted in beta-elimination of glycosylated threonine and/or serine residues, and the liberation of N-acetylglucosaminitol, galactobiosyl-, galactotriosyl-, galactotetraosyl- and galactopentaosyl-N-acetylglucosaminitol. The structures of these oligosaccharide alditols were established by n.m.r. spectroscopy and methylation analysis as: Galf beta 1-4(Galp beta 1-6)GlcNAc-ol; Galp beta 1-3Galp beta 1-6(Galf beta 1-4)GlcNAc-ol; [(Galp beta 1-3)(Galp beta 1-2)Galp beta 1-6](Galf beta 1-4)GlcNAc-ol; [(Galp beta 1-3)(Galp beta 1-2)Galp beta 1-6](Galp beta 1-2Galf beta 1-4)GlcNAc-ol.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida I. C., Milani S. R., Gorin P. A., Travassos L. R. Complement-mediated lysis of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes by human anti-alpha-galactosyl antibodies. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2394–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener Z. Biology of Trypanosoma cruzi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:347–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell A. F.A.B.-mass spectrometry of carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1987;45:19–72. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann-Schuppert A., Bause E., Schwarz R. T. Studies on O-glycans of Plasmodium-falciparum-infected human erythrocytes. Evidence for O-GlcNAc and O-GlcNAc-transferase in malaria parasites. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 15;216(3):779–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero-García M. A., Trombetta S. E., Sánchez D. O., Reglero A., Frasch A. C., Parodi A. J. The action of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase on glycolipids and glycoproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 15;213(2):765–771. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournet B., Strecker G., Leroy Y., Montreuil J. Gas--liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry of methylated and acetylated methyl glycosides. Application to the structural analysis of glycoprotein glycans. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 15;116(2):489–502. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90393-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G. Tritium labeling of cell-surface glycoproteins and glycolipids using galactose oxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:204–206. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiwanger R. S., Kelly W. G., Roquemore E. P., Blomberg M. A., Dong L. Y., Kreppel L., Chou T. Y., Hart G. W. Glycosylation of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins is ubiquitous and dynamic. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):264–269. doi: 10.1042/bst0200264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Rietschel E. T. Methylation analysis of glucosaminitol and glucosaminyl-glucosaminitol disaccharides. Formation of 2-deoxy-2-(N-acetylacetamido)-glucitol derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbel R., Collart M. Oligosaccharides in urine of patients with glycoprotein storage diseases. I. Rapid detection by thin-layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Apr 16;60(2):143–145. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearse K. P., Hart G. W. Topology of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine in murine lymphocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Nov 1;290(2):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner L., Bax A. Application of new, high-sensitivity, 1H-13C-n.m.r.-spectral techniques to the study of oligosaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1987 Aug 15;166(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(87)80042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça-Previato L., Gorin P. A., Braga A. F., Scharfstein J., Previato J. O. Chemical structure and antigenic aspects of complexes obtained from epimastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):4980–4987. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyame K., Cummings R. D., Damian R. T. Schistosoma mansoni synthesizes glycoproteins containing terminal O-linked N-acetylglucosamine residues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7990–7995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras M. M., Henríquez D., Piras R. The effect of fetuin and other sialoglycoproteins on the in vitro penetration of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes into fibroblastic cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jan 15;22(2-3):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Andrade A. F., Pessolani M. C., Mendonça-Previato L. Incorporation of sialic acid into Trypanosoma cruzi macromolecules. A proposal for a new metabolic route. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jun;16(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Gorin P. A., Mazurek M., Xavier M. T., Fournet B., Wieruszesk J. M., Mendonça-Previato L. Primary structure of the oligosaccharide chain of lipopeptidophosphoglycan of epimastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2518–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance M., Sørensen O. W., Bodenhausen G., Wagner G., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. Improved spectral resolution in cosy 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C. L., Penhoet E. E., Ballou C. E. Carbohydrate structure of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5600–5612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz R. de C., Rigoni V. L., Gonzalez J., Yoshida N. The 35/50 kDa surface antigen of Trypanosoma cruzi metacyclic trypomastigotes, an adhesion molecule involved in host cell invasion. Parasite Immunol. 1993 Feb;15(2):121–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1993.tb00591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Ferguson M. A., Heise N., de Almeida M. L., Mortara R. A., Yoshida N. Mucin-like glycoproteins linked to the membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor are the major acceptors of sialic acid in a reaction catalyzed by trans-sialidase in metacyclic forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jun;59(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90227-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Jiang M. S., Hart G. W., Nussenzweig V. A novel cell surface trans-sialidase of Trypanosoma cruzi generates a stage-specific epitope required for invasion of mammalian cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1117–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90008-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Hogan M., Miller R., DeGaetano D. A nuclear specific glycoprotein representative of a unique pattern of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1254–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaidman B. B., Yoshida N., Gorin P. A., Travassos L. R. Cross-reactive polysaccharides from Trypanosoma cruzi and fungi (especially Dactylium dendroides). J Protozool. 1986 May;33(2):186–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Ferguson M. A., McConville M. J., Mehlert A., Homans S. W., Bordier C. Structure of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of the Leishmania major promastigote surface protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16955–16964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Gómez C. M., Plummer T. H., Jr Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4665–4671. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove F., Schenkman S., Pontes de Carvalho L., Tomlinson S., Kiso M., Yoshida M., Hasegawa A., Nussenzweig V. Substrate specificity of the Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase. Glycobiology. 1992 Dec;2(6):541–548. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.6.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]