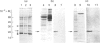Abstract
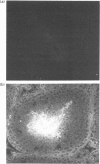
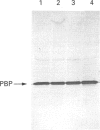
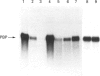
The cellular origin of a soluble phospholipid-binding protein (PBP) in rat testicular and epididymal secretions has been investigated genetically and immunologically. PBP is ubiquitous in tissue cytosols but is not present in blood serum, lymph or milk. The relatively large amounts present in cauda epididymal plasma (CEP) and rete testis fluid suggested therefore that it may be secreted specifically by these tissues. However, when PBP cDNAs from testis and epididymis were cloned and sequenced, they did not contain a signal peptide and only one size of transcript was obtained on Northern blots of RNAs from liver, brain, placenta, testis and epididymis. Moreover, PBP could not be detected in sperm-free CEP from castrated, androgen-stimulated animals or in medium from Sertoli cell cultures. Spermatozoa, on the other hand, contained significant amounts of PBP that could be solubilized by washing cells in dissociating reagents or high-salt solutions. These results indicate that, contrary to previous interpretations, PBP is not secreted by classical pathways in either the testis or epididymis but that its presence in CEP and rete testis fluid is attributable largely to release from spermatozoa. Thus, spermatozoa have a significant influence on the composition of CEP as well as on the secretory and absorptive activity of the epididymal epithelium. A possible role for PBP in membrane biogenesis and maintenance of antigen segregation in spermatozoa is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernier I., Tresca J. P., Jollès P. Ligand-binding studies with a 23 kDa protein purified from bovine brain cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 12;871(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E. Characterization of a 22 kDa protein with widespread tissue distribution but which is uniquely present in secretions of the testis and epididymis and on the surface of spermatozoa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 26;841(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E., Higgins S. J. Characterization and androgen-dependence of proteins associated with luminal fluid and spermatozoa in the rat epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1980 Jul;59(2):363–375. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0590363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E., Means A. R., Wright E. J., Singh S. P., Tiver K. K. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for androgen-dependent sperm-coating glycoproteins secreted by the rat epididymis. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):13–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E., Means A. R., Wright E. J., Singh S. P., Tiver K. K. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for two major androgen-dependent secretory proteins of 18.5 kilodaltons synthesized by the rat epididymis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4956–4961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. Y., Mather J. P., Byer A. L., Bardin C. W. Identification of hormonally responsive proteins in primary Sertoli cell culture medium by anion-exchange high performance liquid chromatography. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):480–488. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girotti M., Jones R., Emery D. C., Chia W., Hall L. Structure and expression of the rat epididymal secretory protein I gene. An androgen-regulated member of the lipocalin superfamily with a rare splice donor site. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):203–210. doi: 10.1042/bj2810203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz J. F., Veerkamp J. H. A radiochemical procedure for the assay of fatty acid binding by proteins. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandy D. K., Hanneman E., Bunzow J., Shih M., Machida C. A., Bidlack J. M., Civelli O. Purification, cloning, and tissue distribution of a 23-kDa rat protein isolated by morphine affinity chromatography. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1370–1376. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S. E., Whittall R., Minty A., Buckingham M., Williamson R. There are approximately 20 actin gene in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4895–4908. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Brown C. R. Identification and characterization of the 2D6 and Mr 23,000 antigens on the plasma membrane of rat spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):353–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2410353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Brown C. R., Von Glós K. I., Parker M. G. Hormonal regulation of protein synthesis in the rat epididymis. Characterization of androgen-dependent and testicular fluid-dependent proteins. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1880667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Hall L. A 23 kDa protein from rat sperm plasma membranes shows sequence similarity and phospholipid binding properties to a bovine brain cytosolic protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 11;1080(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90114-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., von Glos K. I., Brown C. R. Changes in the protein composition of rat spermatozoa during maturation in the epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1983 Mar;67(2):299–306. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0670299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinefelter G. R., Hamilton D. W. Synthesis and secretion of proteins by perifused caput epididymal tubules, and association of secreted proteins with spermatozoa. Biol Reprod. 1985 Nov;33(4):1017–1027. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod33.4.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzio J. P., Brake B., Banting G., Howell K. E., Braghetta P., Stanley K. K. Identification, sequencing and expression of an integral membrane protein of the trans-Golgi network (TGN38). Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2700097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore A., Ensrud K., Baker J., Wenstrom J., Hamilton D. W. Preliminary observations on a second Mr approximately equal to 24,000 membrane molecule from rat spermatozoa. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;513:204–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb25010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesch A., Hartmann E., Rohde K., Rubartelli A., Sitia R., Rapoport T. A. A novel pathway for secretory proteins? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90186-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myles D. G., Primakoff P., Bellvé A. R. Surface domains of the guinea pig sperm defined with monoclonal antibodies. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page A. P., Rudin W., Fluri E., Blaxter M. L., Maizels R. M. Toxocara canis: a labile antigenic surface coat overlying the epicuticle of infective larvae. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Aug;75(1):72–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90123-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A. C., Jones R., Barker P. J., Hall L. A mammalian epididymal protein with remarkable sequence similarity to snake venom haemorrhagic peptides. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):671–675. doi: 10.1042/bj2860671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A. C., Jones R., Hall L. Isolation and characterization of a rat cDNA clone encoding a secreted superoxide dismutase reveals the epididymis to be a major site of its expression. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 1;293(Pt 1):21–25. doi: 10.1042/bj2930021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. D., Peterson R. N., Russell T. A., Hunt W. Electrophoretic map of boar sperm plasma membrane polypeptides and localization and fractionation of specific polypeptide subclasses. Biol Reprod. 1983 Mar;28(2):393–413. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod28.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoentgen F., Saccoccio F., Jollès J., Bernier I., Jollès P. Complete amino acid sequence of a basic 21-kDa protein from bovine brain cytosol. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 15;166(2):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierula M. E., Araki Y., Rankin T. L., Tulsiani D. R., Orgebin-Crist M. C. Immunolocalization of a 25-kilodalton protein in mouse testis and epididymis. Biol Reprod. 1992 Nov;47(5):844–856. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod47.5.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voglmayr J. K., Fairbanks G., Jackowitz M. A., Colella J. R. Post-testicular developmental changes in the ram sperm cell surface and their relationship to luminal fluid proteins of the reproductive tract. Biol Reprod. 1980 Apr;22(3):655–667. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/22.3.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Jones R., Moore A., Hamilton D. W., Hall L. Analysis of major androgen-regulated cDNA clones from the rat epididymis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Nov 12;74(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90205-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D. E., Maynard V. M., McKinnon C. A., Melchior D. L. Lipid domains in the ram sperm plasma membrane demonstrated by differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6893–6896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]