Abstract
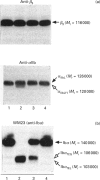
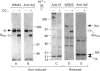
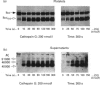
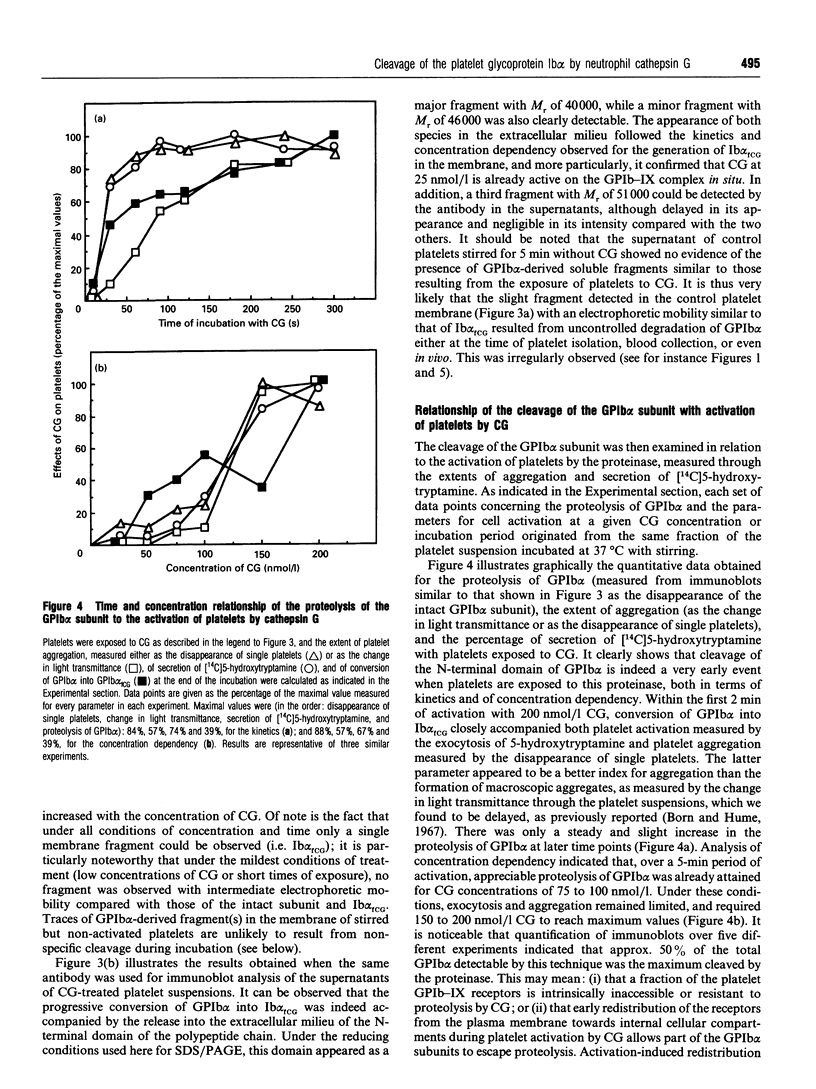
The proteolytic activity of the neutrophil serine-proteinase cathepsin G (CG) on platelet adherence receptors, the glycoprotein (GP) Ib-IX complex and the integrin alpha IIb beta 3, has been investigated. In the range 50 to 200 nmol/l, CG is a potent platelet agonist which induces shape change, granule exocytosis and aggregation. Investigation of the proteolysis of the receptors' subunits during the course of platelet activation by CG was performed by immunoblot analysis of platelet proteins using a panel of specific antibodies. Exposure of platelets for 3 min at 37 degrees C to CG at a concentration that induces full cell activation resulted in an extensive cleavage of the N-terminal region of the extracellular domain of GPIb alpha, the largest (relative molecular mass, M(r), 143,000) of the three subunits constituting the GPIb-IX complex. In contrast, no detectable proteolytic modification of the two other subunits, GPIb beta and GPIX, was detected. Similarly, we observed that neither of the two subunits of the alpha IIb beta 3 receptor were proteolytically modified by CG. Cleavage of GPIb alpha by CG leaves a remnant of the polypeptide chain with M(r) approx. 106,000 in the plasma membrane, while releasing into the extracellular milieu the N-terminal domain with M(r) in the range 40,000 to 46,000. N-terminal sequencing of the CG-derived fragments of GPIb alpha indicated that the Leu275-Tyr276 peptide bond was the primary cleavage site for this proteinase. Proteolysis of GPIb alpha was already detectable at concentrations of CG as low as 25 nmol/l, while with 200 nmol/l the cleavage was detected as soon as 10 s after exposure of platelets to the proteinase. Comparison of the kinetics and concentration dependency for the proteolysis of GPIb alpha and for the activation of platelets by CG showed that cleavage of the GPIb-IX receptor is an early event that accompanies exocytosis and aggregation. Quantitative evaluation of the conversion of GPIb alpha into its membrane fragment indicated that, under optimal conditions, a maximum of approx. 50% of the total GPIb alpha can be affected by proteolysis. However, this proteolysis was > 90% complete when platelets were in the presence of the potent antagonist prostacyclin, suggesting that cellular redistribution of the GPIb-IX receptor may also occur during activation by CG. These results thus indicate that the very early phase of platelet activation by CG is accompanied by extensive modifications in the structure and expression of the GPIb-IX receptor, an effect that might be of functional significance for the interaction of platelets with the vessel wall.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. K., Booth W. J., Gorman J. J., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Purification of botrocetin from Bothrops jararaca venom. Analysis of the botrocetin-mediated interaction between von Willebrand factor and the human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8317–8326. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt M. C., Du X. P., Booth W. J. Ristocetin-dependent reconstitution of binding of von Willebrand factor to purified human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):633–640. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt M. C., Phillips D. R. Purification and preliminary physicochemical characterization of human platelet membrane glycoprotein V. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born G. V., Hume M. Effects of the numbers and sizes of platelet aggregates on the optical density of plasma. Nature. 1967 Sep 2;215(5105):1027–1029. doi: 10.1038/2151027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Hoxie J. A., Manning D. R. Signaling through G proteins and G protein-coupled receptors during platelet activation. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M. S., Levin R. I., Garry K. Human neutrophil elastase modulates platelet function by limited proteolysis of membrane glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):657–666. doi: 10.1172/JCI111744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bykowska K., Kaczanowska J., Karpowicz M., Lopaciuk S., Kopeć M. Alterations of blood platelet function induced by neutral proteases from human leukocytes. Thromb Res. 1985 Jun 1;38(5):535–546. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bykowska K., Kaczanowska J., Karpowicz M., Stachurska J., Kopeć M. Effect of neutral proteases from blood leukocytes on human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Dec 30;50(4):768–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa J. L., Murphy D. L. Platelet 5-HT uptake and release stopped rapidly by formaldehyde. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):407–408. doi: 10.1038/255407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer E. M., Lu H., Caen J. P., Soria C., Berndt M. C., Tenza D. Differential redistribution of platelet glycoproteins Ib and IIb-IIIa after plasmin stimulation. Blood. 1991 Feb 15;77(4):694–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Maschio A., Evangelista V., Rajtar G., Chen Z. M., Cerletti C., De Gaetano G. Platelet activation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes exposed to chemotactic agents. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H870–H879. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early T. S., Reiman E. M., Raichle M. E., Spitznagel E. L. Left globus pallidus abnormality in never-medicated patients with schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):561–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista V., Rajtar G., de Gaetano G., White J. G., Cerletti C. Platelet activation by fMLP-stimulated polymorphonuclear leukocytes: the activity of cathepsin G is not prevented by antiproteinases. Blood. 1991 Jun 1;77(11):2379–2388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-Lopez P., Renesto P., Schattner M., Bassot S., Laurent P., Chignard M. Activation of human platelets by C5a-stimulated neutrophils: a role for cathepsin G. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1100–C1107. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R. Modulation of human platelet function by prostacyclin and thromboxane A2. Fed Proc. 1979 Jan;38(1):83–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco N. J., Jamieson G. A. High and moderate affinity pathways for alpha-thrombin-induced platelet activation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Dec;198(3):792–799. doi: 10.3181/00379727-198-43321d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa M., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Ruggeri Z. M. The von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Characterization by monoclonal antibodies and partial amino acid sequence analysis of proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12579–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess D., Schaller J., Rickli E. E., Clemetson K. J. Identification of the disulphide bonds in human platelet glycocalicin. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey M. J., Hagen F. S., Yagi M., Roth G. J. Human platelet glycoprotein V: characterization of the polypeptide and the related Ib-V-IX receptor system of adhesive, leucine-rich glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8327–8331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg P. J., Owensby D. A., Chesterman C. N. Thrombospondin 1 is a tight-binding competitive inhibitor of neutrophil cathepsin G. Determination of the kinetic mechanism of inhibition and localization of cathepsin G binding to the thrombospondin 1 type 3 repeats. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21811–21818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Setkowsky Dangelmaier C. A. Adenine nucleotide metabolism of blood platelets. X. Formaldehyde stops centrifugation-induced secretion after A23187-stimulation and causes breakdown of metabolic ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):46–61. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourdillé P., Heilmann E., Combrié R., Winckler J., Clemetson K. J., Nurden A. T. Thrombin induces a rapid redistribution of glycoprotein Ib-IX complexes within the membrane systems of activated human platelets. Blood. 1990 Oct 15;76(8):1503–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri Y., Hayashi Y., Yamamoto K., Tanoue K., Kosaki G., Yamazaki H. Localization of von Willebrand factor and thrombin-interactive domains on human platelet glycoprotein Ib. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Feb 19;63(1):122–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornecki E., Ehrlich Y. H., Egbring R., Gramse M., Seitz R., Eckardt A., Lukasiewicz H., Niewiarowski S. Granulocyte-platelet interactions and platelet fibrinogen receptor exposure. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):H651–H658. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.3.H651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Harris T. S., Moake J. L., Handin R. I., Schafer A. I. von Willebrand factor binding to platelet GpIb initiates signals for platelet activation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1568–1573. doi: 10.1172/JCI115468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F., Morales M., de La Salle C., Cazenave J. P., Clemetson K. J., Shimomura T., Phillips D. R. Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the human platelet glycoprotein V. A member of the leucine-rich glycoprotein family cleaved during thrombin-induced platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20801–20807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Papayannopoulou T., Roth G. J. Cloning of the alpha chain of human platelet glycoprotein Ib: a transmembrane protein with homology to leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martodam R. R., Baugh R. J., Twumasi D. Y., Liener I. E. A rapid procedure for the large scale purification of elastase and cathepsin G from human sputum. Prep Biochem. 1979;9(1):15–31. doi: 10.1080/00327487908061669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer S., Kresbach G., Häring P., Schumpp-Vonach B., Clemetson K. J., Hadváry P., Steiner B. Expression and characterization of functionally active fragments of the platelet glycoprotein (GP) Ib-IX complex in mammalian cells. Incorporation of GP Ib alpha into the cell surface membrane. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20555–20562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. D. Thrombin-induced down-regulation of the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1992 Jan;18(1):18–27. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modderman P. W., Admiraal L. G., Sonnenberg A., von dem Borne A. E. Glycoproteins V and Ib-IX form a noncovalent complex in the platelet membrane. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):364–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molino M., Di Lallo M., Martelli N., de Gaetano G., Cerletti C. Effects of leukocyte-derived cathepsin G on platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX and IIb-IIIa complexes: a comparison with thrombin. Blood. 1993 Oct 15;82(8):2442–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molino M., Di Lallo M., de Gaetano G., Cerletti C. Intracellular Ca2+ rise in human platelets induced by polymorphonuclear-leucocyte-derived cathepsin G. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):741–745. doi: 10.1042/bj2880741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Vaheri A., Choate J. J., Gahmberg C. G. Action of thrombin on surface glycoproteins of human platelets. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):437–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Dupuis D., Kunicki T. J., Caen J. P. Analysis of the glycoprotein and protein composition of Bernard-Soulier platelets by single and two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1431–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen E., Handin R. I. Transient expression of recombinant glycoprotein Ib alpha polypeptides in COS cells that inhibit von Willebrand factor binding to the platelet glycoprotein Ib/IX complex. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Aug 3;68(2):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Charo I. F., Parise L. V., Fitzgerald L. A. The platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):831–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidard D., Frelinger A. L., Bouillot C., Nurden A. T. Activation of the fibrinogen receptor on human platelets exposed to alpha chymotrypsin. Relationship with a major proteolytic cleavage at the carboxyterminus of the membrane glycoprotein IIb heavy chain. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):437–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. Fibrinogen, fibrinogen receptors, and the peptides that inhibit these interactions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 1;36(23):4035–4040. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renesto P., Chignard M. Enhancement of cathepsin G-induced platelet activation by leukocyte elastase: consequence for the neutrophil-mediated platelet activation. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renesto P., Ferrer-Lopez P., Chignard M. Interference of recombinant eglin C, a proteinase inhibitor extracted from leeches, with neutrophil-mediated platelet activation. Lab Invest. 1990 Apr;62(4):409–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renesto P., Kadiri C., Chignard M. Combined activation of platelets by cathepsin G and platelet activating factor, two neutrophil-derived agonists. Br J Haematol. 1992 Feb;80(2):205–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb08902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J. Developing relationships: arterial platelet adhesion, glycoprotein Ib, and leucine-rich glycoproteins. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):5–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Ware J. The structure and function of von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jun 1;67(6):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage B., Shattil S. J., Ruggeri Z. M. Modulation of platelet function through adhesion receptors. A dual role for glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (integrin alpha IIb beta 3) mediated by fibrinogen and glycoprotein Ib-von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11300–11306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selak M. A. Cathepsin G and thrombin: evidence for two different platelet receptors. Biochem J. 1994 Jan 15;297(Pt 2):269–275. doi: 10.1042/bj2970269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selak M. A., Chignard M., Smith J. B. Cathepsin G is a strong platelet agonist released by neutrophils. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):293–299. doi: 10.1042/bj2510293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selak M. A. Neutrophil elastase potentiates cathepsin G-induced platelet activation. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Nov 10;68(5):570–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selak M. A., Smith J. B. Cathepsin G binding to human platelets. Evidence for a specific receptor. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/bj2660055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura T., Fujimura K., Maehama S., Takemoto M., Oda K., Fujimoto T., Oyama R., Suzuki M., Ichihara-Tanaka K., Titani K. Rapid purification and characterization of human platelet glycoprotein V: the amino acid sequence contains leucine-rich repetitive modules as in glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2349–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Minematsu Y., Reilly C. F., Travis J., Powers J. C. Human leukocyte cathepsin G. Subsite mapping with 4-nitroanilides, chemical modification, and effect of possible cofactors. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):2040–2047. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todrick A., Tait A. C. The inhibition of human platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake by tricyclic antidepressive drugs. The relation between structure and potency. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;21(11):751–762. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1969.tb08164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J. Structure, function, and control of neutrophil proteinases. Am J Med. 1988 Jun 24;84(6A):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente V., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a site in the alpha chain of platelet glycoprotein Ib that participates in von Willebrand factor binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):274–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente V., Kostel P. J., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and functional characterization of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain located between residues His1-Arg293 of the alpha-chain of glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18473–18479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallvik J., Suontaka A. M., Blombäck M. Proteolytic activity during storage of platelets in plasma. Transfus Med. 1992 Jun;2(2):135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.1992.tb00147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicki A. N., Clemetson K. J. Structure and function of platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and V. Effects of leukocyte elastase and other proteases on platelets response to von Willebrand factor and thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicki A. N., Clemetson K. J. The glycoprotein Ib complex of human blood platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]