Abstract
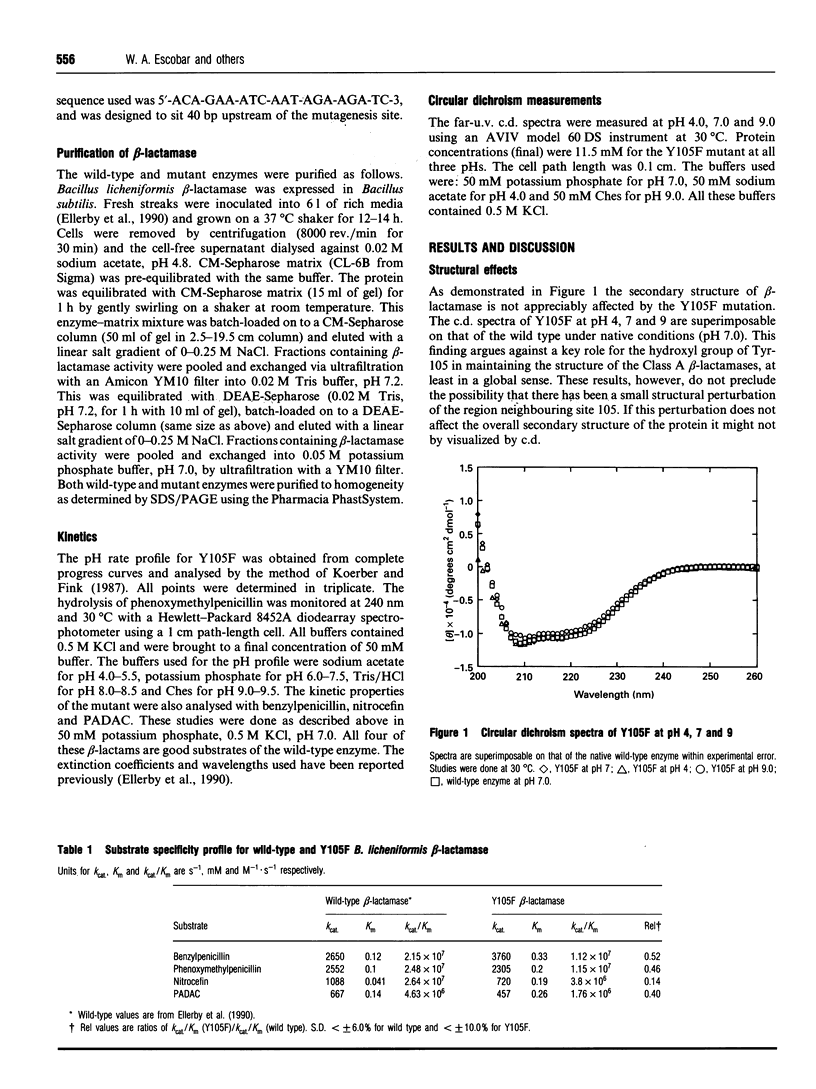
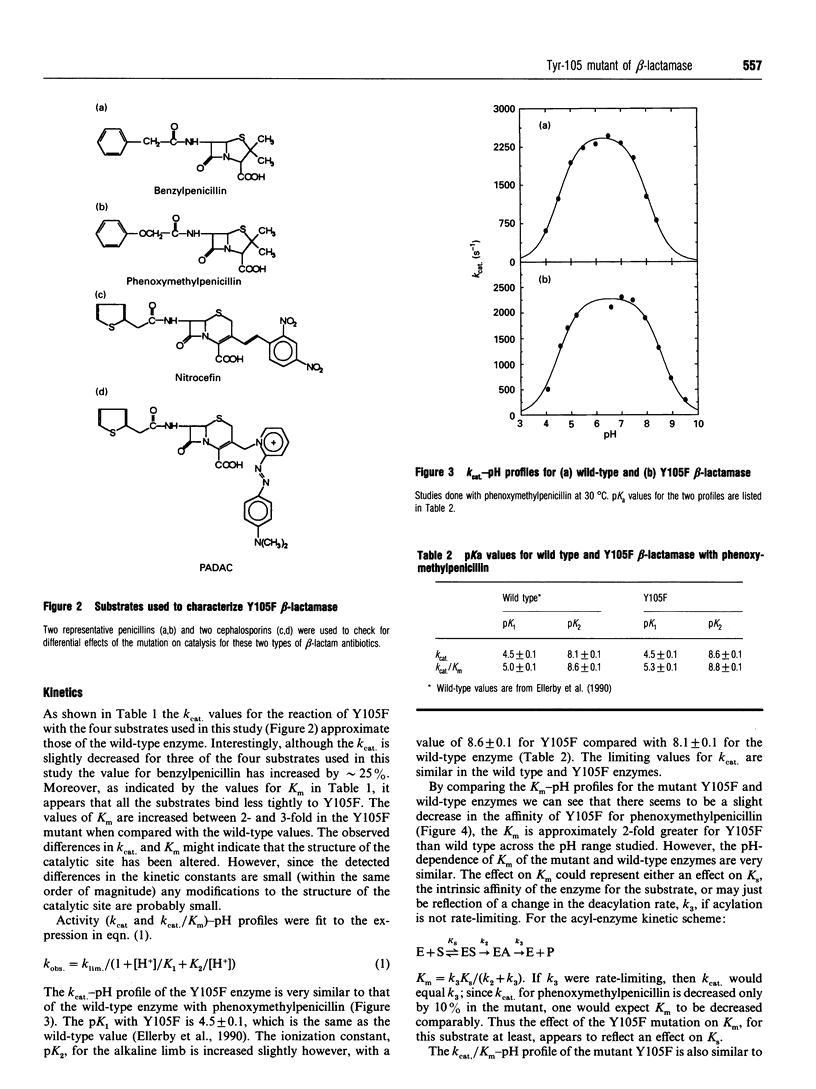
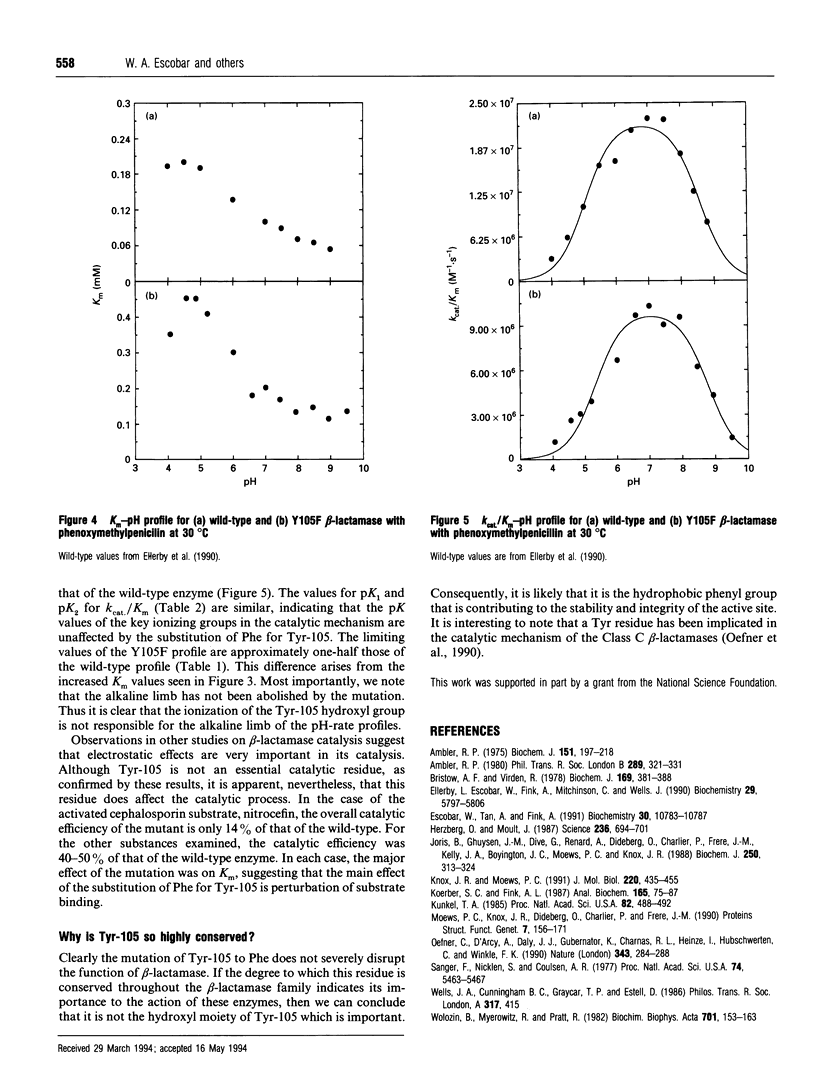
Tyr-105 is a conserved residue in the Class A beta-lactamases and is in close proximity to the active-site. Tyr-105 in beta-lactamase from Bacillus licheniformis was converted into Phe by site-directed mutagenesis. This mutation caused no significant effect on the structure of the enzyme and had only small effects on the catalytic properties. In particular, in comparison to the wild-type, kcat. for benzylpenicillin was increased slightly, whereas it was decreased slightly for several other substrates. For each substrate examined, Km increased 3-4-fold in the mutant compared with the wild-type enzyme. Examination of the effect of pH on the catalytic reaction revealed only small perturbations in the pK values for the acidic and basic limbs of the kcat./Km pH profiles due to the mutation. Overall effects of the Y105F substitution on the catalytic efficiency for different penicillin and cephalosporin substrates ranged from 14% to 56% compared with the wild-type activity. We conclude that Tyr-105 is not an essential residue for beta-lactamase catalysis, but does contribute to substrate binding.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of Staphylococcus aureus penicillinase. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):197–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1510197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow A. F., Virden R. Preferential nitration with tetranitromethane of a specific tyrosine residue in penicillinase from Staphylococcus aureus PCl. Evidence that the preferentially nitrated residue is not part of the active site but that loss of activity is due to intermolecular cross-linking. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 1;169(2):381–388. doi: 10.1042/bj1690381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerby L. M., Escobar W. A., Fink A. L., Mitchinson C., Wells J. A. The role of lysine-234 in beta-lactamase catalysis probed by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5797–5806. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar W. A., Tan A. K., Fink A. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of beta-lactamase leading to accumulation of a catalytic intermediate. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10783–10787. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1 at 2.5 A resolution. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):694–701. doi: 10.1126/science.3107125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. R., Moews P. C. Beta-lactamase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C. Refinement at 2 A resolution and analysis of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):435–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90023-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerber S. C., Fink A. L. The analysis of enzyme progress curves by numerical differentiation, including competitive product inhibition and enzyme reactivation. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Knox J. R., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M. Beta-lactamase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C at 2 A resolution. Proteins. 1990;7(2):156–171. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oefner C., D'Arcy A., Daly J. J., Gubernator K., Charnas R. L., Heinze I., Hubschwerlen C., Winkler F. K. Refined crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Citrobacter freundii indicates a mechanism for beta-lactam hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):284–288. doi: 10.1038/343284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Myerowitz R., Pratt R. F. Specific chemical modification of the readily nitrated tyrosine of the RTEM beta-lactamase and of bacillus cereus beta-lactamase I. The role of the tyrosine in beta-lactamase catalysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 18;701(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


