Abstract
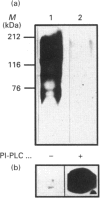
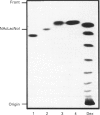
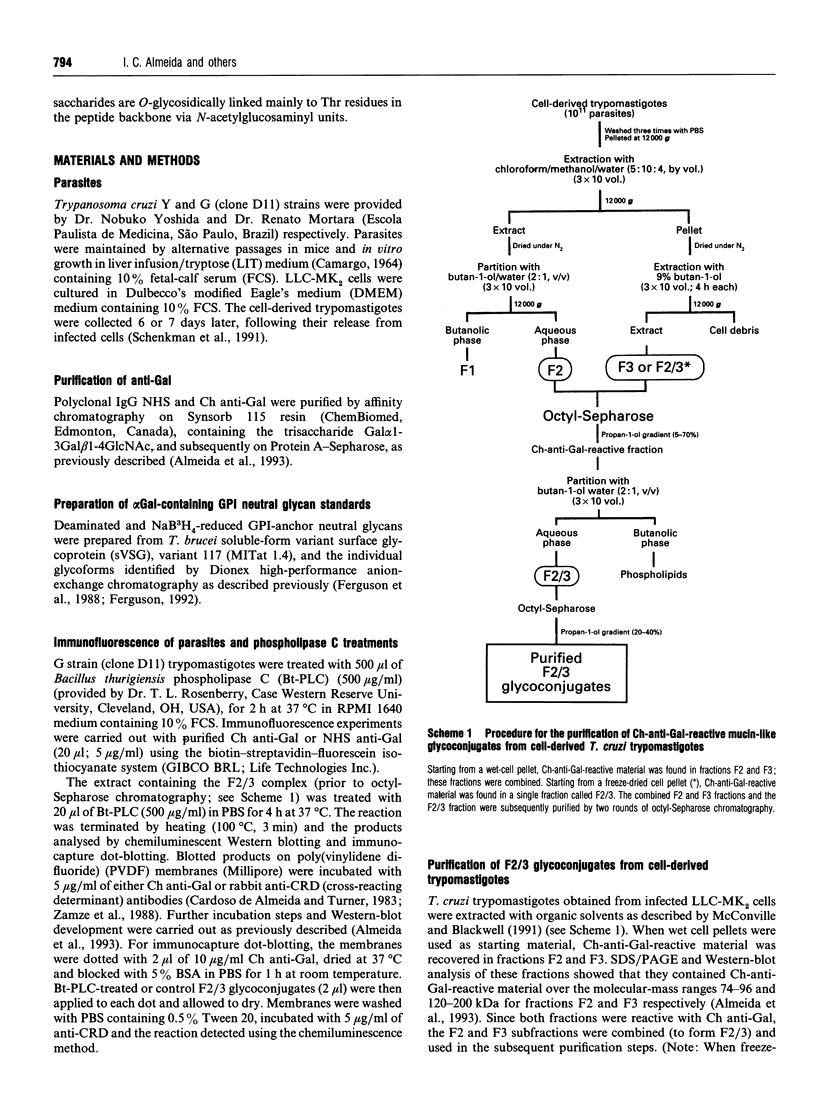
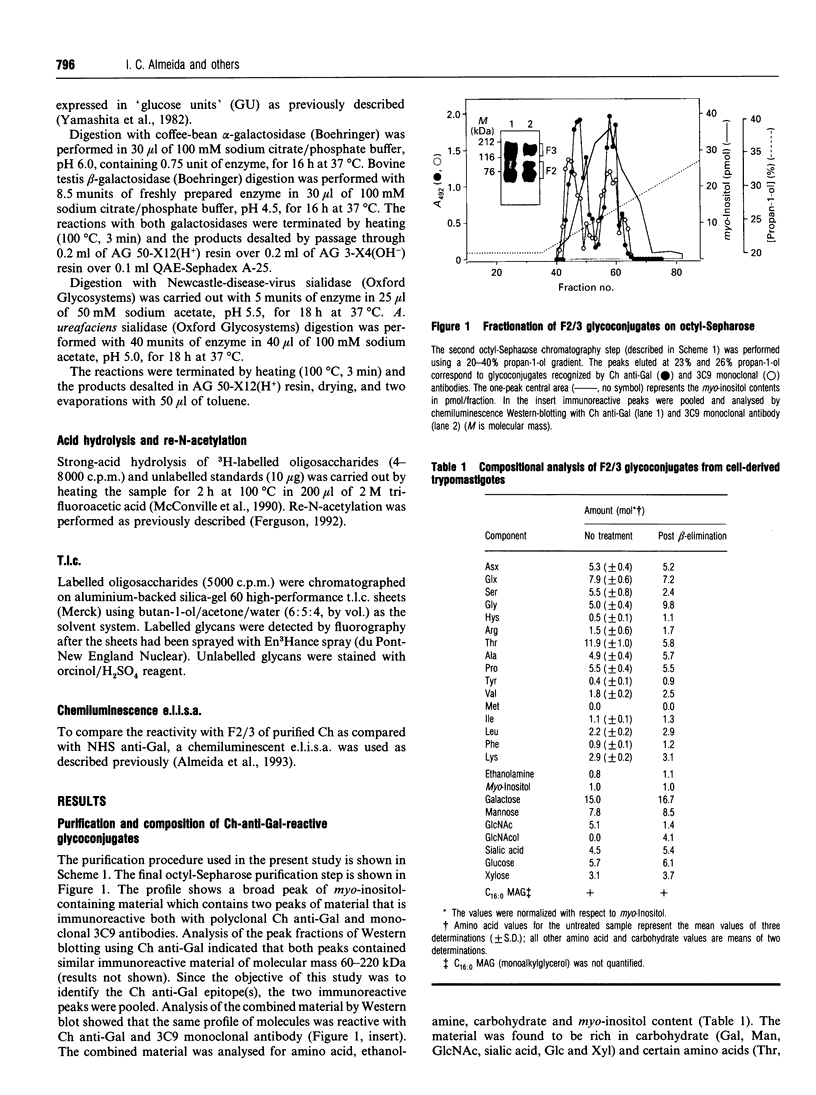
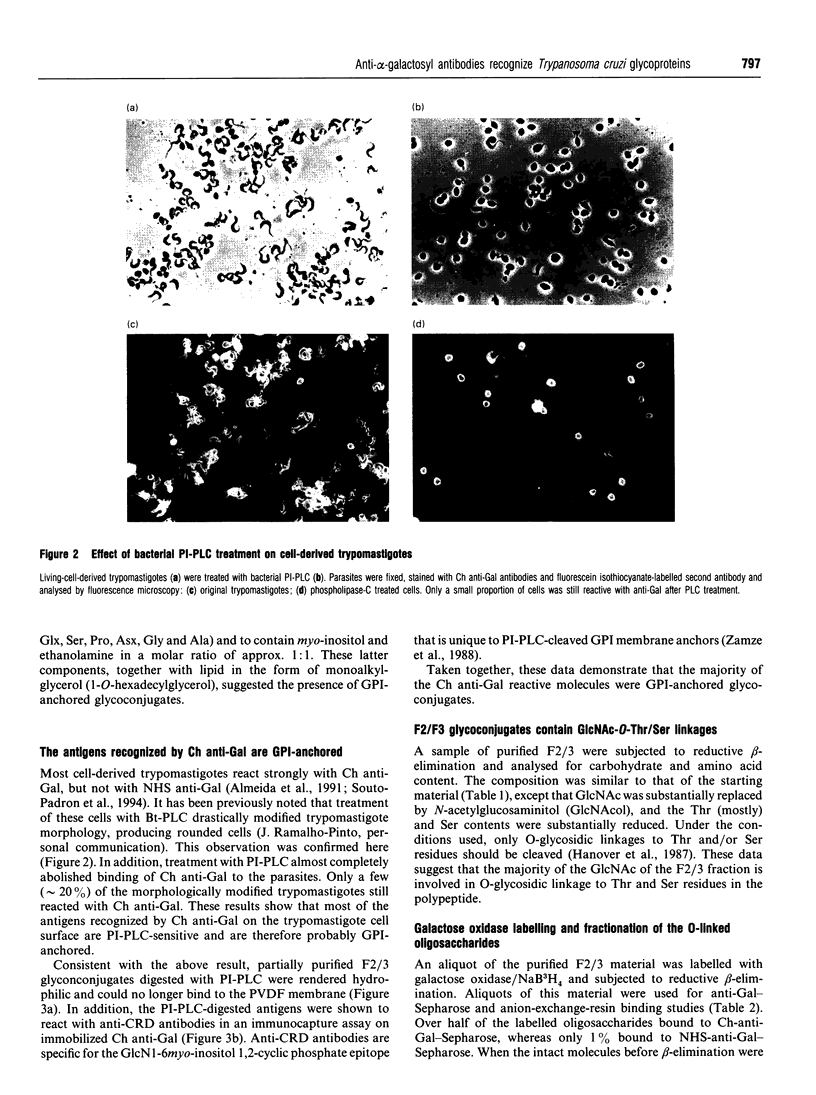
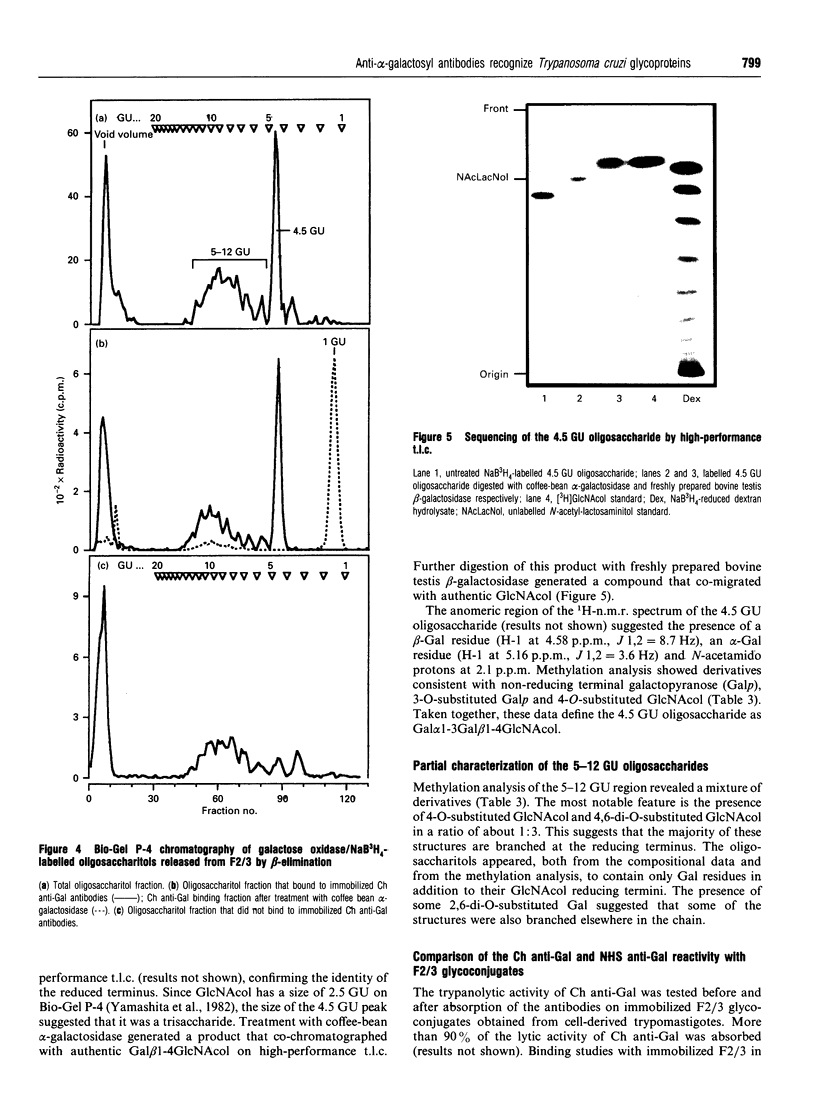
Sera of patients with chronic Chagas' disease (American trypanosomiasis) contain elevated levels of anti-alpha-galactosyl antibodies that are lytic to Trypanosoma cruzi. The T. cruzi trypomastigote F2/3 antigen complex recognized by these antibodies runs as a broad smear on SDS/PAGE [Almeida, Krautz, Krettli and Travassos (1993) J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 7, 307-316]. Treatment of T. cruzi trypomastigote cells with bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) abolished most of their reactivity to chronic Chagas'-disease ((Chagasic, Ch) anti-alpha-galactosyl antibodies (anti-Gal). The F2/3 antigen complex, purified by solvent extraction and hydrophobic-interaction chromatography, contained 60% carbohydrate by weight and substantial amounts of Thr, Ser, Glx, Asx, Gly, Ala and Pro, but relatively few hydrophobic amino acids. The presence of myoinositol, ethanolamine and 1-O-hexadecylglycerol suggested the presence of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. This was confirmed by PI-PLC treatment, which rendered the F2/3 molecules hydrophilic and reactive to anti-(cross-reacting determinant) antibodies. The majority of the GlcNAc content of the F2/3 antigens was found at the reducing termini of oligosaccharides in O-glycosidic linkage to Thr residues. These O-linked oligosaccharides could be released by beta-elimination and by mild hydrazinolysis. The smallest released oligosaccharitol that was reactive with the Ch anti-Gal was Gal alpha 1-3Gal beta 1-4GlcNAcol (where GlcNAcol is N-acetyl-glucosaminitol). Several other Gal-containing oligosaccharitols were observed, most of which were branched and contained 4,6-di-O-substituted GlcNAcol at their reducing termini. About half of the total released oligosaccharitols could bind to immobilized Ch anti-Gal, but none of them bound to the anti-Gal isolated from normal human sera. These data suggest that the specificities of the Ch anti-Gal are quite different from the natural anti-Gal isolated from normal human sera. Therefore, these novel T. cruzi O-linked oligosaccharides are highly immunogenic under the conditions of natural infection and are the targets for lytic Ch anti-Gal.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida I. C., Krautz G. M., Krettli A. U., Travassos L. R. Glycoconjugates of Trypanosoma cruzi: a 74 kD antigen of trypomastigotes specifically reacts with lytic anti-alpha-galactosyl antibodies from patients with chronic Chagas disease. J Clin Lab Anal. 1993;7(6):307–316. doi: 10.1002/jcla.1860070603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida I. C., Milani S. R., Gorin P. A., Travassos L. R. Complement-mediated lysis of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes by human anti-alpha-galactosyl antibodies. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2394–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Hong K. S., Robbins E. S., Nussenzweig V. Stage-specific surface antigens expressed during the morphogenesis of vertebrate forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Dec;64(3):474–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Acosta A. Glycoinositol phospholipids from American Leishmania and Trypanosoma spp: partial characterization of the glycan cores and the human humoral immune response to them. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2305–2312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2305-2312.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Galili U. Immunogenic Gal alpha 1----3Gal carbohydrate epitopes are present on pathogenic American Trypanosoma and Leishmania. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2828–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Velazquez-Avila G. Characterization of a natural human antibody with anti-galactosyl(alpha 1-2)galactose specificity that is present at high titers in chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Oct;47(4):413–421. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMARGO E. P. GROWTH AND DIFFERENTIATION IN TRYPANOSOMA CRUZI. I. ORIGIN OF METACYCLIC TRYPANOSOMES IN LIQUID MEDIA. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1964 May-Jun;6:93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Turner M. J. The membrane form of variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):349–352. doi: 10.1038/302349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann-Schuppert A., Bause E., Schwarz R. T. Studies on O-glycans of Plasmodium-falciparum-infected human erythrocytes. Evidence for O-GlcNAc and O-GlcNAc-transferase in malaria parasites. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 15;216(3):779–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):753–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3340856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U. Evolution and pathophysiology of the human natural anti-alpha-galactosyl IgG (anti-Gal) antibody. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1993;15(2-3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00201098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Shohet S. B., Kobrin E., Stults C. L., Macher B. A. Man, apes, and Old World monkeys differ from other mammals in the expression of alpha-galactosyl epitopes on nucleated cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17755–17762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvao L. M., Nunes R. M., Cançado J. R., Brener Z., Krettli A. U. Lytic antibody titre as a means of assessing cure after treatment of Chagas disease: a 10 years follow-up study. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1993 Mar-Apr;87(2):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(93)90501-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greis K. D., Turco S. J., Thomas J. R., McConville M. J., Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A. Purification and characterization of an extracellular phosphoglycan from Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5876–5881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiwanger R. S., Blomberg M. A., Hart G. W. Glycosylation of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins. Purification and characterization of a uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine:polypeptide beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9005–9013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Barnett L. D., Osborn A. H., Goding J. W., Murray P. J. Identification, characterisation and genomic cloning of a O-linked N-acetylglucosamine-containing cytoplasmic Leishmania glycoprotein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Nov;62(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90178-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanover J. A., Cohen C. K., Willingham M. C., Park M. K. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine is attached to proteins of the nuclear pore. Evidence for cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9887–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt G. D., Hart G. W. The subcellular distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine moieties. Localization of a novel protein-saccharide linkage, O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8049–8057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krettli A. U., Brener Z. Protective effects of specific antibodies in Trypanosoma cruzi infections. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krettli A. U., Brener Z. Resistance against Trypanosoma cruzi associated to anti-living trypomastigote antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2009–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Blackwell J. M. Developmental changes in the glycosylated phosphatidylinositols of Leishmania donovani. Characterization of the promastigote and amastigote glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15170–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Thomas-Oates J. E., Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W. Structure of the lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania major. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19611–19623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T., Bruce J., Merry A., Bigge C., Wormald M., Jaques A., Parekh R. Use of hydrazine to release in intact and unreduced form both N- and O-linked oligosaccharides from glycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):679–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Andrade A. F., Pessolani M. C., Mendonça-Previato L. Incorporation of sialic acid into Trypanosoma cruzi macromolecules. A proposal for a new metabolic route. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jun;16(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Jones C., Gonçalves L. P., Wait R., Travassos L. R., Mendonça-Previato L. O-glycosidically linked N-acetylglucosamine-bound oligosaccharides from glycoproteins of Trypanosoma cruzi. Biochem J. 1994 Jul 1;301(Pt 1):151–159. doi: 10.1042/bj3010151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Ferguson M. A., Heise N., de Almeida M. L., Mortara R. A., Yoshida N. Mucin-like glycoproteins linked to the membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor are the major acceptors of sialic acid in a reaction catalyzed by trans-sialidase in metacyclic forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jun;59(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90227-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Jiang M. S., Hart G. W., Nussenzweig V. A novel cell surface trans-sialidase of Trypanosoma cruzi generates a stage-specific epitope required for invasion of mammalian cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1117–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90008-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Ferguson M. A., McConville M. J., Mehlert A., Homans S. W., Bordier C. Structure of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of the Leishmania major promastigote surface protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16955–16964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Ralton J. E., McConville M. J., Ferguson M. A. Analysis of the neutral glycan fractions of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositols by thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1993 Apr;210(1):106–112. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Braun P. E., Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Sherman W. R. Direct measurement of inositol in bovine myelin basic protein. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):285–288. doi: 10.1042/bj2480285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souto-Padron T., Almeida I. C., de Souza W., Travassos L. R. Distribution of alpha-galactosyl-containing epitopes on Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigote and amastigote forms from infected Vero cells detected by Chagasic antibodies. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1994 Jan-Feb;41(1):47–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1994.tb05933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travassos L. R., Almeida I. C. Carbohydrate immunity in American trypanosomiasis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1993;15(2-3):183–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00201100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Mizuochi T., Kobata A. Analysis of oligosaccharides by gel filtration. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:105–126. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamze S. E., Ferguson M. A., Collins R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Characterization of the cross-reacting determinant (CRD) of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):527–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]