Abstract
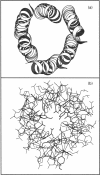
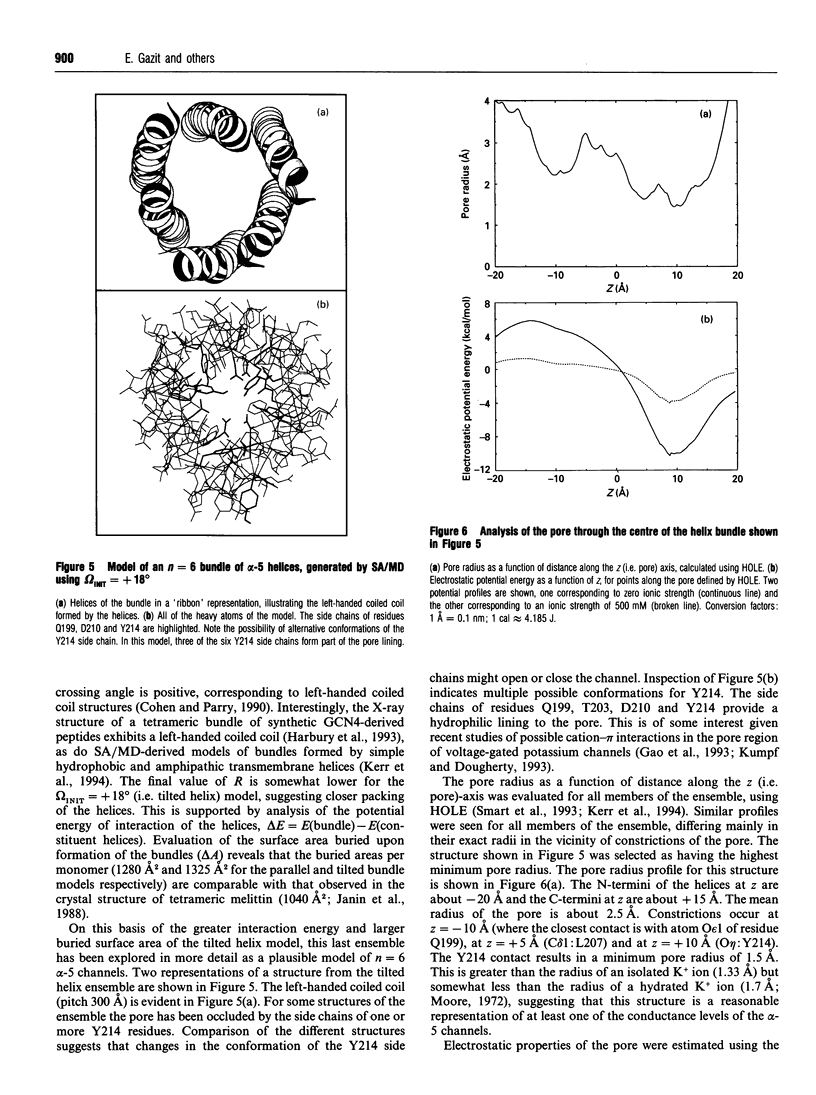
A peptide with a sequence corresponding to the highly conserved alpha-5 segment of the Cry delta-endotoxin family (amino acids 193-215 of Bacillus thuringiensis CryIIIA [Gazit and Shai (1993) Biochemistry 32, 3429-3436]), was investigated with respect to its interaction with insect membranes, cytotoxicity in vitro towards Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf-9) cells, and its propensity to form ion channels in planar lipid membranes (PLMs). Selectively labelled analogues of alpha-5 at either the N-terminal amino acid or the epsilon-amine of its lysine, were used to monitor the interaction of the peptides with insect membranes. The fluorescent emission spectra of the 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-4-yl (NBD)-labelled alpha-5 peptides displayed a blue shift upon binding to insect (Spodoptera littoralis) mid-gut membranes, reflecting the relocation of the fluorescent probes to an environment of increased apolarity, i.e. within the lipidic constituent of the membrane. Moreover, midgut membrane-bound NBD-labelled alpha-5 peptides were protected from enzymic proteolysis. Functional characterization of alpha-5 has revealed that it is cytotoxic to Sf-9 insect cells, and that it forms ion channels in PLMs with conductances ranging from 30 to 1000 pS. A proline-substituted analogue of alpha-5 is less cytolytic and slightly more exposed to enzymic digestion. Molecular modelling utilizing simulated annealing via molecular dynamics suggests that a transbilayer pore may be formed by alpha-5 monomers that assemble to form a left-handed coiled coil of approximately parallel helices. These findings further support a role for alpha-5 in the toxic mechanism of delta-endotoxins, and assign alpha-5 as one of the transmembrane helices which form the toxic pore. The suggested role is consistent with the recent finding that cleavage of CryIVB delta-endotoxin in a loop between alpha-5 and alpha-6 is highly important for its larvicidal activity [Angsuthanasombat, Crickmore and Ellar (1993) FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 111, 255-262].
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad W., Ellar D. J. Directed mutagenesis of selected regions of a Bacillus thuringiensis entomocidal protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90132-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angsuthanasombat C., Crickmore N., Ellar D. J. Effects on toxicity of eliminating a cleavage site in a predicted interhelical loop in Bacillus thuringiensis CryIVB delta-endotoxin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Aug 1;111(2-3):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I. The two faces of Bacillus thuringiensis: insecticidal proteins and post-exponential survival. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(4):489–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Efraim I., Bach D., Shai Y. Spectroscopic and functional characterization of the putative transmembrane segment of the minK potassium channel. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2371–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R. Differentiation of lipid-associating helices by use of three-dimensional molecular hydrophobicity potential calculations. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16120–16127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay A., London E. Parallax method for direct measurement of membrane penetration depth utilizing fluorescence quenching by spin-labeled phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):39–45. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Levitt M., Richardson D. Helix to helix packing in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):215–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Parry D. A. Alpha-helical coiled coils and bundles: how to design an alpha-helical protein. Proteins. 1990;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Latorre R. Phospholipid bilayers made from monolayers on patch-clamp pipettes. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84343-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings C. E., Armstrong G., Hodgman T. C., Ellar D. J. Structural and functional studies of a synthetic peptide mimicking a proposed membrane inserting region of a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. Mol Membr Biol. 1994 Apr-Jun;11(2):87–92. doi: 10.3109/09687689409162225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Chou L. W., Auerbach A. The nature of cation-pi binding: interactions between tetramethylammonium ion and benzene in aqueous solution. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81031-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit E., Shai Y. Structural and functional characterization of the alpha 5 segment of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3429–3436. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge A. Z., Shivarova N. I., Dean D. H. Location of the Bombyx mori specificity domain on a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4037–4041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P., Stroud R. M. Ion channels formed by a highly charged peptide. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3551–3557. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. S., Cowles E. A., Pietrantonio P. V. The mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxins. Annu Rev Entomol. 1992;37:615–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt R. E., Blatt Y., Montal M. The structure of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel. Inferences derived from computer-aided analysis of the Electrophorus electricus channel primary structure. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove A., Tomich J. M., Montal M. A molecular blueprint for the pore-forming structure of voltage-gated calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6418–6422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Seetharamulu P. Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. B., Zhang T., Kim P. S., Alber T. A switch between two-, three-, and four-stranded coiled coils in GCN4 leucine zipper mutants. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1401–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.8248779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hink W. F. Established insect cell line from the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):466–467. doi: 10.1038/226466b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfte H., Whiteley H. R. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):242–255. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.242-255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M. A three-dimensional molecular assembly model of a lipoprotein from the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Miller S., Chothia C. Surface, subunit interfaces and interior of oligomeric proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90606-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsh L. P., Ellena J. F., Cafiso D. S. Determination of the molecular dynamics of alamethicin using 13C NMR: implications for the mechanism of gating of a voltage-dependent channel. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 9;31(22):5136–5144. doi: 10.1021/bi00137a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. D., Sankararamakrishnan R., Smart O. S., Sansom M. S. Parallel helix bundles and ion channels: molecular modeling via simulated annealing and restrained molecular dynamics. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1501–1515. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80624-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. D., Sansom M. S. Hydrophilic surface maps of channel-forming peptides: analysis of amphipathic helices. Eur Biophys J. 1993;22(4):269–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00180261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpf R. A., Dougherty D. A. A mechanism for ion selectivity in potassium channels: computational studies of cation-pi interactions. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1708–1710. doi: 10.1126/science.8378771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langosch D., Hartung K., Grell E., Bamberg E., Betz H. Ion channel formation by synthetic transmembrane segments of the inhibitory glycine receptor--a model study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 18;1063(1):36–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90350-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear J. D., Wasserman Z. R., DeGrado W. F. Synthetic amphiphilic peptide models for protein ion channels. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1177–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.2453923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. K., Milne R. E., Ge A. Z., Dean D. H. Location of a Bombyx mori receptor binding region on a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3115–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. D., Carroll J., Ellar D. J. Crystal structure of insecticidal delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):815–821. doi: 10.1038/353815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor I. R., Thomas D. H., Sansom M. S. Properties of ion channels formed by Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 21;942(2):280–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. G., Williamson H., Fuller S., Hudson B. Melittin induces fusion of unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 10;732(3):668–674. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Nagayama K., Ohnishi S. Membrane fusion activity of succinylated melittin is triggered by protonation of its carboxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):4056–4062. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges M., Brünger A. T. Automated modeling of coiled coils: application to the GCN4 dimerization region. Protein Eng. 1991 Aug;4(6):649–659. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.6.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oiki S., Danho W., Madison V., Montal M. M2 delta, a candidate for the structure lining the ionic channel of the nicotinic cholinergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8703–8707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oiki S., Danho W., Montal M. Channel protein engineering: synthetic 22-mer peptide from the primary structure of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel forms ionic channels in lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2393–2397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. W., Pattus F. Rendering a membrane protein soluble in water: a common packing motif in bacterial protein toxins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Oct;18(10):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouny Y., Shai Y. Interaction of D-amino acid incorporated analogues of pardaxin with membranes. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 6;31(39):9482–9490. doi: 10.1021/bi00154a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajarathnam K., Hochman J., Schindler M., Ferguson-Miller S. Synthesis, location, and lateral mobility of fluorescently labeled ubiquinone 10 in mitochondrial and artificial membranes. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3168–3176. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport D., Danin M., Gazit E., Shai Y. Membrane interactions of the sodium channel S4 segment and its fluorescently-labeled analogues. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8868–8875. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport D., Shai Y. Aggregation and organization of pardaxin in phospholipid membranes. A fluorescence energy transfer study. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6502–6509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom M. S. The biophysics of peptide models of ion channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1991;55(3):139–235. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(91)90004-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. L., Garneau L., Masson L., Brousseau R. Early response of cultured lepidopteran cells to exposure to delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis: involvement of calcium and anionic channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 18;1065(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shai Y., Bach D., Yanovsky A. Channel formation properties of synthetic pardaxin and analogues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20202–20209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shai Y., Hadari Y. R., Finkels A. pH-dependent pore formation properties of pardaxin analogues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22346–22354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatin S. L., Abrams C. K., English L. Delta-endotoxins form cation-selective channels in planar lipid bilayers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90397-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart O. S., Goodfellow J. M., Wallace B. A. The pore dimensions of gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2455–2460. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81293-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Andreu D., Merrifield R. B. Binding and action of cecropin and cecropin analogues: antibacterial peptides from insects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):260–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1983 Mar;60:181–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.60.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Levy J. J., Caporale L. H., Rosenblatt M., Tosteson D. C. Solid-phase synthesis of melittin: purification and functional characterization. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6627–6631. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., McGaughey W. H., Johnson D. E., Barnett B. D., Van Mellaert H. Mechanism of insect resistance to the microbial insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2294593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Aronson A. I. Localized mutagenesis defines regions of the Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin involved in toxicity and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2311–2317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]