Abstract
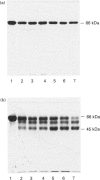
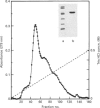
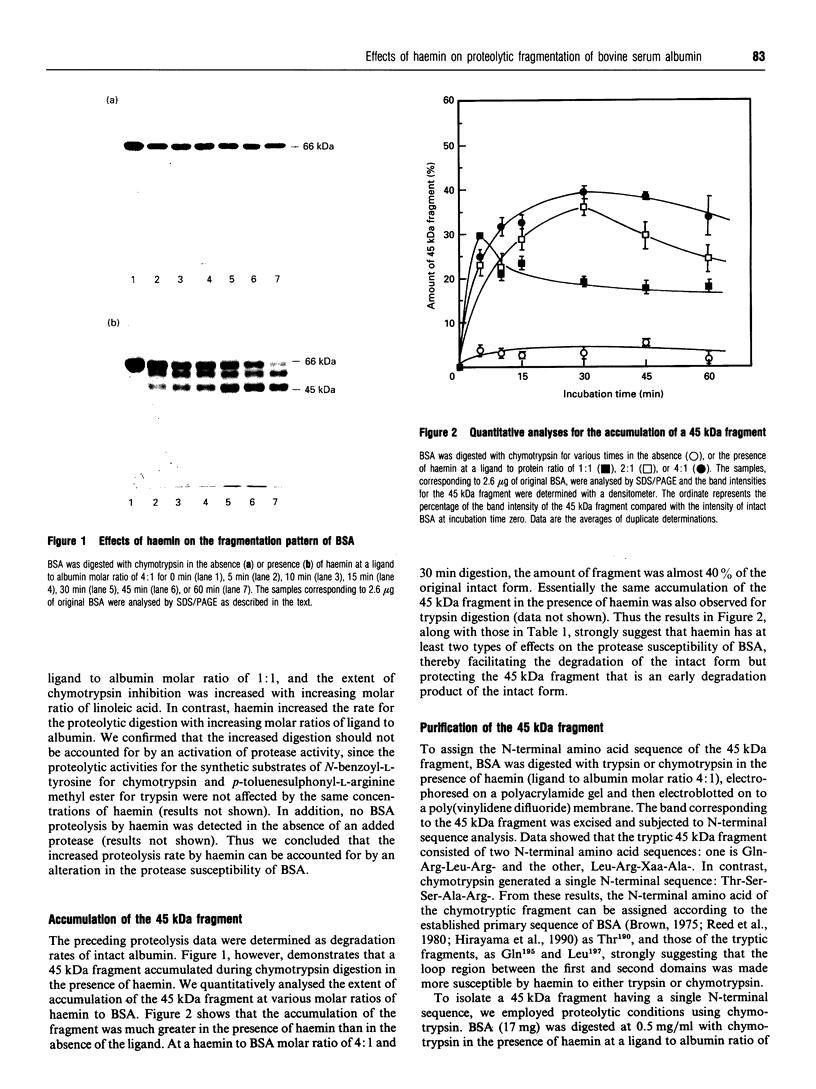
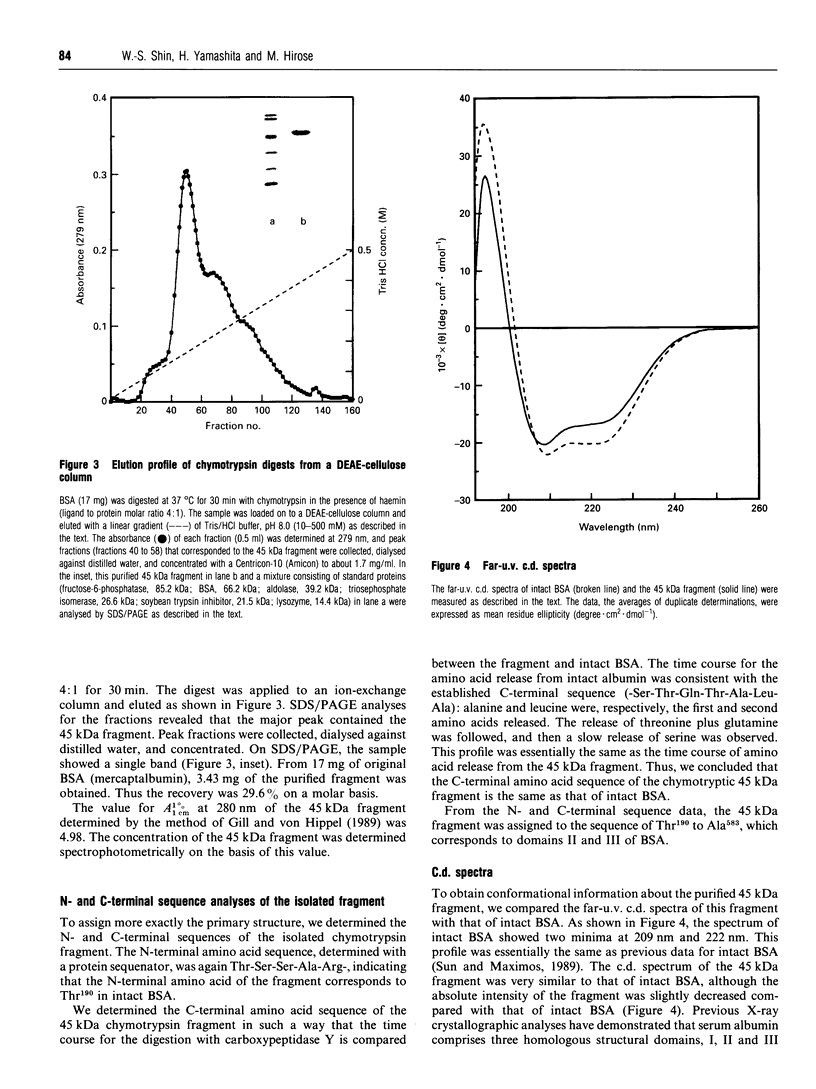
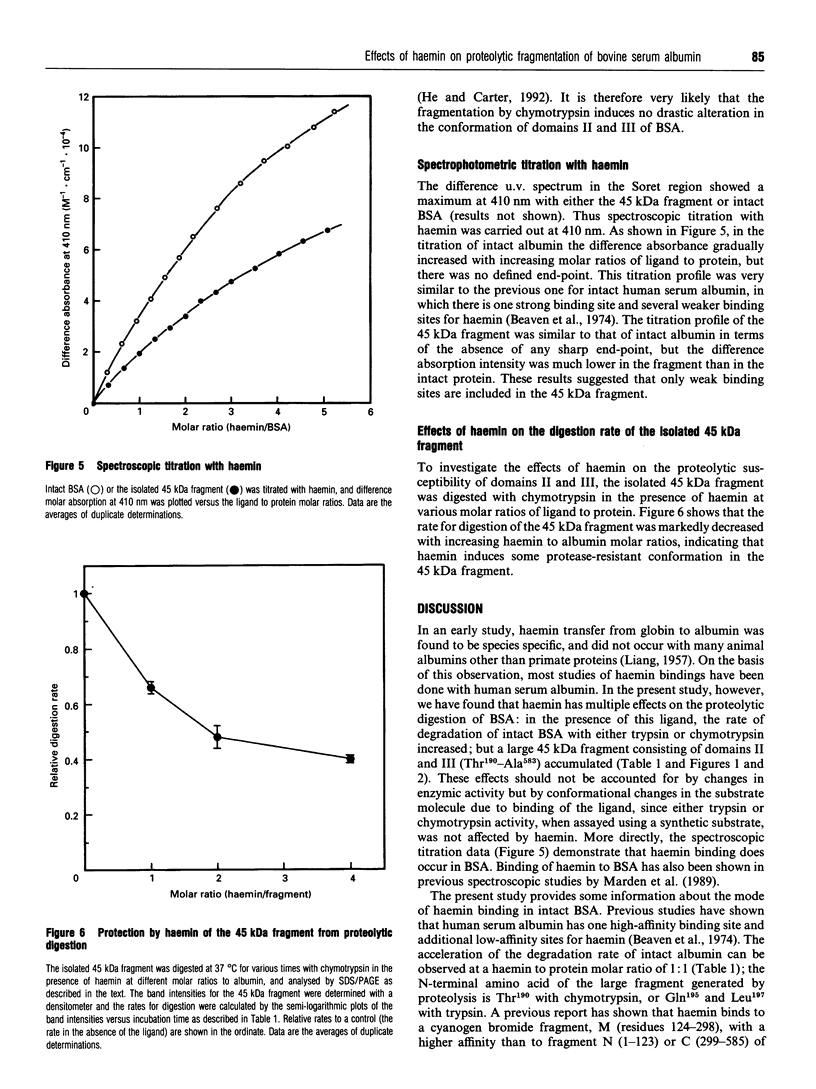
The effects of ligand binding on the proteolytic susceptibility of BSA were investigated. The rate for proteolytic digestion with either trypsin or chymotrypsin decreased in the presence of bilirubin and fatty acids, suggesting that overall albumin conformation is stabilized by these ligands. In contrast, haemin showed multiple effects on a proteolytic digestion pattern: the rate for the degradation of intact albumin greatly increased, but a large 45 kDa fragment accumulated during proteolytic digestion in the presence of this ligand. This unique fragmentation pattern allowed us to isolate the 45 kDa fragment at a high yield (about 30% on a molar basis) by one-step purification. Sequence analyses indicated that this fragment lies between residues Thr190 and Ala583, which constitutes domains II and III of the albumin molecule. Far-u.v. c.d. spectra strongly suggested that the secondary structure in the intact albumin is almost retained in the 45 kDa fragment. The isolated 45 kDa fragment showed haemin-binding ability, as evaluated by spectroscopic titration; upon re-digestion of the 45 kDa fragment, haemin showed strong protective effects. These results were consistent with the idea that haemin binding to BSA induces an increased protease susceptibility in the loop region between domains I and II, but in the overall conformation of domains II and III, a protease-resistant property.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaven G. H., Chen S. H., d' Albis A., Gratzer W. B. A spectroscopic study of the haemin--human-serum-albumin system. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 1;41(3):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos O. J., Fischer M. J., Wilting J., Janssen L. H. Drug-binding and other physicochemical properties of a large tryptic and a large peptic fragment of human serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 2;953(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldhoff R. C., Peters T., Jr Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Isolation and characterization of peptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4508–4514. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Beaven G. H. Large fragments of human serum albumin. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):619–625. doi: 10.1042/bj1610619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Carter D. C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):209–215. doi: 10.1038/358209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama K., Akashi S., Furuya M., Fukuhara K. Rapid confirmation and revision of the primary structure of bovine serum albumin by ESIMS and Frit-FAB LC/MS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):639–646. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrkal Z., Kodícek M., Vodrázka Z., Meloun B., Morávek L. Haeme binding to human serum albumin and to the three large cyanogen bromide albumin fragments. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(5):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P. Limited pepsin digestion of bovine plasma albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Spencer M. Structural studies and organic ligand-binding properties of bovine plasma albumin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6134–6148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIANG C. C. The formation of complexes between haemoglobins and plasma proteins in a variety of animals. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):552–558. doi: 10.1042/bj0660552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Hirose M. Partially folded state of the disulfide-reduced form of human serum albumin as an intermediate for reversible denaturation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14753–14758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marden M. C., Hazard E. S., Leclerc L., Gibson Q. H. Flash photolysis of the serum albumin-heme-CO complex. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4422–4426. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., McClintock D. K., Castellani B. A. Ligand-stabilized conformations in serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4402–4408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. K., Hunter M. J. Bovine mercaptalbumin and non-mercaptalbumin monomers. Interconversions and structural differences. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7391–7406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr, Feldhoff R. C. Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Isolation and characterization of tryptic fragments. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3384–3391. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. G., Burrington C. M. The albumin receptor effect may be due to a surface-induced conformational change in albumin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9867–9872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. G., Putnam F. W., Peters T., Jr Sequence of residues 400--403 of bovine serum albumin. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 1;191(3):867–868. doi: 10.1042/bj1910867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. F., Maximos A. S. Circular dichroism of bovine serum albumin in divalent salt solutions. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1989 Jul;34(1):46–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1989.tb01007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Harrington W. F. An enzyme-probe method to detect structural changes in the myosin rod. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):35–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]