Abstract
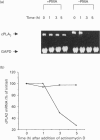
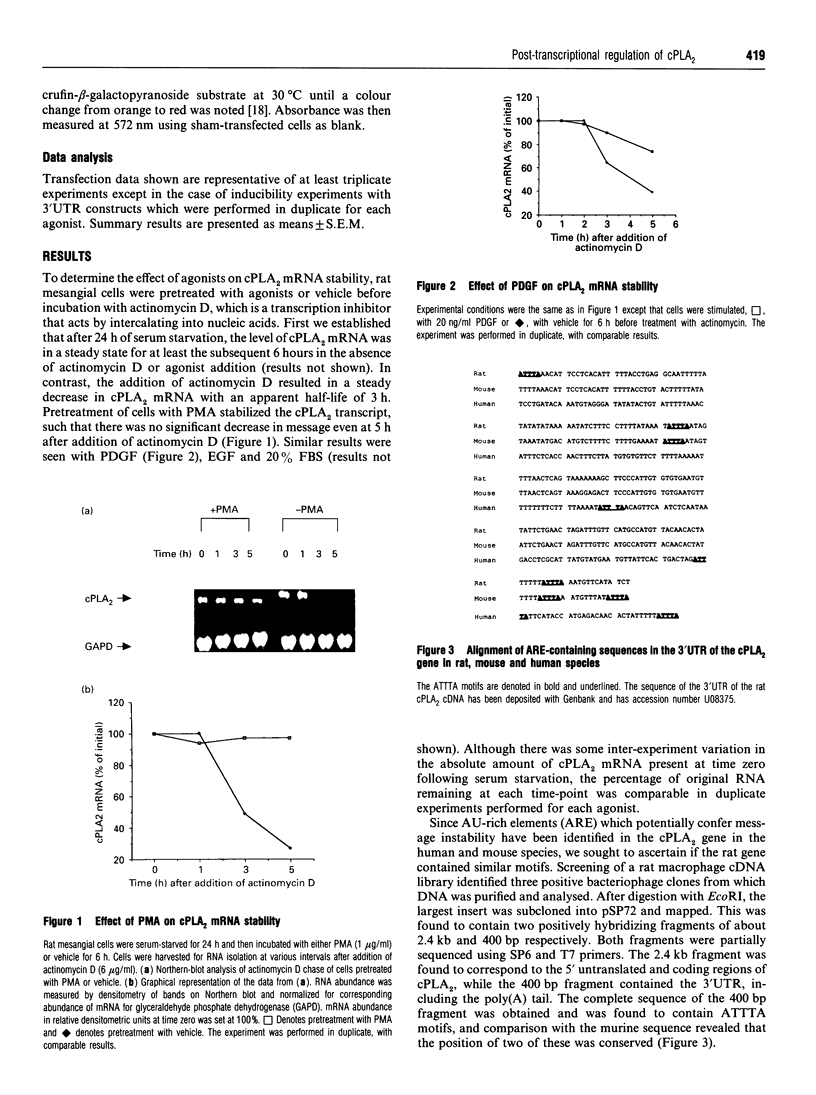
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) is thought to be the rate-limiting enzyme in the arachidonic acid/eicosanoid cascade. The ability of various agonists to increase steady-state cPLA2 mRNA levels has previously been reported. The current study delineates the contributions of transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes to the regulation of cPLA2 gene expression in response to a variety of agonists in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, serum and phorbol myristate acetate all increase the half-life of cPLA2 mRNA transcripts, indicating a role for post-transcriptional modulation of gene expression. The presence of three ATTTA motifs in the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of the rat cPLA2 cDNA is ascertained. Heterologous expression of chimeric constructs with different 3'UTRs ligated into the 3' end of the luciferase coding region reveals that the presence of the cPLA2 3'UTR results in reduced luciferase activity compared with constructs without the cPLA2 3'UTR. Furthermore, the luciferase activity in the constructs with the cPLA2 3'UTR is increased in response to the same agonists which stabilize endogenous cPLA2 mRNA. A negligible effect of these agonists on transcriptional control of cPLA2 is evident using promoter-reporter constructs expressed in transient and stable transfectants. Taken together, these results indicate predominant post-transcriptional regulation of cPLA2 mRNA levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonventre J. V. Phospholipase A2 and signal transduction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Aug;3(2):128–150. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V32128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W. G., Ramesha C. S., Chang D. J., Fan N., Heller R. A. Cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 activity and gene expression are stimulated by tumor necrosis factor: dexamethasone blocks the induced synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4475–4479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer S. G., Zeng W., Sridhara S., Skorecki K. L. Multiple signaling pathways for Cl(-)-dependent depolarization of mesangial cells: role of Ca2+, PKC, and G proteins. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):F668–F678. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.4.F668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S., Miyamoto N. G. Point mutational analysis of the human c-fos serum response factor binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1177–1195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Wartmann M., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L., Seth A., Davis R. J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90666-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A. P., Goldberg H. J., Tay A. H., Li Z. G., Arbus G. S., Skorecki K. L. Epidermal growth factor and phorbol myristate acetate increase expression of the mRNA for cytosolic phospholipase A2 in glomerular mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 1;295(Pt 3):763–766. doi: 10.1042/bj2950763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Lin L. L., Kharbanda S., Knopf J., Kufe D. Macrophage colony stimulating factor activates phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by cytoplasmic phospholipase A2. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4917–4922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Winitz S., Qian N. X., Van Putten V., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. Phosphorylation and activation of a high molecular weight form of phospholipase A2 by p42 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1960–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D. Arachidonic acid in cell signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. D., White D. L., Chiou X. G., Goodson T., Gamboa G. C., McClure D., Burgett S., Hoskins J., Skatrud P. L., Sportsman J. R. Molecular cloning and expression of human Ca(2+)-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14850–14853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tay A., Maxwell P., Li Z., Goldberg H., Skorecki K. Isolation of promoter for cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 6;1217(3):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. M., Kao M. Y., Gordon D. F., Ridgway E. C. Thyroid hormone regulates the mouse thyrotropin beta-subunit gene promoter in transfected primary thyrotropes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14840–14847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W., Merrill J. R., Bradshaw W. S., Simmons D. L. Structural determination and promoter analysis of the chicken mitogen-inducible prostaglandin G/H synthase gene and genetic mapping of the murine homolog. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jan;300(1):247–252. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]