Abstract
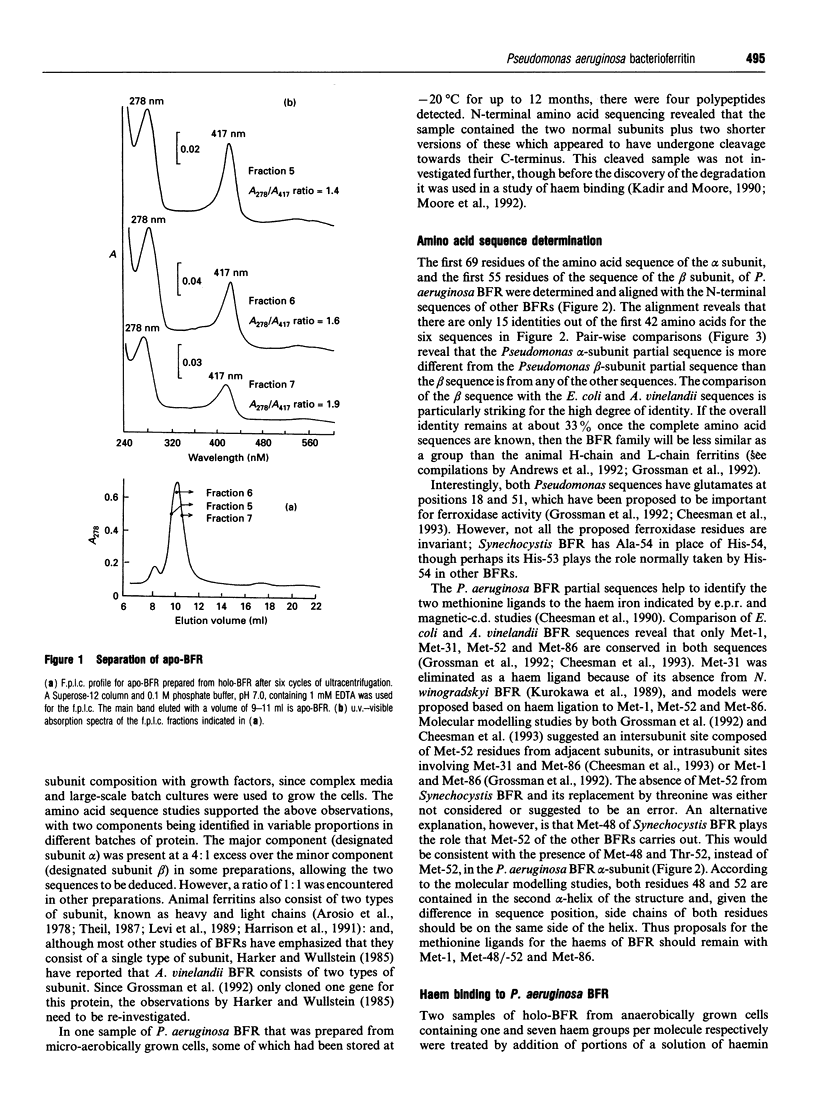
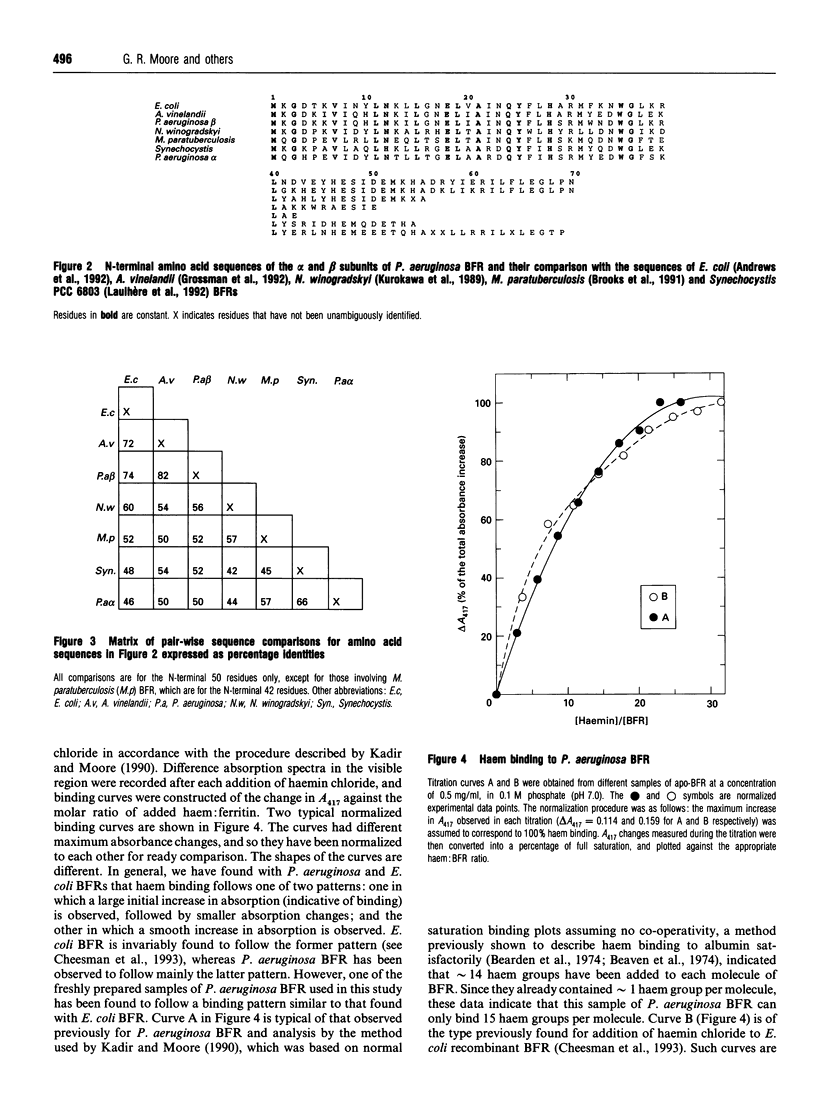
The subunit composition, amino acid sequence and haem-binding characteristics of bacterioferritin (BFR) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa have been studied. Unlike other BFRs, P. aeruginosa BFR was found to contain two subunit types, designated alpha and beta, which differed considerably in their amino acid sequences. The N-terminal 69 and 55 amino acids of the alpha and beta subunits respectively were determined. The alpha subunit differed most from other BFRs. The two subunits were present in variable proportions in different preparations. The maximum stoichiometry of haem binding was found to be sample-dependent and to be different from the previously reported one per subunit [Kadir and Moore (1990) FEBS Lett. 271, 141-143]. This previous haem-binding study was shown to have been carried out with damaged protein, which contained both normal alpha and beta subunits and shorter versions of these that appeared to have been produced by cleavage of the normal subunits. The possibility that aging processes degrade ferritins and affect their haem-binding characteristics is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews S. C., Arosio P., Bottke W., Briat J. F., von Darl M., Harrison P. M., Laulhère J. P., Levi S., Lobreaux S., Yewdall S. J. Structure, function, and evolution of ferritins. J Inorg Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;47(3-4):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(92)84062-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews S. C., Harrison P. M., Guest J. R. Cloning, sequencing, and mapping of the bacterioferritin gene (bfr) of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3940–3947. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3940-3947.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arosio P., Adelman T. G., Drysdale J. W. On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4451–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearden A. J., Morgan W. T., Muller-Eberhard U. Heme complexes of rabbit hemopexin, human hemopexin and human serum albumin: electron spin resonance and Mssbauer spectroscopic studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90562-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven G. H., Chen S. H., d' Albis A., Gratzer W. B. A spectroscopic study of the haemin--human-serum-albumin system. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 1;41(3):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. W., Young N. M., Watson D. C., Robertson R. H., Sugden E. A., Nielsen K. H., Becker S. A. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis antigen D: characterization and evidence that it is a bacterioferritin. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1652–1658. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1652-1658.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesman M. R., Kadir F. H., al-Basseet J., al-Massad F., Farrar J., Greenwood C., Thomson A. J., Moore G. R. E.p.r. and magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopic characterization of bacterioferritin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2860361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesman M. R., Thomson A. J., Greenwood C., Moore G. R., Kadir F. Bis-methionine axial ligation of haem in bacterioferritin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):771–773. doi: 10.1038/346771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesman M. R., le Brun N. E., Kadir F. H., Thomson A. J., Moore G. R., Andrews S. C., Guest J. R., Harrison P. M., Smith J. M., Yewdall S. J. Haem and non-haem iron sites in Escherichia coli bacterioferritin: spectroscopic and model building studies. Biochem J. 1993 May 15;292(Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1042/bj2920047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolow F., Kalb A. J., Yariv J. Location of haem in bacterioferritin of E. coli. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Nov 1;49(Pt 6):597–600. doi: 10.1107/S0907444993007073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M. J., Hinton S. M., Minak-Bernero V., Slaughter C., Stiefel E. I. Unification of the ferritin family of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2419–2423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Wullstein L. H. Evidence for two nonidentical subunits of bacterioferritin from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):651–655. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.651-655.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Rivoire B., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Brennan P. J. The major native proteins of the leprosy bacillus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14065–14068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadir F. H., Moore G. R. Bacterial ferritin contains 24 haem groups. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80391-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadir F. H., al-Massad F. K., Moore G. R. Haem binding to horse spleen ferritin and its effect on the rate of iron release. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):867–870. doi: 10.1042/bj2820867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laulhère J. P., Labouré A. M., Van Wuytswinkel O., Gagnon J., Briat J. F. Purification, characterization and function of bacterioferritin from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis P.C.C. 6803. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):785–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2810785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Salfeld J., Franceschinelli F., Cozzi A., Dorner M. H., Arosio P. Expression and structural and functional properties of human ferritin L-chain from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5179–5184. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochrome composition of the purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 31;807(3):308–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Kadir F. H., al-Massad F. Haem binding to ferritin and possible mechanisms of physiological iron uptake and release by ferritin. J Inorg Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;47(3-4):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(92)84063-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Mann S., Bannister J. V. Isolation and properties of the complex nonheme-iron-containing cytochrome b557 (bacterioferritin) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Inorg Biochem. 1986 Oct-Nov;28(2-3):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(86)80097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr S. R., Barber D., Greenwood C. A purification procedure for the soluble cytochrome oxidase and some other respiratory proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):423–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1570423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Ford G. C., Harrison P. M., Yariv J., Kalb A. J. Molecular size and symmetry of the bacterioferritin of Escherichia coli. X-ray crystallographic characterization of four crystal forms. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):465–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Quirk A. V., Plank R. W., Diffin F. M., Ford G. C., Harrison P. M. The identity of Escherichia coli bacterioferritin and cytochrome b1. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):737–740. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiefel E. I., Watt G. D. Azotobacter cytochrome b557.5 is a bacterioferritin. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):81–83. doi: 10.1038/279081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil E. C. Ferritin: structure, gene regulation, and cellular function in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Sperling R., Bauminger E. R., Cohen S. G., Ofer S. The composition and the structure of bacterioferritin of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):171–175. doi: 10.1042/bj1970171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Massad F. K., Kadir F. H., Moore G. R. Animal ferritin and bacterioferritin contain quinones. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):177–180. doi: 10.1042/bj2830177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


