Abstract
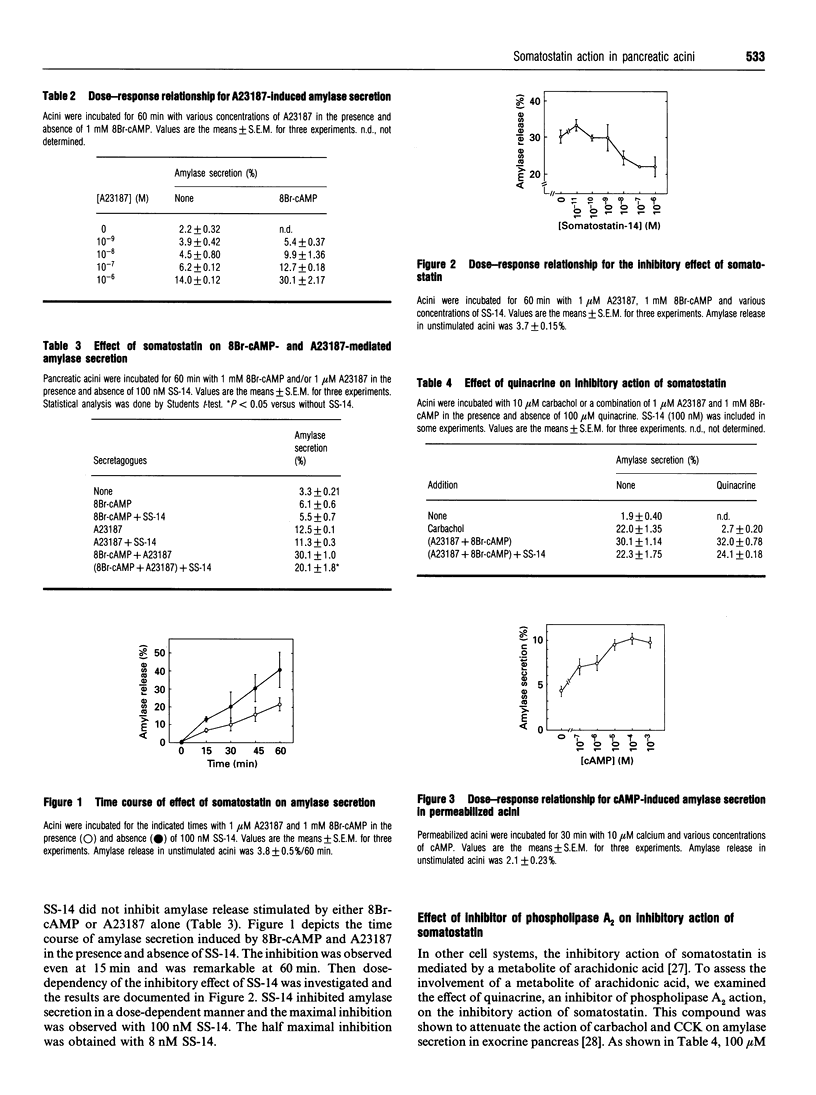
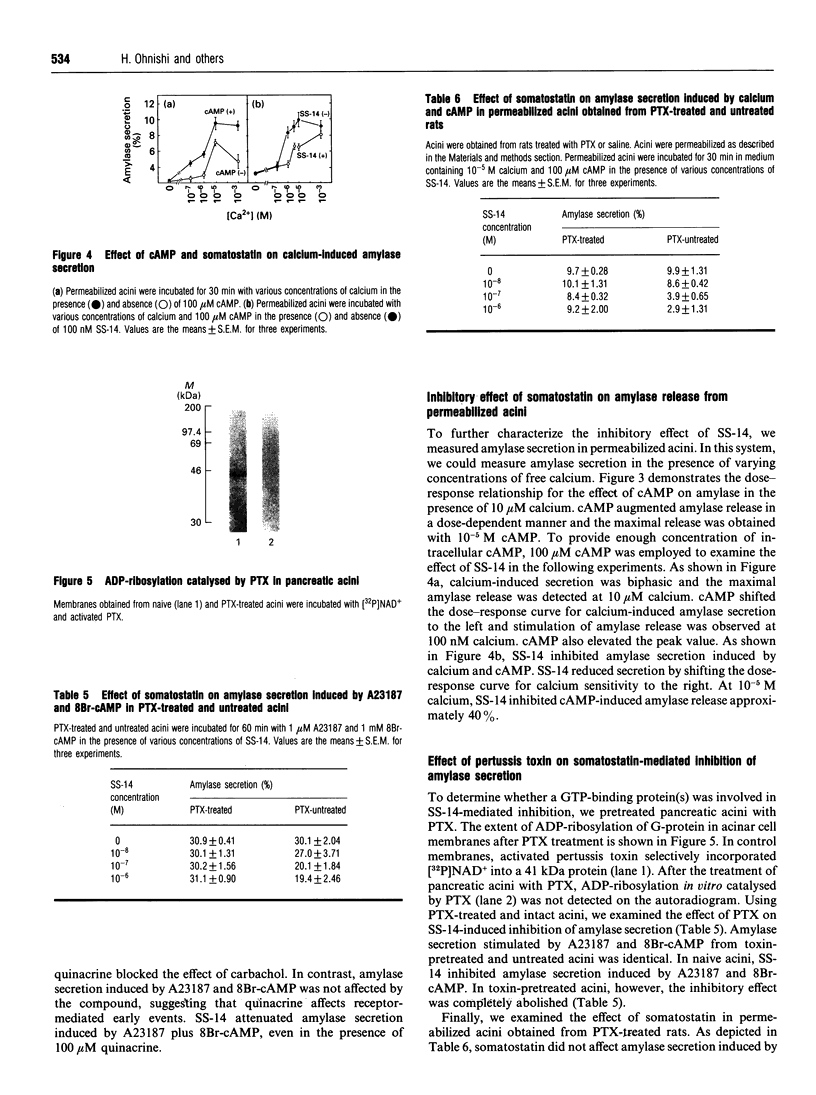
It has recently been shown that somatostatin inhibits amylase secretion from isolated pancreatic acini by reducing cyclic AMP (cAMP) production [Matsushita, Okabayashi, Hasegawa, Koide, Kido, Okutani, Sugimoto and Kasuga (1993) Gastroenterology 104, 1146-1152]. To date, however, little is known as to the other mechanism(s) by which somatostatin inhibits amylase secretion in exocrine pancreas. To investigate the action of somatostatin independent of cAMP generation, we examined the effect of somatostatin in isolated rat pancreatic acini stimulated by 1 microM calcium ionophore A23187 and 1 mM 8-bromo-cyclic AMP (8Br-cAMP). Somatostatin inhibited amylase secretion evoked by a combination of A23187 and 8Br-cAMP in a dose-dependent manner. The maximum inhibition was obtained by 10(-7) M somatostatin, and at this concentration somatostatin inhibited the effect of A23187 and 8Br-cAMP by approximately 30%. In electrically permeabilized acini, an elevation of free calcium concentration resulted in an increase in amylase secretion and cAMP enhanced the secretion evoked by calcium. cAMP shifted the dose-response curve for calcium-induced secretion leftwards and elevated the peak value of secretion. Somatostatin inhibited the effect of cAMP on calcium-induced amylase secretion by shifting the dose-response curve to the right. To determine the involvement of a G-protein(s), we examined the effect of somatostatin in acini pretreated with pertussis toxin. Pretreatment of acini with pertussis toxin completely blocked somatostatin-inhibition of amylase-secretion evoked by A23187 and 8Br-cAMP. These results indicate that somatostatin decreases amylase secretion induced by cAMP and calcium by reducing the calcium sensitivity of exocytosis. A pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein is also involved in this step.
Full text
PDF



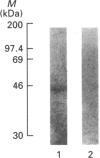
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aridor M., Rajmilevich G., Beaven M. A., Sagi-Eisenberg R. Activation of exocytosis by the heterotrimeric G protein Gi3. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1569–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.7504324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Sivitz M. C., Owen O. E., Essa-Koumar N., Landor J. H. Somatostatin suppresses secretin and pancreatic exocrine secretion. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):163–165. doi: 10.1126/science.1166308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. J., Schonbrunn A. Affinity purification of a somatostatin receptor-G-protein complex demonstrates specificity in receptor-G-protein coupling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6668–6676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A. Regulated exocytosis. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):305–316. doi: 10.1042/bj2930305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteve J. P., Susini C., Vaysse N., Antoniotti H., Wunsch E., Berthon G., Ribet A. Binding of somatostatin to pancreatic acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 1):G62–G69. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.1.G62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteve J. P., Vaysse N., Susini C., Kunsch J. M., Fourmy D., Pradayrol L., Wunsch E., Moroder L., Ribet A. Bimodal regulation of pancreatic exocrine function in vitro by somatostatin-28. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):G208–G216. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.2.G208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry D. J., Garry M. G., Williams J. A., Mahoney W. C., Sorenson R. L. Effects of islet hormones on amylase secretion and localization of somatostatin binding sites. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):G897–G904. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.5.G897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosfils K., Gomez F., Dehaye J. P. Inhibition by mepacrine and amylase secretion from intact and permeabilized rat pancreatic acini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyr K., Beglinger C., Köhler E., Trautzl U., Keller U., Bloom S. R. Circulating somatostatin. Physiological regulator of pancreatic function? J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1595–1600. doi: 10.1172/JCI112994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habara Y., Kanno T. Dose-dependency in spatial dynamics of [Ca2+]c in pancreatic acinar cells. Cell Calcium. 1991 Sep;12(8):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90073-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Aktories K., Schultz G. A nucleotide regulatory site for somatostatin inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cells. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):177–178. doi: 10.1038/303177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluxen F. W., Bruns C., Lübbert H. Expression cloning of a rat brain somatostatin receptor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4618–4622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Blalock J. B., Schonbrunn A. Characterization of the cyclic AMP-independent actions of somatostatin in GH cells. I. An increase in potassium conductance is responsible for both the hyperpolarization and the decrease in intracellular free calcium produced by somatostatin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):216–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Dorflinger L. J., Schonbrunn A. Pertussis toxin blocks both cyclic AMP-mediated and cyclic AMP-independent actions of somatostatin. Evidence for coupling of Ni to decreases in intracellular free calcium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13138–13145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Schonbrunn A. Characterization of the cyclic AMP-independent actions of somatostatin in GH cells. II. An increase in potassium conductance initiates somatostatin-induced inhibition of prolactin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):226–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Tasler J., Obtulowicz W., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Effect of growth hormone-release inhibiting hormone on hormones stimulating exocrine pancreatic secretion. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Sakamoto C., Nagao M., Nishizaki H., Baba S. G protein in stimulation of PI hydrolysis by CCK in isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):E652–E659. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.5.E652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Okabayashi Y., Hasegawa H., Koide M., Kido Y., Okutani T., Sugimoto Y., Kasuga M. In vitro inhibitory effect of somatostatin on secretin action in exocrine pancreas of rats. Gastroenterology. 1993 Apr;104(4):1146–1152. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90286-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. D., Madamba S. G., Joëls M., Siggins G. R. Somatostatin augments the M-current in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):278–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2892268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill S. J., Bunnett N. W., Goto Y., Debas H. T. Somatostatin inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion via a neural mechanism. Metabolism. 1990 Sep;39(9 Suppl 2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto I., Hata Y., Ogata E., Kojima I. Insulin-like growth factor II stimulates calcium influx in competent BALB/c 3T3 cells primed with epidermal growth factor. Characteristics of calcium influx and involvement of GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12120–12126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Jamieson J. D. Activation of protein kinase C is not an absolute requirement for amylase release from permeabilized rat pancreatic acini. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):597–601. doi: 10.1042/bj2850597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. L., Korenbrot J. I., Williams J. A. Intracellular free calcium concentrations in isolated pancreatic acini; effects of secretagogues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):122–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91549-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan M. G., Florio T., Stork P. J. G protein activation of a hormone-stimulated phosphatase in human tumor cells. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1215–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnappa B. C., Dormer R. L., Williams J. A. Characterization of an ATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake system in mouse pancreatic microsomes. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):G122–G129. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.2.G122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin S. Somatostatin. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 15;309(24):1495–1501. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312153092406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer L., Raulf F., Bruns C., Buettner R., Hofstaedter F., Schüle R. Cloning and characterization of a fourth human somatostatin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto C., Goldfine I. D., Williams J. A. The somatostatin receptor on isolated pancreatic acinar cell plasma membranes. Identification of subunit structure and direct regulation by cholecystokinin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9623–9627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnefel S., Pröfrock A., Hinsch K. D., Schulz I. Cholecystokinin activates Gi1-, Gi2-, Gi3- and several Gs-proteins in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2690483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer P., Madamba S., Champagnat J., Siggins G. R. Somatostatin inhibition of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: mediation by arachidonic acid and its metabolites. J Neurosci. 1993 May;13(5):2033–2049. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-05-02033.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer P., Madamba S., Siggins G. R. Arachidonic acid metabolites as mediators of somatostatin-induced increase of neuronal M-current. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):464–467. doi: 10.1038/346464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Asada I., Owlia A., Collins T. J., Thompson J. C. Somatostatin inhibits VIP-stimulated amylase release from perifused guinea pig pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 1):G217–G223. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.2.G217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Bruzzone R., Biden T. J., Farese R. V. Secretin induces rapid increases in inositol trisphosphate, cytosolic Ca2+ and diacylglycerol as well as cyclic AMP in rat pancreatic acini. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):257–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2390257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Prentki M., Wollheim C. B. Somatostatin inhibition of Ca2(+)-induced insulin secretion in permeabilized HIT-T15 cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2700273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viguerie N., Tahiri-Jouti N., Esteve J. P., Clerc P., Logsdon C., Svoboda M., Susini C., Vaysse N., Ribet A. Functional somatostatin receptors on a rat pancreatic acinar cell line. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 1):G113–G120. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.1.G113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Gimble J. M., Goodman D. B., Rasmussen H. Studies of the Ca2+ transport mechanism of human erythrocyte inside-out plasma membrane vesicles. I. Regulation of the Ca2+ pump by calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Lee M. Pancreatic acinar cells: use of Ca++ ionophore to separate enzyme release from the earlier steps in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):542–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A. Regulation of pancreatic acinar cell function by intracellular calcium. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):G269–G279. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.238.4.G269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima Y., Akita Y., Saito T. Pertussis toxin blocks the inhibitory effects of somatostatin on cAMP-dependent vasoactive intestinal peptide and cAMP-independent thyrotropin releasing hormone-stimulated prolactin secretion of GH3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2684–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Post S. R., Wang K., Tager H. S., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and functional characterization of a family of human and mouse somatostatin receptors expressed in brain, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Reisine T., Law S. F., Ihara Y., Kubota A., Kagimoto S., Seino M., Seino Y., Bell G. I., Seino S. Somatostatin receptors, an expanding gene family: cloning and functional characterization of human SSTR3, a protein coupled to adenylyl cyclase. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2136–2142. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1337145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Shibuya N., Ogata E. Hyperpolarization of the membrane potential caused by somatostatin in dissociated human pituitary adenoma cells that secrete growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6198–6202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]