Abstract
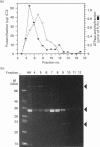
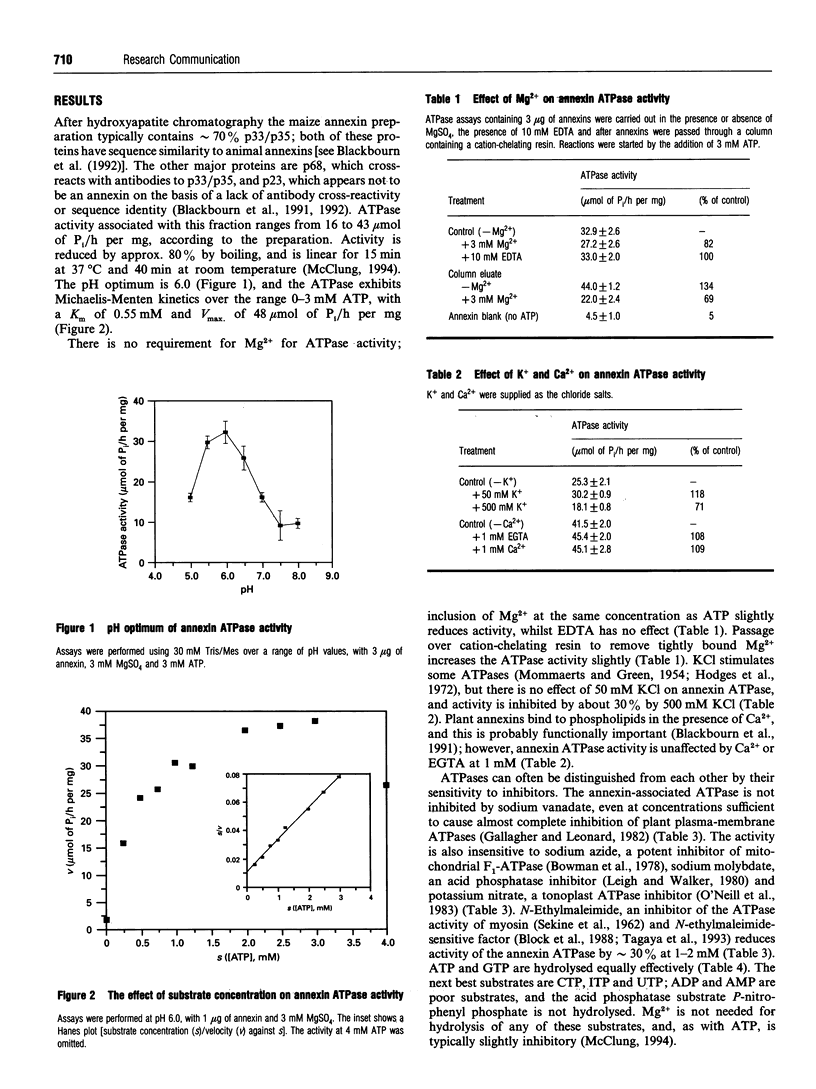
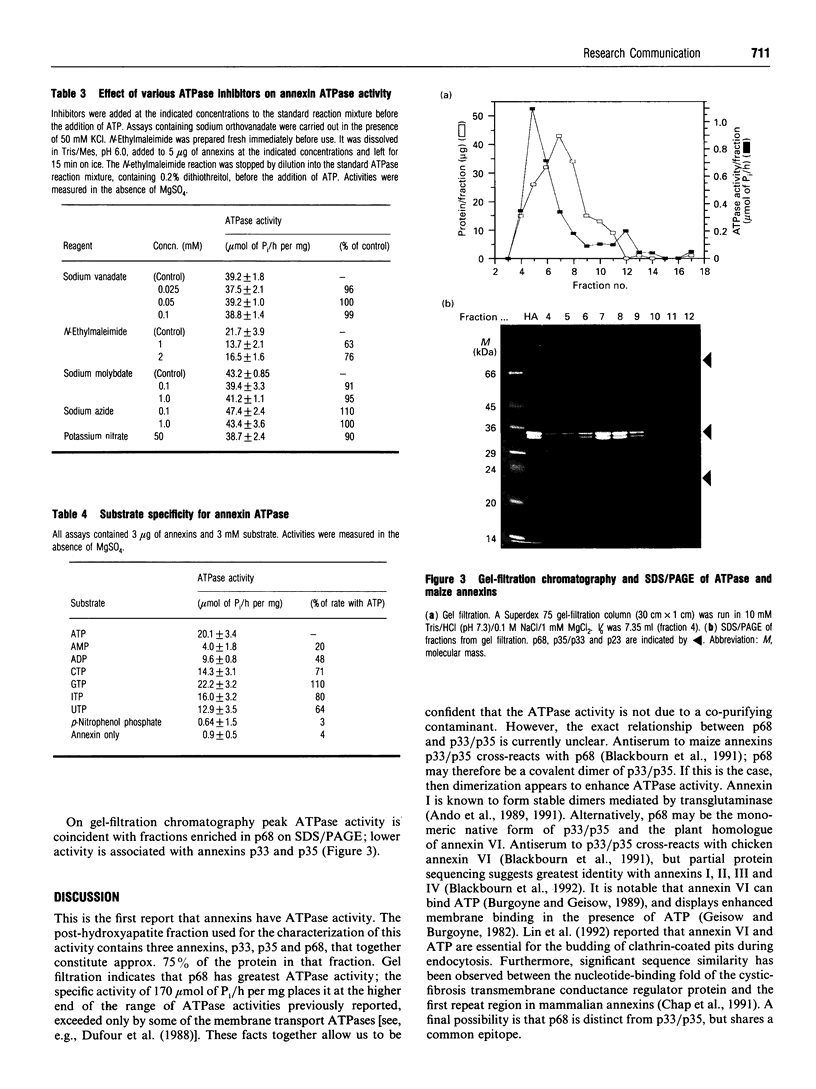
An ATPase activity is associated with maize (Zea mays) annexins. It has a pH optimum of 6.0, shows Michaelis-Menten kinetics and is not stimulated by Ca2+, Mg2+, EDTA or KCl; it is not inhibited by vanadate, molybdate, nitrate or azide, but N-ethylmaleimide inhibits by approximately 30% at 1-2 mM. These properties indicate that the activity is unlike other ATPases, although it has many features in common with the myosin ATPase. Gel filtration shows that the ATPase activity is mainly associated with a 68 kDa protein that is extracted with the p33/p35 annexins and cross-reacts with antibodies to these proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. M., Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):313–315. doi: 10.1038/340313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Imamura S., Owada M. K., Kakunaga T., Kannagi R. Cross-linking of lipocortin I and enhancement of its Ca2+ sensitivity by tissue transglutaminase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):944–951. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Imamura S., Owada M. K., Kannagi R. Calcium-induced intracellular cross-linking of lipocortin I by tissue transglutaminase in A431 cells. Augmentation by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1101–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrawis A., Solomon M., Delmer D. P. Cotton fiber annexins: a potential role in the regulation of callose synthase. Plant J. 1993 Jun;3(6):763–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1993.00763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWEN W. J., KERWIN T. D. A study of the effects of ethylenediamine-tetra-acetic acid on myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackbourn H. D., Barker P. J., Huskisson N. S., Battey N. H. Properties and partial protein sequence of plant annexins. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jul;99(3):864–871. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. R., Glick B. S., Wilcox C. A., Wieland F. T., Rothman J. E. Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7852–7856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Mainzer S. E., Allen K. E., Slayman C. W. Effects of inhibitors on the plasma membrane and mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatases of Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 11;512(1):13–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Geisow M. J. The annexin family of calcium-binding proteins. Review article. Cell Calcium. 1989 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. B., Dauwalder M., Roux S. J. Purification and immunolocalization of an annexin-like protein in pea seedlings. Planta. 1992;187:1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. The annexins and exocytosis. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):924–931. doi: 10.1126/science.1439804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour J. P., Amory A., Goffeau A. Plasma membrane ATPase from the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:513–528. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIESS E. T. The effect of a chelating agent on myosin ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jul;51(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Effect of vanadate, molybdate, and azide on membrane-associated ATPase and soluble phosphatase activities of corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1335–1340. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Calcium-dependent binding of cytosolic proteins by chromaffin granules from adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1735–1741. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Emans N. Annexins in membrane traffic. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;3(7):224–227. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90116-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACH W. Die Nukleosidtriphosphatase-Aktivität von L-Myosin und Aktomyosin in Abhängigkeit von den ionalen Bedingungen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Aug;25(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T., Bracker C. E., Keenan T. W. Purification of an ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots: association with plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Südhof T. C., Anderson R. G. Annexin VI is required for budding of clathrin-coated pits. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90102-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOMMAERTS W. F., GREEN I. Adenosinetriphosphatase systems of muscle. III. A survey of the adenosinetriphosphatase activity of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):833–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUEHLRAD A., FABIAN F., BIRO N. A. ON THE ACTIVATION OF MYOSIN ATPASE BY EDTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 8;89:186–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neill S. D., Bennett A. B., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of a NO(3)-Sensitive H-ATPase from Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):837–846. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Doberstein S. K., Zot H. G. Myosin-I. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:653–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal P., Pollard H. B. Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 5;1197(1):63–93. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEKINE T., BARNETT L. M., KIELLEY W. W. The active site of myosin adenosine triphosphatase. I. Localization of one of the sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2769–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. C. The effects of monovalent and divalent cations on the ATPase activity of myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 21;189(2):162–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood M., Keen J. N., Bowles D. J. Purification and partial sequence analysis of plant annexins. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):157–161. doi: 10.1042/bj2700157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya M., Wilson D. W., Brunner M., Arango N., Rothman J. E. Domain structure of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein involved in vesicular transport. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2662–2666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]