Abstract
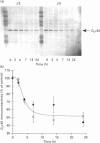
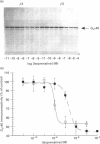
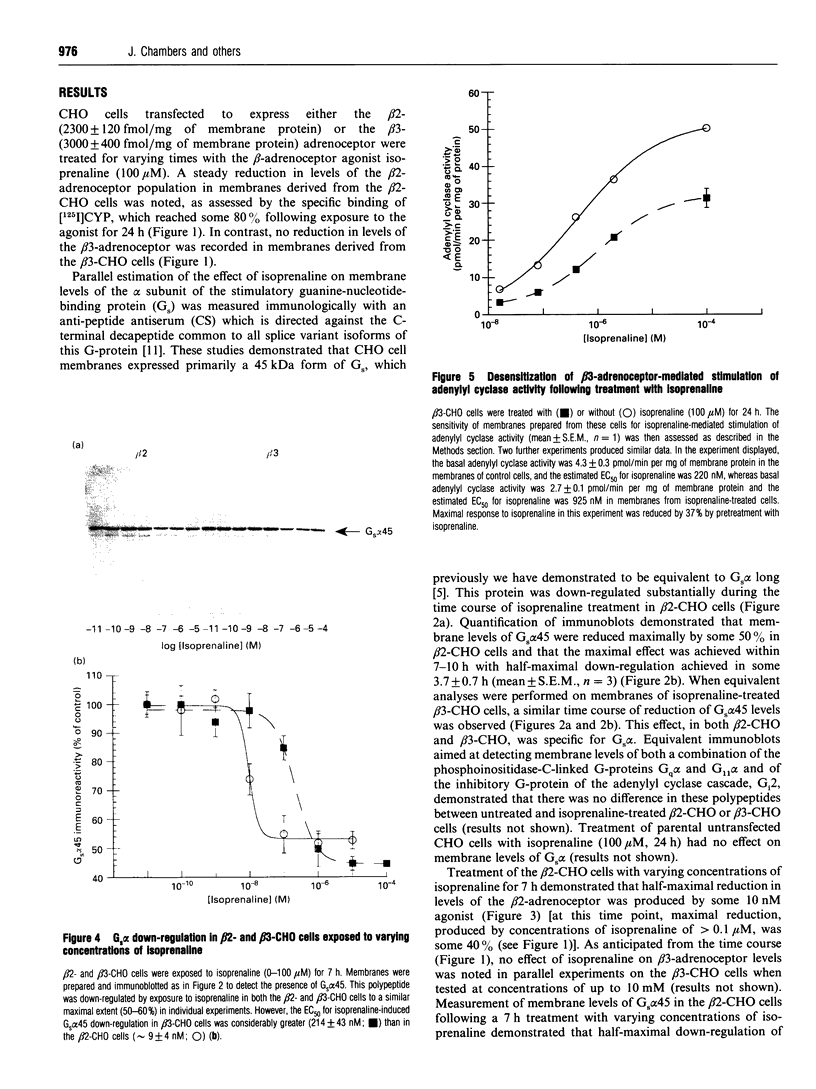
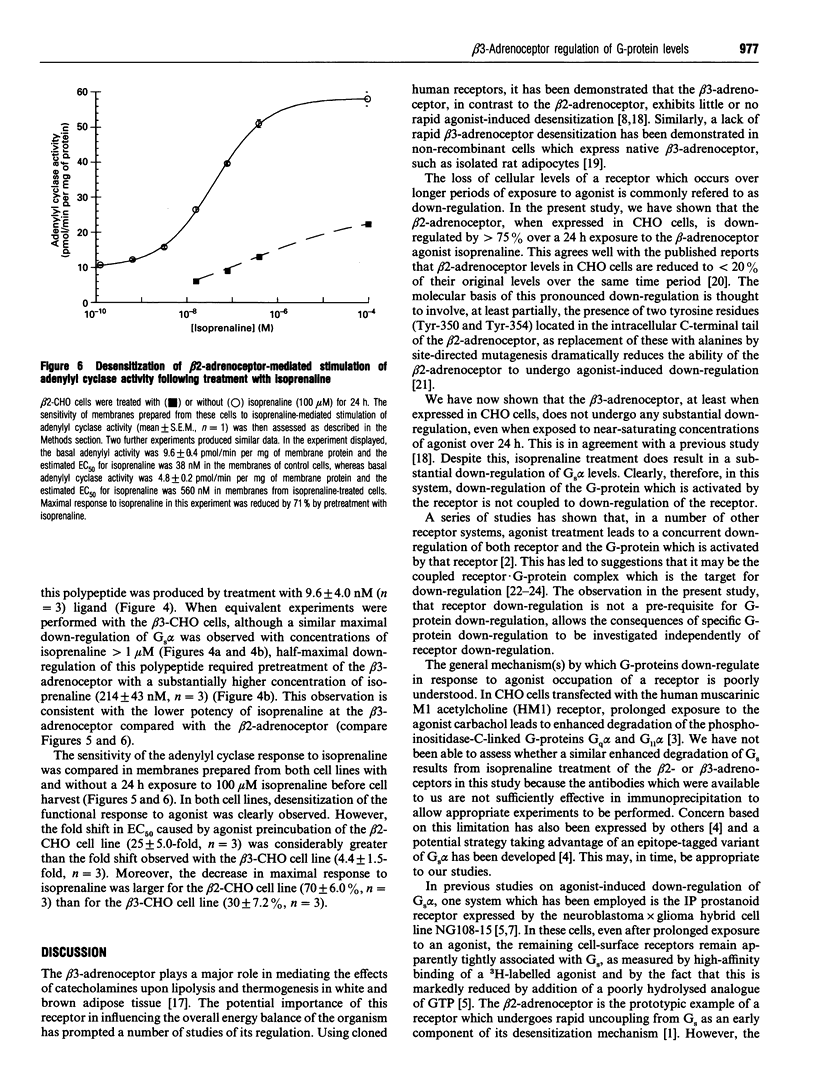
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells transfected to express human beta 2- or beta 3-adrenoceptors (beta 2-CHO and beta 3-CHO cells) were exposed to the beta-adrenoceptor agonist isoprenaline at various concentrations and for differing times. Sustained exposure of the beta 2-CHO but not beta 3-CHO cells to isoprenaline resulted in a time- and concentration-dependent down-regulation of the receptor as measured by a reduction in specific binding of [125I]cyanopindolol. Such maintained exposure of cells expressing either receptor to the agonist produced a marked down-regulation of immunologically detectable levels of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gs. This effect was specific for Gs because levels of both G12 alpha and Gq alpha/G11 alpha were unaltered by isoprenaline treatment of both beta 2-CHO and beta 3-CHO cells. The effect of isoprenaline on Gs alpha down-regulation was some 30-fold more potent in the beta 2-CHO than in the beta 3-CHO cells. Time courses of isoprenaline-induced down-regulation of Gs alpha were not different, however, in the two cell lines. Isoprenaline treatment of the beta 3-CHO cells produced a desensitization of agonist-mediated regulation of adenylyl cyclase, manifested by a 4-fold reduction in the potency and a 30% reduction in maximal effect of the agonist, whereas desensitization of the beta 2-CHO cells was considerably greater (25-fold reduction in potency and 70% reduction in maximal effect). These results demonstrate that agonist-induced down-regulation of the G-protein which interacts with a receptor can be produced by both beta 2- and beta 3-adrenoceptors. Despite apparent concurrence of down-regulation of receptors and G-proteins in other systems [e.g. Adie, Mullaney, McKenzie and Milligan (1992) Biochem. J. 285, 529-536], agonist-induced receptor down-regulation does not appear to be a prerequisite for down-regulation of the G-protein. Furthermore, the results suggest that agonist-induced down-regulation of a G-protein may be sufficient, in the absence of receptor regulation, to induce some agonist desensitization of effector function.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adie E. J., Milligan G. Agonist regulation of cellular levels of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein, Gs, in wild type and transfected neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):432–435. doi: 10.1042/bst0210432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adie E. J., Mullaney I., McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Concurrent down-regulation of IP prostanoid receptors and the alpha-subunit of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gs) during prolonged exposure of neuroblastoma x glioma cells to prostanoid agonists. Quantification and functional implications. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):529–536. doi: 10.1042/bj2850529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Kaumann A. J. Beta 3 and atypical beta-adrenoceptors. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):663–729. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. T., Hnatowich M., O'Dowd B. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P. Mutations of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor that impair coupling to Gs interfere with receptor down-regulation but not sequestration. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):192–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eason M. G., Liggett S. B. Subtype-selective desensitization of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Different mechanisms control short and long term agonist-promoted desensitization of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25473–25479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Lasnier F., Blin N., Baude B., Nahmias C., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Atypical beta-adrenergic receptor in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Pharmacological and molecular relationship with the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20329–20336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales J. M., O'Donnell J. K., Stadel J. M., Sweet R. W., Molinoff P. B. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by pindolol in Gs alpha-transfected S49 cyc- murine lymphoma cells. J Neurochem. 1992 Mar;58(3):1093–1103. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G. Effects of agonist exposure on the coupling of beta 1 and beta 3 adrenergic receptors to adenylyl cyclase in isolated adipocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):638–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Rao D. D. Rodent and human beta 3-adrenergic receptor genes contain an intron within the protein-coding block. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):964–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L., Milligan G. Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Activation of the alpha subunit of Gs in intact cells alters its abundance, rate of degradation, and membrane avidity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1297–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B., Freedman N. J., Schwinn D. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Structural basis for receptor subtype-specific regulation revealed by a chimeric beta 3/beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J. Molecular mechanisms of membrane receptor desensitization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90139-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Delta-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase is transduced specifically by the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gi2. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2670391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Prostaglandin E1-mediated, cyclic AMP-independent, down-regulation of Gs alpha in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17084–17093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Agonist regulation of cellular G protein levels and distribution: mechanisms and functional implications. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Nov;14(11):413–418. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90064-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Regional distribution and quantitative measurement of the phosphoinositidase C-linked guanine nucleotide binding proteins G11 alpha and Gq alpha in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1993 Sep;61(3):845–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Unson C. G. Persistent activation of the alpha subunit of Gs promotes its removal from the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):837–841. doi: 10.1042/bj2600837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Buckley N. J., Milligan G. Enhanced degradation of the phosphoinositidase C-linked guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gq alpha/G11 alpha following activation of the human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in CHO cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):495–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2930495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Mullaney I., Godfrey P. P., Arkinstall S. J., Wakelam M. J., Milligan G. Widespread distribution of Gq alpha/G11 alpha detected immunologically by an antipeptide antiserum directed against the predicted C-terminal decapeptide. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney I., Dodd M. W., Buckley N., Milligan G. Agonist activation of transfected human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in CHO cells results in down-regulation of both the receptor and the alpha subunit of the G-protein Gq. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2890125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nantel F., Bonin H., Emorine L. J., Zilberfarb V., Strosberg A. D., Bouvier M., Marullo S. The human beta 3-adrenergic receptor is resistant to short term agonist-promoted desensitization. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;43(4):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Nguyen C. T., Nantel F., Bonin H., Valiquette M., Frielle T., Bouvier M. Distinct regulation of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):542–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate K. M., Briend-Sutren M. M., Emorine L. J., Delavier-Klutchko C., Marullo S., Strosberg A. D. Expression of three human beta-adrenergic-receptor subtypes in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. F., Holt B. D., Schwinn D. A., Liggett S. B. Long-term agonist exposure induces upregulation of beta 3-adrenergic receptor expression via multiple cAMP response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valiquette M., Bonin H., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Involvement of tyrosine residues located in the carboxyl tail of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor in agonist-induced down-regulation of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5089–5093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]