Abstract
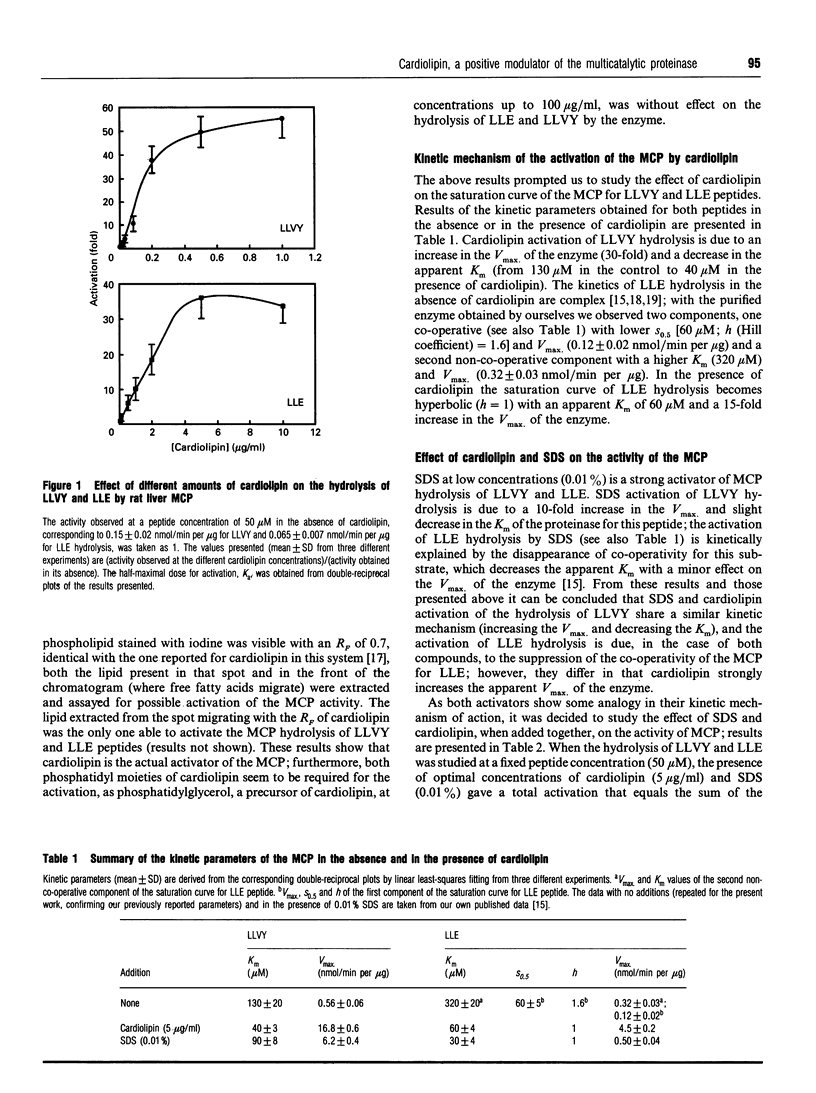
The effect of phospholipids on the trypsin-like, chymotrypsin-like and peptidylglutamyl-peptide-hydrolysing activities of the so-called latent form of the rat liver multicatalytic proteinase was studied, assaying them with the following substrates: N-Cbz-ARR-4MNA (N-Cbz, N-benzyloxycarbonyl; 4MNA, 4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamide), N-Suc-LLVY-MCA (N-Suc, N-succinyl; MCA, methylcoumarin) and N-Cbz-LLE-beta-NA (beta-NA, beta-naphthylamide) respectively (amino acids are shown as their one-letter symbol). For the most part neither lysophospholipids nor phospholipids at 20 micrograms/ml have any effect on the activity of the enzyme (assayed at 50 microM peptide), except for phosphatidylserine, which activates 2-fold the hydrolysis of N-Suc-LLVY-MCA, and phosphatidylinositol, which inhibits by 20% the hydrolysis of N-Cbz-LLE-beta-NA. By contrast, cardiolipin (diphosphatidylglycerol) is a strong activator of the hydrolysis of N-Suc-LLVY-MCA (60-fold) and N-Cbz-LLE-beta-NA (30-fold), with half-maximal activation at concentrations of 0.15 micrograms/ml and 1.5 micrograms/ml respectively. The activation of N-Suc-LLVY-MCA hydrolysis is due to an increase of the affinity of the enzyme for the peptide and to an increase in the Vmax. (30-fold). The activation of N-Cbz-LLE-beta-NA hydrolysis is explained by suppressing the co-operativity for this substrate, producing hyperbolic kinetics with a Km of 60 microM and a 15-fold increase in the Vmax. of the enzyme. This activation by cardiolipin was completely suppressed by micromolar concentrations of fluophenazine, a drug known to inhibit other phospholipid-regulated process. Cardiolipin activation and the known activation by SDS are additive, either at suboptimal or optimal concentrations of both activators. Cardiolipin also activates the in vitro degradation of some proteins from metabolically labelled total cellular extracts by the latent multicatalytic proteinase. These results clearly show that cardiolipin is a natural positive modulator of the peptidase and proteolytic activities of the multicatalytic proteinase, probably acting through a binding site different from that of SDS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arribas J., Castaño J. G. Kinetic studies of the differential effect of detergents on the peptidase activities of the multicatalytic proteinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13969–13973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arribas J., Luz Rodríguez M., Alvarez-Do Forno R., Castaño J. G. Autoantibodies against the multicatalytic proteinase in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):423–427. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Tanaka K., Goldberg A. L., Welch W. J. Identity of the 19S 'prosome' particle with the large multifunctional protease complex of mammalian cells (the proteasome). Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):192–194. doi: 10.1038/331192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Niedel B., Pfeifer G., Hegerl R., Baumeister W. The multicatalytic proteinase (prosome) is ubiquitous from eukaryotes to archaebacteria. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Rutschmann M., Kuehn L., Reinauer H. Activation of the multicatalytic proteinase from rat skeletal muscle by fatty acids or sodium dodecyl sulphate. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):171–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2280171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G. Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):1–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djaballah H., Rivett A. J. Peptidylglutamyl-peptide hydrolase activity of the multicatalytic proteinase complex: evidence for a new high-affinity site, analysis of cooperative kinetics, and the effect of manganese ions. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):4133–4141. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Sano M., Kamakura K., Sugita H. Isolation of two forms of the high-molecular-mass serine protease, ingensin, from porcine skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80854-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Yamamoto T., Nojima M., Sugita H. Ingensin, a fatty acid-activated serine proteinase from rat liver cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 16;882(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanayama H., Tanaka K., Aki M., Kagawa S., Miyaji H., Satoh M., Okada F., Sato S., Shimbara N., Ichihara A. Changes in expressions of proteasome and ubiquitin genes in human renal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6677–6685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Hügle B., Grund C., Franke W. W. The 22 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. I. Biochemical and electron microscopic characterization. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):143–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C. P., Slaughter C. A., DeMartino G. N. Identification, purification, and characterization of a protein activator (PA28) of the 20 S proteasome (macropain). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10515–10523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire M. J., McCullough M. L., Croall D. E., DeMartino G. N. The high molecular weight multicatalytic proteinase, macropain, exists in a latent form in human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 6;995(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Cardozo C., Hidalgo M. C., Michaud C. Regulation of the peptidylglutamyl-peptide hydrolyzing activity of the pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 18;30(24):5999–6005. doi: 10.1021/bi00238a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C. Pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Specificity of components and aspects of proteolytic activity. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9270–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M. The multicatalytic proteinase complex, a major extralysosomal proteolytic system. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10289–10297. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Wilk S. A multicatalytic protease complex from pituitary that forms enkephalin and enkephalin containing peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):814–822. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91823-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J., Knecht E. Protein turnover: proteasome location. Curr Biol. 1993 Feb;3(2):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90173-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J., Palmer A., Knecht E. Electron microscopic localization of the multicatalytic proteinase complex in rat liver and in cultured cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Aug;40(8):1165–1172. doi: 10.1177/40.8.1619280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. The multicatalytic proteinase of mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jan;268(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. The multicatalytic proteinase. Multiple proteolytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12215–12219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh Y., Yokosawa H., Ishii S. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-induced conformational and enzymatic changes of multicatalytic proteinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):334–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92000-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Kornberg A. Cardiolipin activation of dnaA protein, the initiation protein of replication in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7131–7135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ii K., Ichihara A., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. A high molecular weight protease in the cytosol of rat liver. I. Purification, enzymological properties, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15197–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A. Role of substrate in reversible activation of proteasomes (multi-protease complexes) by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biochem. 1989 Sep;106(3):495–500. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Kumatori A., Ichihara A., Ikai A., Nishigai M., Kameyama K., Takagi T. Proteasomes (multi-protease complexes) as 20 S ring-shaped particles in a variety of eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16209–16217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk S., Orlowski M. Evidence that pituitary cation-sensitive neutral endopeptidase is a multicatalytic protease complex. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):842–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari R., Baker C. R., Amirgholami A., Canizaro P. C., Behal F. J. A multicatalytic high-molecular-weight neutral endopeptidase from human kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Oct;258(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]