Abstract
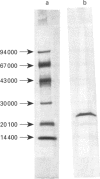
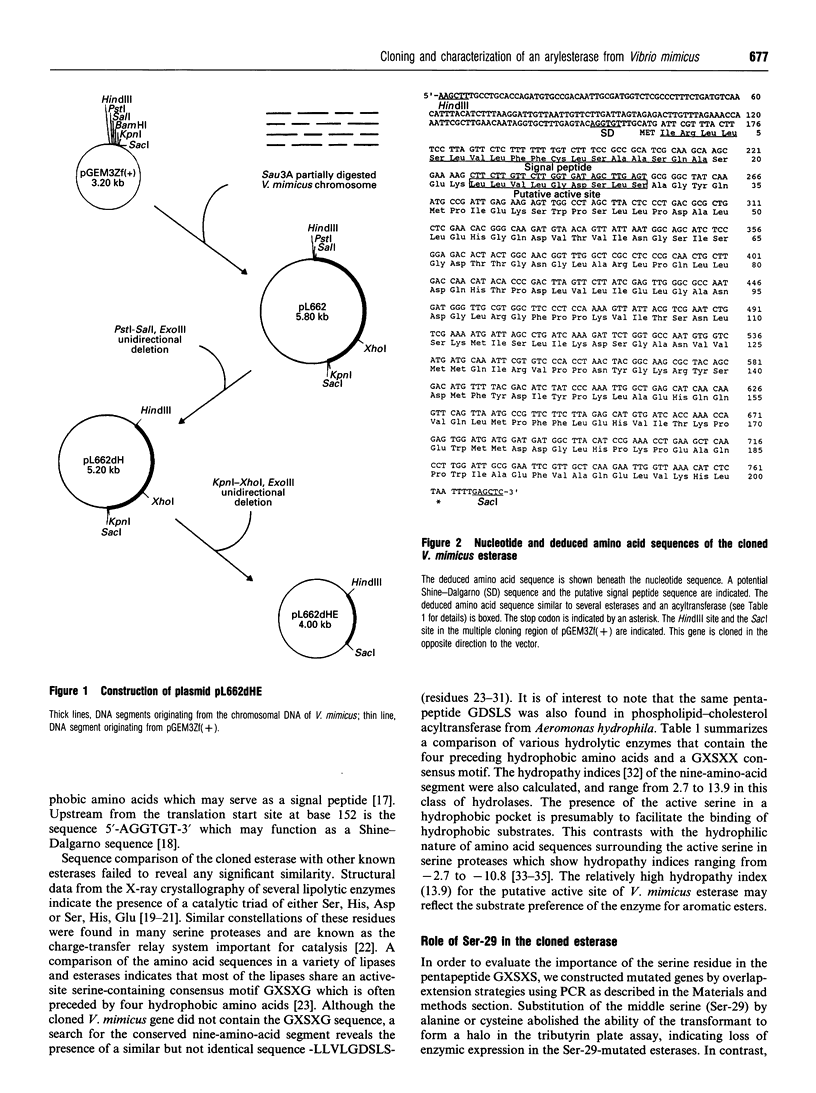
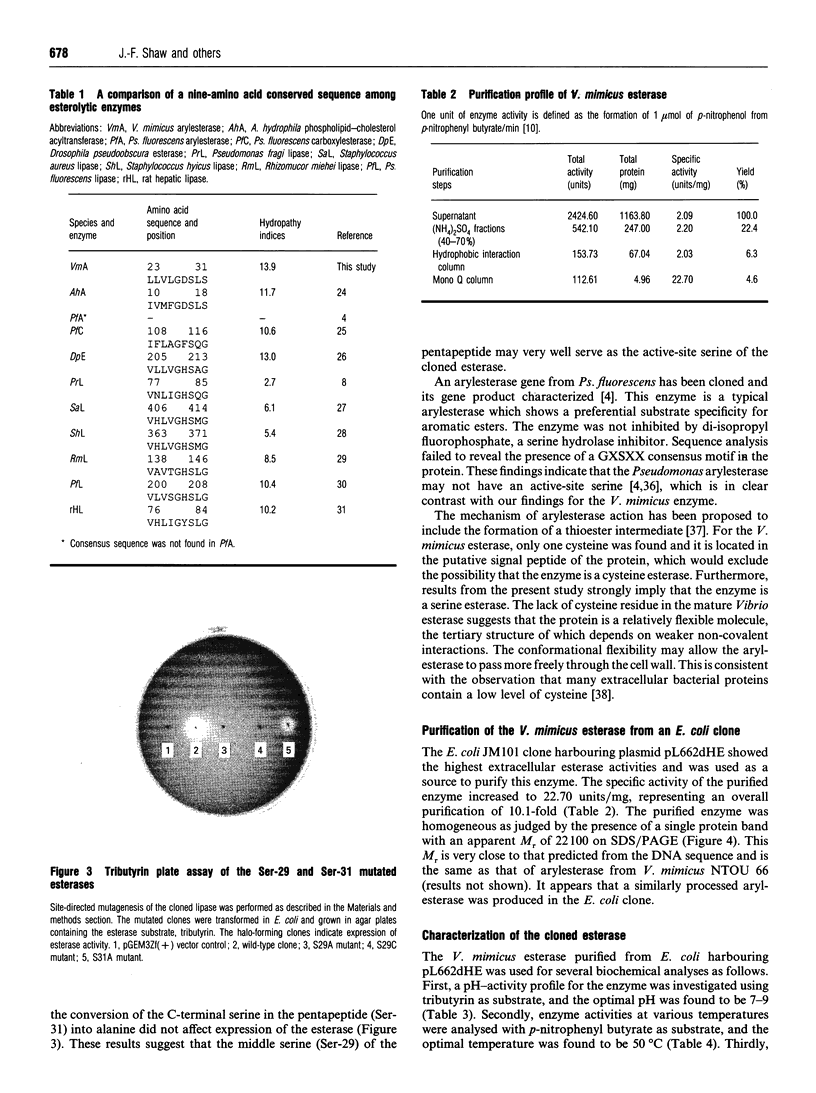
A gene coding for an arylesterase of Vibrio mimicus was cloned. Sequence determination reveals that the esterase gene has an open reading frame of 600 nucleotides which encodes a protein of M(r) 22,300. The deduced amino acid sequence contain a pentapeptide GDSLS (residues 27-31), which was also found in the phospholipid-cholesterol acyltransferase from Aeromonas hydrophila. Substitution of Ser-29 by alanine or cysteine in the cloned gene abolished the esterase activity in the tributyrin plate assay. On the other hand, the activity was not lost when Ser-31 was changed to alanine. The cloned gene was expressed in Escherichia coli, and the protein purified by a four-step procedure. The purified protein migrated on SDS/PAGE as a single band with an apparent M(r) of 22,100. This enzyme favoured the hydrolysis of several arylesters and was classified as an arylesterase (EC 3.1.1.2). N-Terminal analysis showed that Ser-20 was the first amino acid of the mature secreted protein, suggesting that the N-terminal 19 hydrophobic amino acids served as a signal peptide.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUGUSTINSSON K. B. ARYLESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Oct;12:744–747. doi: 10.1177/12.10.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boel E., Huge-Jensen B., Christensen M., Thim L., Fiil N. P. Rhizomucor miehei triglyceride lipase is synthesized as a precursor. Lipids. 1988 Jul;23(7):701–706. doi: 10.1007/BF02535672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. P., Richmond R. C. An evolutionary model for the duplication and divergence of esterase genes in Drosophila. J Mol Evol. 1992 Jun;34(6):506–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00160464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L., Brzozowski A. M., Derewenda Z. S., Dodson E., Dodson G., Tolley S., Turkenburg J. P., Christiansen L., Huge-Jensen B., Norskov L. A serine protease triad forms the catalytic centre of a triacylglycerol lipase. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):767–770. doi: 10.1038/343767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowski A. M., Derewenda U., Derewenda Z. S., Dodson G. G., Lawson D. M., Turkenburg J. P., Bjorkling F., Huge-Jensen B., Patkar S. A., Thim L. A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):491–494. doi: 10.1038/351491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. D., Jeohn G. H., Rhee J. S., Yoo O. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of an esterase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens and expression of the gene in Escherichia coli. Agric Biol Chem. 1990 Aug;54(8):2039–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung G. H., Lee Y. P., Jeohn G. H., Yoo O. J., Rhee J. S. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of thermostable lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens SIK W1. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 Sep;55(9):2359–2365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K., Dougan G., Arbuthnott J. P. Cloning, and expression in Escherichia coli K-12, of the chromosomal hemolysin (phospholipase C) determinant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.909-915.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton S. J., Jones C. G. Mechanism of dye response and interference in the Bradford protein assay. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller G., Thiry M., Gerday C. Nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene lip2 from the antarctic psychrotroph Moraxella TA144 and site-specific mutagenesis of the conserved serine and histidine residues. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):381–388. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Popp F., Korn E., Schleifer K. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene from Staphylococcus hyicus cloned in Staphylococcus carnosus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5895–5906. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K. H., Jang W. H., Choi K. D., Yoo O. J. Characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens carboxylesterase: cloning and expression of the esterase gene in Escherichia coli. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 Nov;55(11):2839–2845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäger S., Demleitner G., Götz F. Lipase of Staphylococcus hyicus: analysis of the catalytic triad by site-directed mutagenesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai H., Yomoda S., Inoue Y. ELISA using monoclonal antibody to human serum arylesterase. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 Oct 31;202(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(91)90052-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. K., Hwang K. Y., Choi K. D., Kang J. H., Yoo O. J., Suh S. W. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of arylesterase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Proteins. 1993 Feb;15(2):213–215. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Selsing E., Wells R. D. A rapid microscale technique for isolation of recombinant plasmid DNA suitable for restriction enzyme analysis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):88–91. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaromy M. C., Schotz M. C. Cloning of rat hepatic lipase cDNA: evidence for a lipase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugimiya W., Otani Y., Hashimoto Y., Takagi Y. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene from Pseudomonas fragi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococcal lipase is caused by insertion of the bacteriophage L54a genome into the lipase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):385–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.385-391.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackness M. I. 'A'-esterases. Enzymes looking for a role? Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 1;38(3):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90376-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R., RICHMOND M. H. Low cyst(e)ine content of bacterial extracellular proteins: its possible physiological significance. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:446–449. doi: 10.1038/194446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky S. D., LaForge K. S., Luc V., Scheele G. Identification of cDNA clones encoding secretory isoenzyme forms: sequence determination of canine pancreatic prechymotrypsinogen 2 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7486–7490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky S. D., LaForge K. S., Scheele G. Differential regulation of trypsinogen mRNA translation: full-length mRNA sequences encoding two oppositely charged trypsinogen isoenzymes in the dog pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2669–2676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabilloud T., Carpentier G., Tarroux P. Improvement and simplification of low-background silver staining of proteins by using sodium dithionite. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jun;9(6):288–291. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrag J. D., Li Y. G., Wu S., Cygler M. Ser-His-Glu triad forms the catalytic site of the lipase from Geotrichum candidum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):761–764. doi: 10.1038/351761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Hartley B. S. Amino-acid sequence of porcine pancreatic elastase and its homologies with other serine proteinases. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):802–806. doi: 10.1038/225802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J., Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Molecular cloning of a phospholipid-cholesterol acyltransferase from Aeromonas hydrophila. Sequence homologies with lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase and other lipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 25;959(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]