Abstract
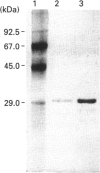
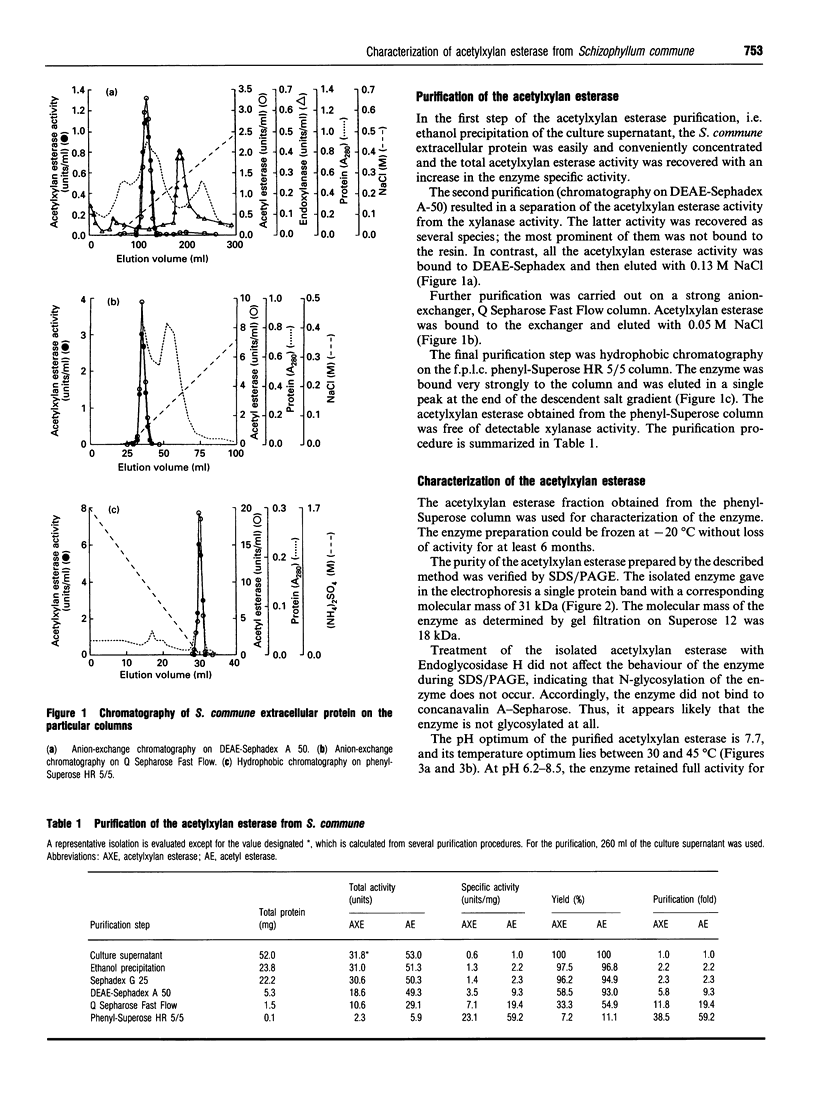
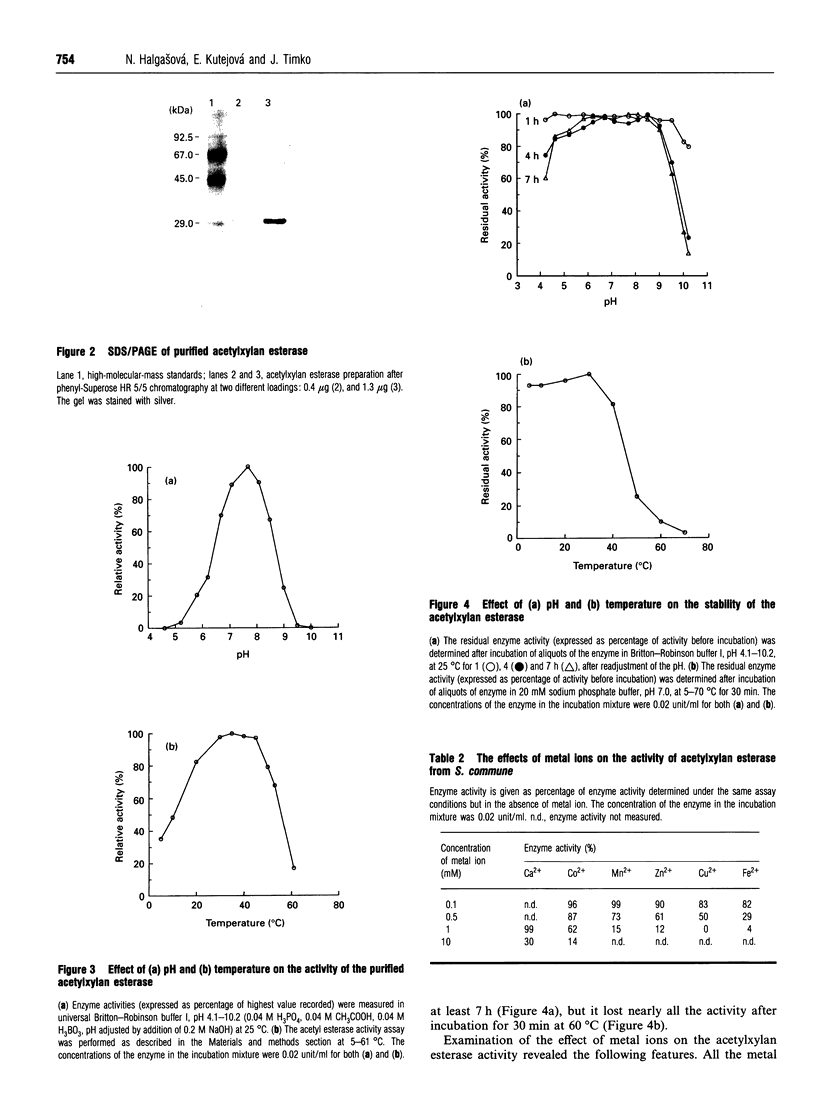
Acetylxylan esterase from Schizophyllum commune was purified using ion-exchange and hydrophobic chromatography. The enzyme has a molecular mass of 31 kDa, as determined by SDS/PAGE, or 18 kDa, according to gel filtration. Glycosylation of the enzyme was not detected. Acetylxylan esterase is relatively stable under laboratory conditions; it retains full activity at pH 6.2-8.5 upon incubation at 25 degrees C for 7 h, but loses nearly the whole activity upon incubation at 60 degrees C for 30 min. The pH optimum of the enzyme activity is 7.7 and its temperature optimum lies between 30 and 45 degrees C. Ca2+ and Co2+ inhibit markedly the activity of acetylxylan esterase at a concentration of 10 mM, as do Mn2+, Zn2+, Fe2+ and Cu2+ at a concentration of 1 mM.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann S. L., McCarthy A. J. Purification and Cooperative Activity of Enzymes Constituting the Xylan-Degrading System of Thermomonospora fusca. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2121–2130. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2121-2130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulds C. B., Williamson G. The purification and characterization of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic (ferulic) acid esterase from Streptomyces olivochromogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2339–2345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert M., Breuil C., Yaguchi M., Saddler J. N. Purification and characterization of a xylanase from the thermophilic ascomycete Thelavia terrestris 255B. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1992 Spring;34-35:247–259. doi: 10.1007/BF02920549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., To R. J., Latta R. K., Biely P., Schneider H. Some Properties of Extracellular Acetylxylan Esterase Produced by the Yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2831–2834. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2831-2834.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthi E., Jasmat N. B., Bergquist P. L. Overproduction of an acetylxylan esterase from the extreme thermophile "Caldocellum saccharolyticum" in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990 Nov;34(2):214–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00166783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid K. P., Forsberg C. W., MacKenzie C. R. Purification and properties of an acetylxylan esterase from Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3805–3810. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3805-3810.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Maley F. Optimizing hydrolysis of N-linked high-mannose oligosaccharides by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]