Abstract
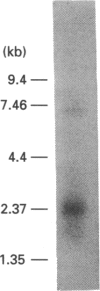
Prostaglandins inhibit platelet activation by stimulating intracellular cyclic AMP formation. We have postulated that intracellular cyclic AMP levels in platelets are buffered by a distinct prostaglandin receptor that mediates inhibition of cyclic AMP formation. In order to provide evidence for the model, we have cloned the cDNA coding for a prostaglandin receptor EP3 subtype, which is coupled to inhibition of adenylate cyclase, from the megakaryocytic cell line human erythroleukaemia (HEL) cells. A PCR-generated hybridization probe, produced using primers based on the sequence of the mouse prostaglandin EP3 receptor published by Sugimoto, Namba, Honda, Hayashi, Negishi, Ichikawa and Narumiya [(1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 6463-6466], was used to screen a lambda gt11 HEL cell cDNA library. The composite full-length cDNA clone HEP3, generated from the two partial clones pHEP3-7 and pHEP3-5, is 1.6 kb long with an open reading frame coding for 390 amino acids. This clone is 83% identical to the alpha subtype of the mouse EP3 receptor. The full-length construct was transfected into COS-1 cells. The cloned receptor exhibited the properties of a prostaglandin EP3 subtype, inhibiting forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP formation in response to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and binding PGE2 with high specificity and a Kd of 3.2 nM. Radiolabelled PGE2 could be displaced by prostaglandins in the order PGE2 = PGE1 > iloprost = PGD2. Northern blot analysis revealed that the receptor is also present in human kidney.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby B., Almonor G. O., Wernick E., Selak M. A. Prostaglandin-concentration-dependent desensitization of adenylate cyclase in human erythroleukaemia (HEL) cells is abolished by pertussis toxin and enhanced by induction by dimethyl sulphoxide. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):801–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2800801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B. Model of prostaglandin-regulated cyclic AMP metabolism in intact platelets: examination of time-dependent effects on adenylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase activities. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;36(6):866–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby B. Novel mechanism of heterologous desensitization of adenylate cyclase: prostaglandins bind with different affinities to both stimulatory and inhibitory receptors on platelets. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):46–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Sugimoto Y., Negishi M., Irie A., Ushikubi F., Kakizuka A., Ito S., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Alternative splicing of C-terminal tail of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP3 determines G-protein specificity. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):166–170. doi: 10.1038/365166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y. Adenylate cyclase assay. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:35–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Namba T., Honda A., Hayashi Y., Negishi M., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for mouse prostaglandin E receptor EP3 subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6463–6466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Negishi M., Hayashi Y., Namba T., Honda A., Watabe A., Hirata M., Narumiya S., Ichikawa A. Two isoforms of the EP3 receptor with different carboxyl-terminal domains. Identical ligand binding properties and different coupling properties with Gi proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2712–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabilio A., Rosa J. P., Testa U., Kieffer N., Nurden A. T., Del Canizo M. C., Breton-Gorius J., Vainchenker W. Expression of platelet membrane glycoproteins and alpha-granule proteins by a human erythroleukemia cell line (HEL). EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):453–459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]