Abstract
Blocks of potential Z-DNA-forming (dA-dC)n.(dG-dT)n sequences are ubiquitous in eukaryotic genomes. We examined whether naturally occurring polyamines, putrescine, spermidine and spermine, could provoke the Z-DNA conformation in plasmids pDHf2 and pDHf14 with 23 and 60 bp inserts respectively of (dA-dC)n.(dG-dT)n sequences using an e.l.i.s.a. Spermidine and spermine could provoke Z-DNA conformation in these plasmids, but putrescine was ineffective. For pDHf2 and pDHf14, the concentration of spermidine at the midpoint of B-DNA to Z-DNA transition was 25 microM, whereas that of spermine was 16 microM. Polyamine structural specificity was evident in the ability of spermidine homologues to induce Z-DNA. Inorganic cations, Co(NH3)6(3+) and Ru(NH3)6(3+), were ineffective. Our experiments also showed increased binding of anti-DNA autoantibodies from lupus patients as well as autoimmune MRL-lpr/lpr mice to pDHf2 and pDHf14 in the presence of polyamines. These data demonstrate that small blocks of (dA-dC)n.(dG-dT)n sequences could assume the Z-DNA conformation in the presence of natural polyamines. Increased concentrations of polyamines in the sera of lupus patients might facilitate immune complex-formation involving circulating DNA and anti-Z-DNA antibodies.
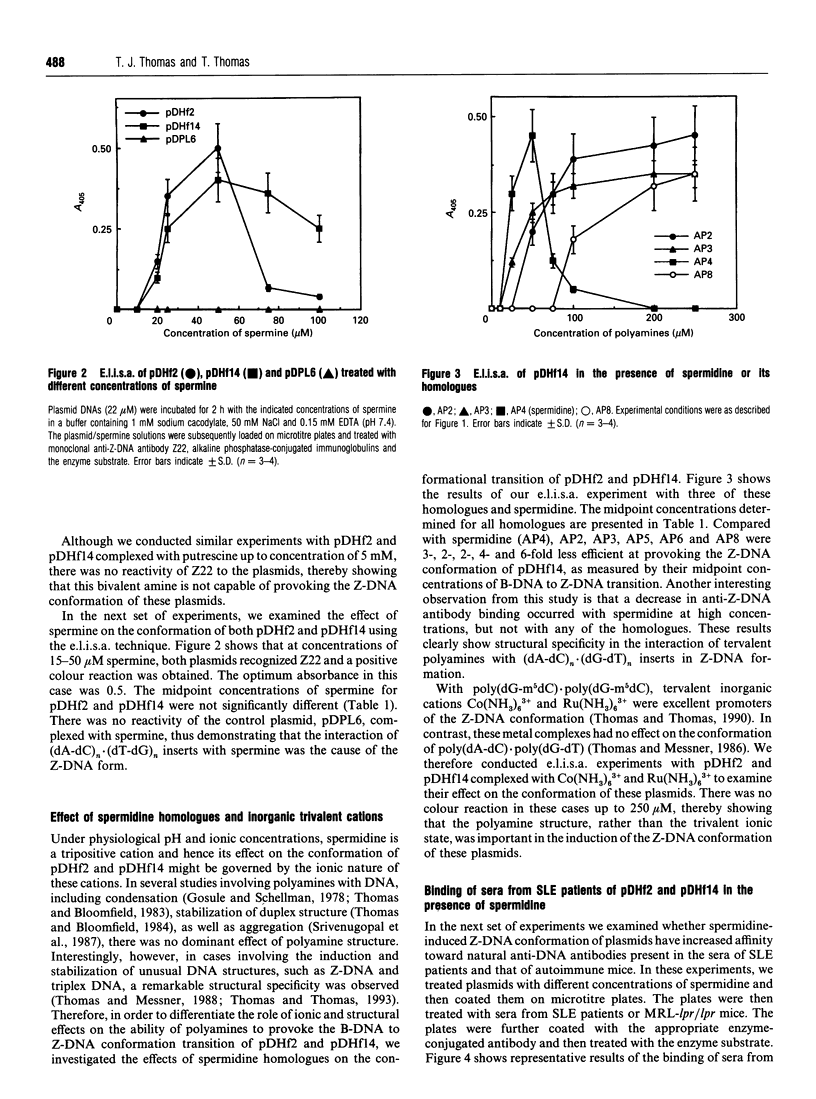
Full text
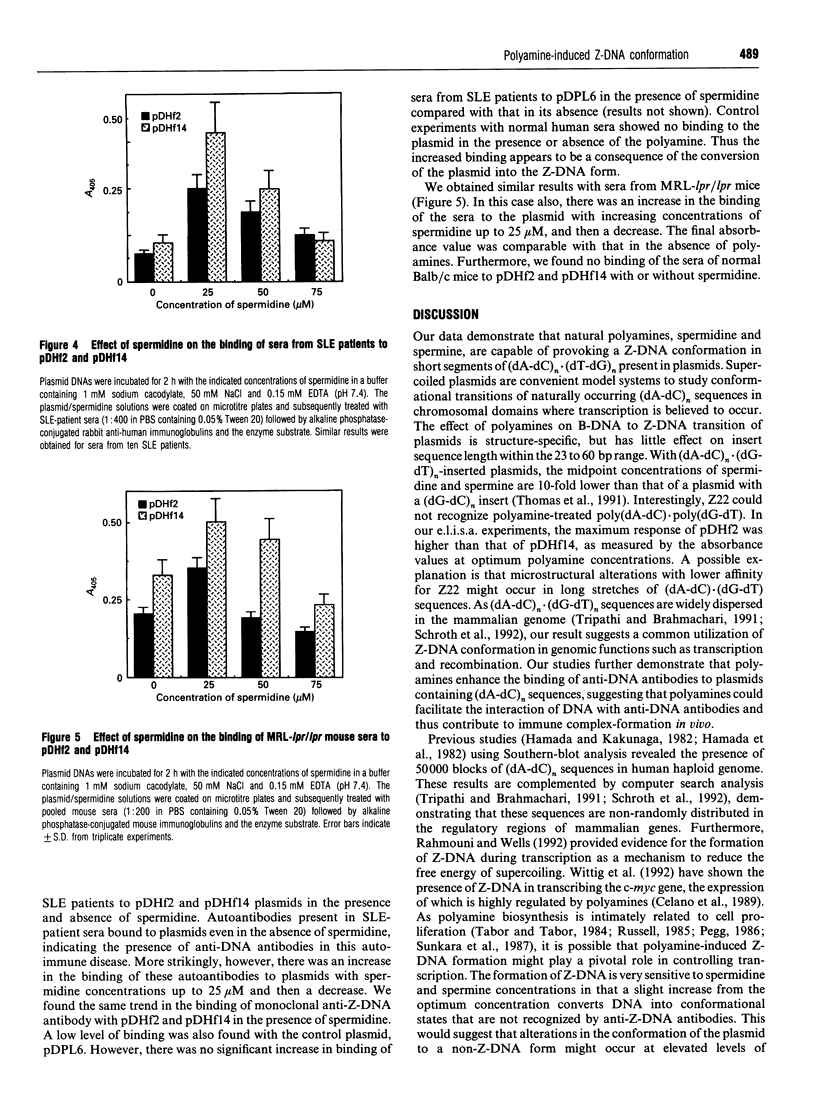
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu H. S., Marton L. J. The interaction of spermine and pentamines with DNA. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):243–246. doi: 10.1042/bj2440243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu H. S., Pellarin M., Feuerstein B. G., Deen D. F., Bergeron R. J., Marton L. J. Effect of N1,N14-bis(ethyl)homospermine on the growth of U-87 MG and SF-126 human brain tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3137–3140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen H. R., 3rd, Losman M. J., O'Connor T., Zacharias W., Larson J. E., Accavitti M. A., Wells R. D., Koopman W. J. Specificity of monoclonal anti-Z-DNA antibodies from unimmunized MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):743–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celano P., Baylin S. B., Casero R. A., Jr Polyamines differentially modulate the transcription of growth-associated genes in human colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8922–8927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Gosule L. C., Schellman A. DNA condensation with polyamines. II. Electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Morris D. R., Coffino P. Sequestered end products and enzyme regulation: the case of ornithine decarboxylase. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):280–290. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.280-290.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delic J., Onclercq R., Moisan-Coppey M. Inhibition and enhancement of eukaryotic gene expression by potential non-B DNA sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1273–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egli M., Williams L. D., Gao Q., Rich A. Structure of the pure-spermine form of Z-DNA (magnesium free) at 1-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 3;30(48):11388–11402. doi: 10.1021/bi00112a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein B. G., Pattabiraman N., Marton L. J. Spermine-DNA interactions: a theoretical study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5948–5952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner R. V., Frederick C. A., Quigley G. J., Rich A., Wang A. H. The molecular structure of the left-handed Z-DNA double helix at 1.0-A atomic resolution. Geometry, conformation, and ionic interactions of d(CGCGCG). J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7921–7935. doi: 10.2210/pdb1dcg/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnia U. B., Amenta P. S., Seibold J. R., Thomas T. J. Successful treatment of lupus nephritis in MRL-lpr/lpr mice by inhibiting ornithine decarboxylase. Kidney Int. 1991 May;39(5):882–890. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnia U. B., Thomas T., Thomas T. J. The effects of polyamines on the immunogenicity of polynucleotides. Immunol Invest. 1991 Jul;20(4):337–350. doi: 10.3109/08820139109057760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Kakunaga T. Potential Z-DNA forming sequences are highly dispersed in the human genome. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):396–398. doi: 10.1038/298396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Seidman M., Howard B. H., Gorman C. M. Enhanced gene expression by the poly(dT-dG).poly(dC-dA) sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2622–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Sakamoto I., Goto N., Kashiwagi K., Honma R., Hirose S. Interaction between polyamines and nucleic acids or phospholipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Dec;219(2):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S., Zon G., Sundaralingam M. Base only binding of spermine in the deep groove of the A-DNA octamer d(GTGTACAC). Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2360–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Ruiz A., Requena J. M., Lopez M. C., Alonso C. A potential Z-DNA-forming sequence is located between two transcription units alternatively expressed during development of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Möller A., Nordheim A., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Antibodies specific for left-handed Z-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Valle R. P., Möller A., Nordheim A., Schur P. H., Rich A., Stollar B. D. Z-DNA-specific antibodies in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):314–321. doi: 10.1172/JCI110771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C., Schwartz R. S. Autoantibodies to DNA. Crit Rev Immunol. 1988;8(3):147–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor L. H., Clark E. M. d(TG)n.d(CA)n sequences upstream of the rat prolactin gene form Z-DNA and inhibit gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1595–1601. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Pardue M. L., Weiner L. M., Lowenhaupt K., Scholten P., Möller A., Rich A., Stollar B. D. Analysis of Z-DNA in fixed polytene chromosomes with monoclonal antibodies that show base sequence-dependent selectivity in reactions with supercoiled plasmids and polynucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):468–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. The sequence (dC-dA)n X (dG-dT)n forms left-handed Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. Recent advances in the biochemistry of polyamines in eukaryotes. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):249–262. doi: 10.1042/bj2340249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M., Jovin T. M. Salt-induced co-operative conformational change of a synthetic DNA: equilibrium and kinetic studies with poly (dG-dC). J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):375–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Bergeron R. J. Spermidine requirement for cell proliferation in eukaryotic cells: structural specificity and quantitation. Science. 1983 Mar 4;219(4588):1083–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.6823570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D., Michalak M., Daisley S. L., Glick R. A method for the purification of E. coli plasmid DNA by homogeneous lysis and polyethylene glycol precipitation. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 Aug;9(3):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00775367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmouni A. R., Wells R. D. Direct evidence for the effect of transcription on local DNA supercoiling in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90721-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H. Ornithine decarboxylase: a key regulatory enzyme in normal and neoplastic growth. Drug Metab Rev. 1985;16(1-2):1–88. doi: 10.3109/03602538508991430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Chou P. J., Ho P. S. Mapping Z-DNA in the human genome. Computer-aided mapping reveals a nonrandom distribution of potential Z-DNA-forming sequences in human genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11846–11855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. T., Stannard B. S., Felsenfeld G. The binding of small cations to deoxyribonucleic acid. Nucleotide specificity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3233–3241. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley J. T., Lee J. S., Decoteau W. E. Left-handed "Z" DNA antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivenugopal K. S., Wemmer D. E., Morris D. R. Aggregation of DNA by analogs of spermidine; enzymatic and structural studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2563–2580. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Antibodies to DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):1–36. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Baarsch M. J., Messner R. P. Immunological detection of B-DNA to Z-DNA transition of polynucleotides by immobilization of the DNA conformation on a solid support. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):358–366. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A., Canellakis Z. N. Differential effects on the B-to-Z transition of poly(dG-me5dC).poly(dG-me5dC) produced by N1- and N8-acetyl spermidine. Biopolymers. 1985 Apr;24(4):725–729. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Collapse of DNA caused by trivalent cations: pH and ionic specificity effects. Biopolymers. 1983 Apr;22(4):1097–1106. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Ionic and structural effects on the thermal helix-coil transition of DNA complexed with natural and synthetic polyamines. Biopolymers. 1984 Jul;23(7):1295–1306. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Gunnia U. B., Thomas T. Polyamine-induced B-DNA to Z-DNA conformational transition of a plasmid DNA with (dG-dC)n insert. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6137–6141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Meryhew N. L., Messner R. P. DNA sequence and conformation specificity of lupus autoantibodies. Preferential binding to the left-handed Z-DNA form of synthetic polynucleotides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):367–377. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Messner R. P. A left-handed (Z) conformation of poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT) induced by polyamines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6721–6733. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Messner R. P. Structural specificity of polyamines in left-handed Z-DNA formation. Immunological and spectroscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Thomas T. Conformational transitions of polynucleotides in the presence of rhodium complexes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Jun;7(6):1221–1235. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10508561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Kiang D. T. A twenty-two-fold increase in the relative affinity of estrogen receptor to poly (dA-dC).poly (dG-dT) in the presence of polyamines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4705–4720. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Thomas T. J. Selectivity of polyamines in triplex DNA stabilization. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 21;32(50):14068–14074. doi: 10.1021/bi00213a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi J., Brahmachari S. K. Distribution of simple repetitive (TG/CA)n and (CT/AG)n sequences in human and rodent genomes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Oct;9(2):387–397. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden P. D. Potential Z-DNA-forming elements in serum DNA from human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vertino P. M., Bergeron R. J., Cavanaugh P. F., Jr, Porter C. W. Structural determinants of spermidine-DNA interactions. Biopolymers. 1987 May;26(5):691–703. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1095–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Read R., Thomas M., Rutman A., Harrison K., Lund V., Cookson B., Goldman W., Lambert H., Cole P. Effects of Bordetella pertussis infection on human respiratory epithelium in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):337–345. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.337-345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Wölfl S., Dorbic T., Vahrson W., Rich A. Transcription of human c-myc in permeabilized nuclei is associated with formation of Z-DNA in three discrete regions of the gene. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4653–4663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisard A., Fazakerley G. V. Ultrapolymorphic DNA: B, A, Z, and Z* conformations of poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT). Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2672–2676. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


