Abstract
Transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium mobaraense was partially purified by ion-exchange chromatography on a weak acid material and hydrophobic chromatography. The separation with a strong acid ion-exchanger produces homogeneous transglutaminase, in a single step and with high yields, directly from the centrifuged and filtered culture fluid of the micro-organism. The procedure reproduced several times could be also carried out on a larger scale with the optimized parameters of the laboratory isolations. The purified enzyme demonstrated good storage stability.
Full text
PDF
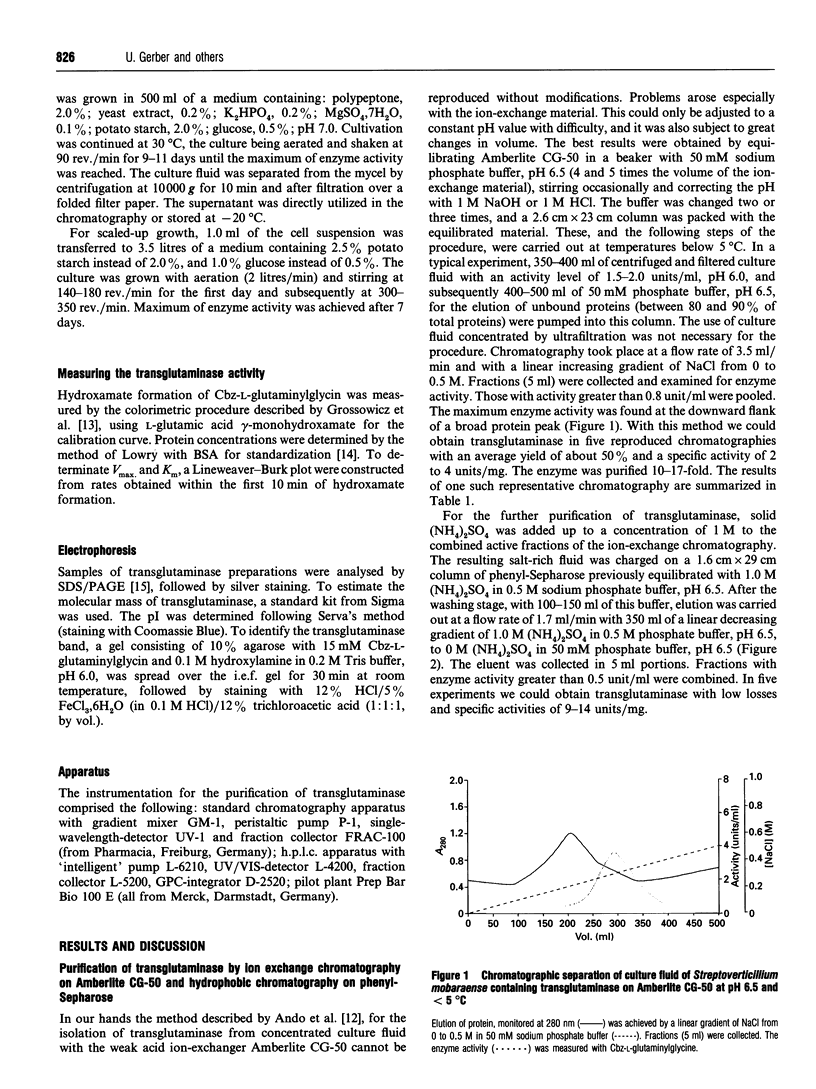
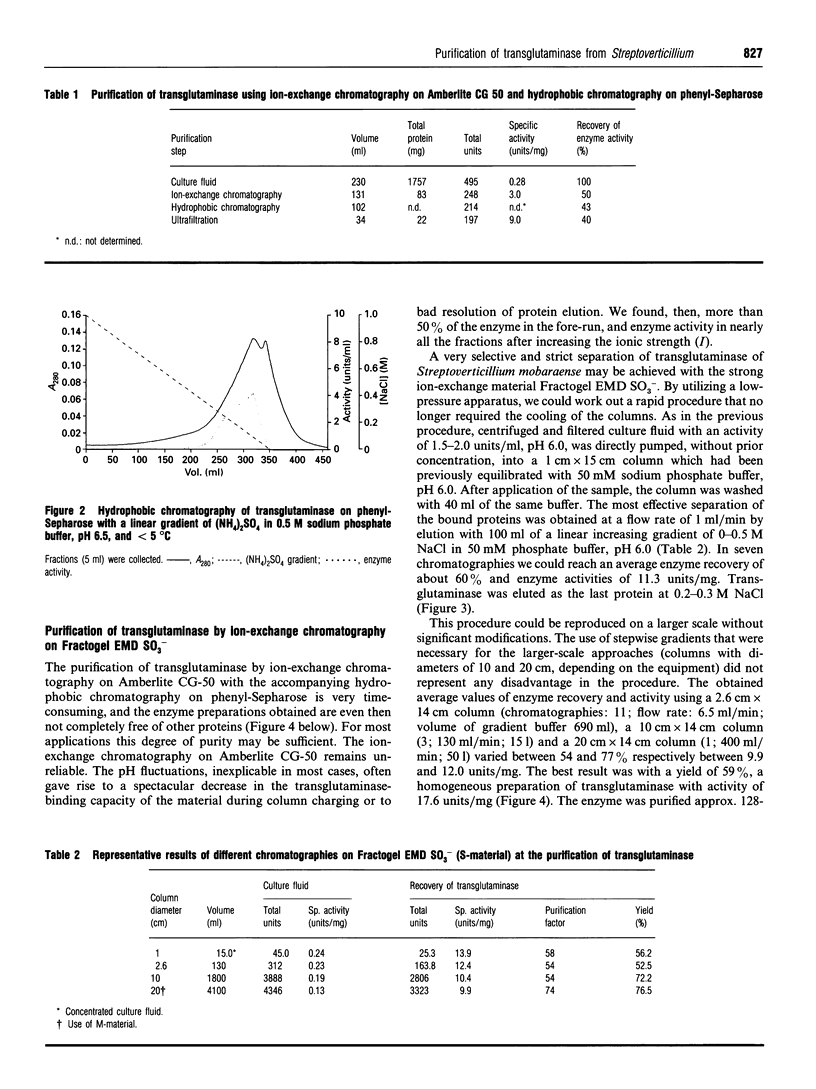
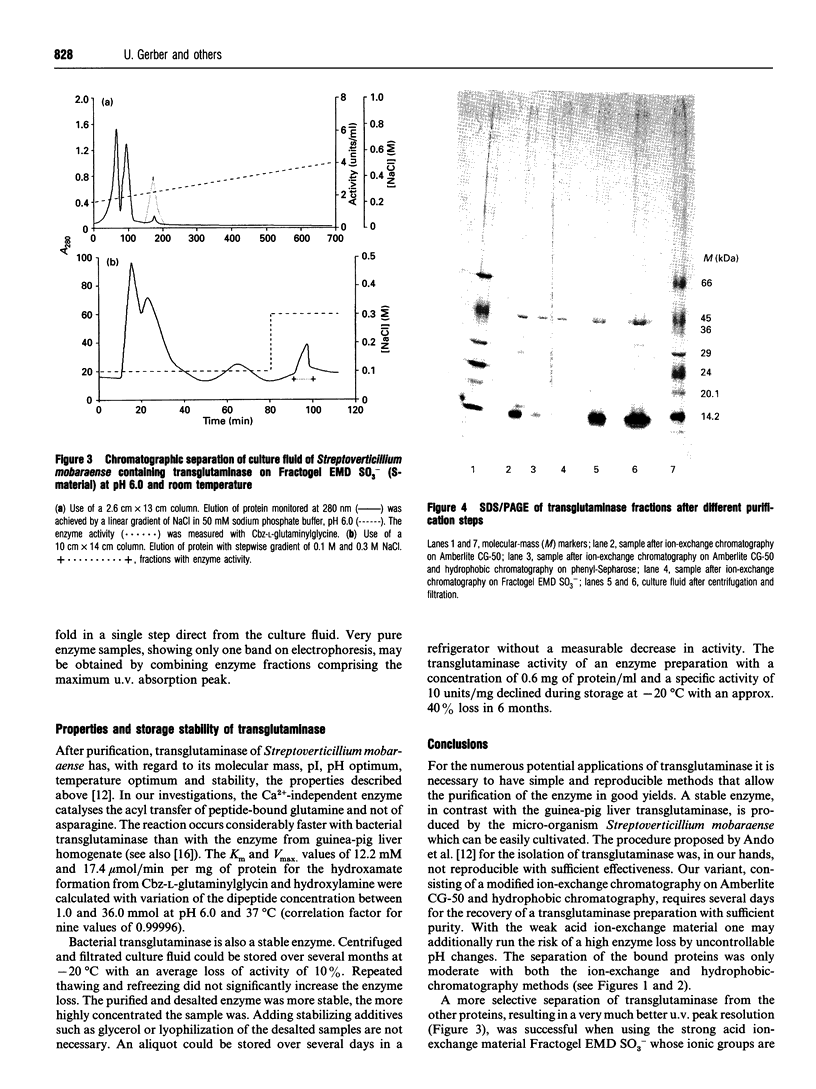

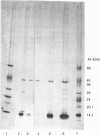
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Folk J. E., Chung S. I. Molecular and catalytic properties of transglutaminases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;38:109–191. doi: 10.1002/9780470122839.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Chung S. I. Transglutaminases. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:358–375. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E. Mechanism and basis for specificity of transglutaminase-catalyzed epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl) lysine bond formation. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;54:1–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470122990.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E. Transglutaminases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:517–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSOWICZ N., WAINFAN E., BOREK E., WAELSCH H. The enzymatic formation of hydroxamic acids from glutamine and asparagine. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):111–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Bottenus R. E., Davie E. W. Structure of transglutaminases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13411–13414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura K., Nasu T., Yokota H., Tsuchiya Y., Sasaki R., Chiba H. Amino acid sequence of guinea pig liver transglutaminase from its cDNA sequence. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2898–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura K., Tsuchiya Y., Sasaki R., Chiba H. Expression of guinea-pig liver transglutaminase cDNA in Escherichia coli. Amino-terminal N alpha-acetyl group is not essential for catalytic function of transglutaminase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):705–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamerling J. P., Aarsen G., de Bree P. K., Duran M., Wadman S. K., Vliegenthart F. G., Tesser G. I., van der Waarde K. M. Nepsilon-(beta-Aspartyl)lysinuria in children with various pathological conditions. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jan 2;82(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klostermeyer H., Rabbel K., Reimerdes E. H. Vorkommen der Isopeptidbindungen Nepsilon-(beta-Aspartyl)lysin und Nepsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysin in Rindercolostrum. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Aug;357(8):1197–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Conrad S. M. Transglutaminases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;58(1-2):9–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00240602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]