Abstract
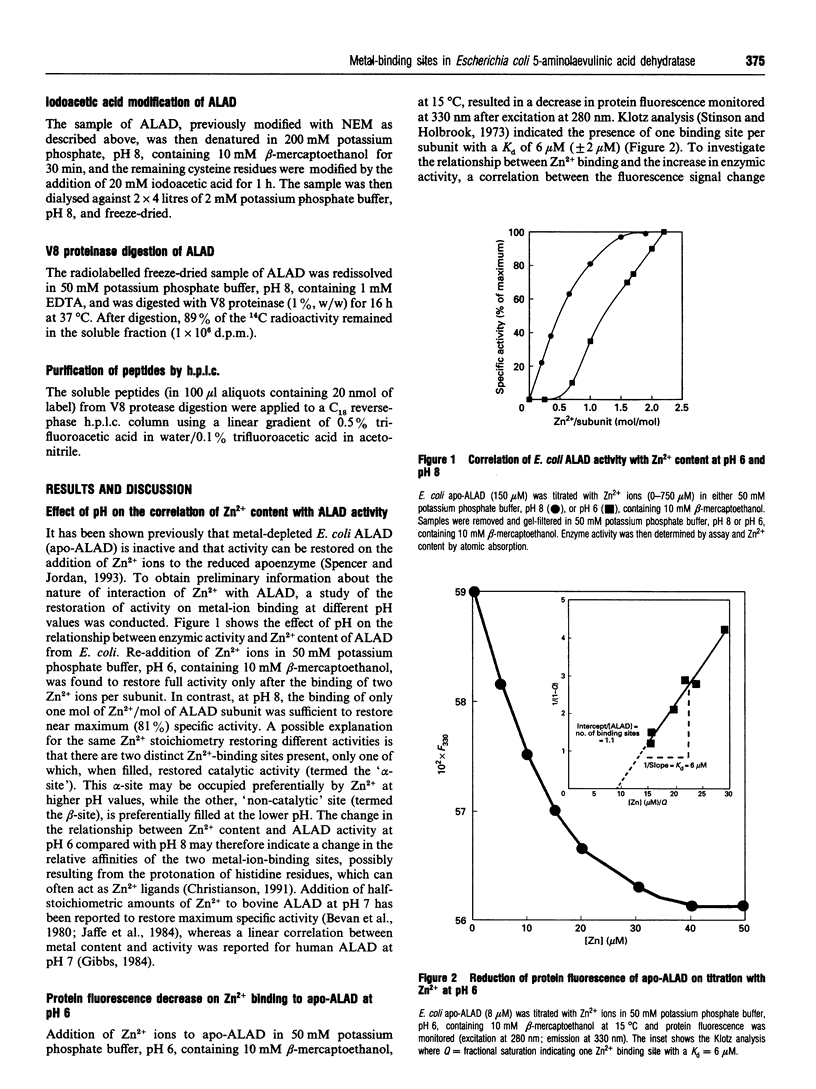
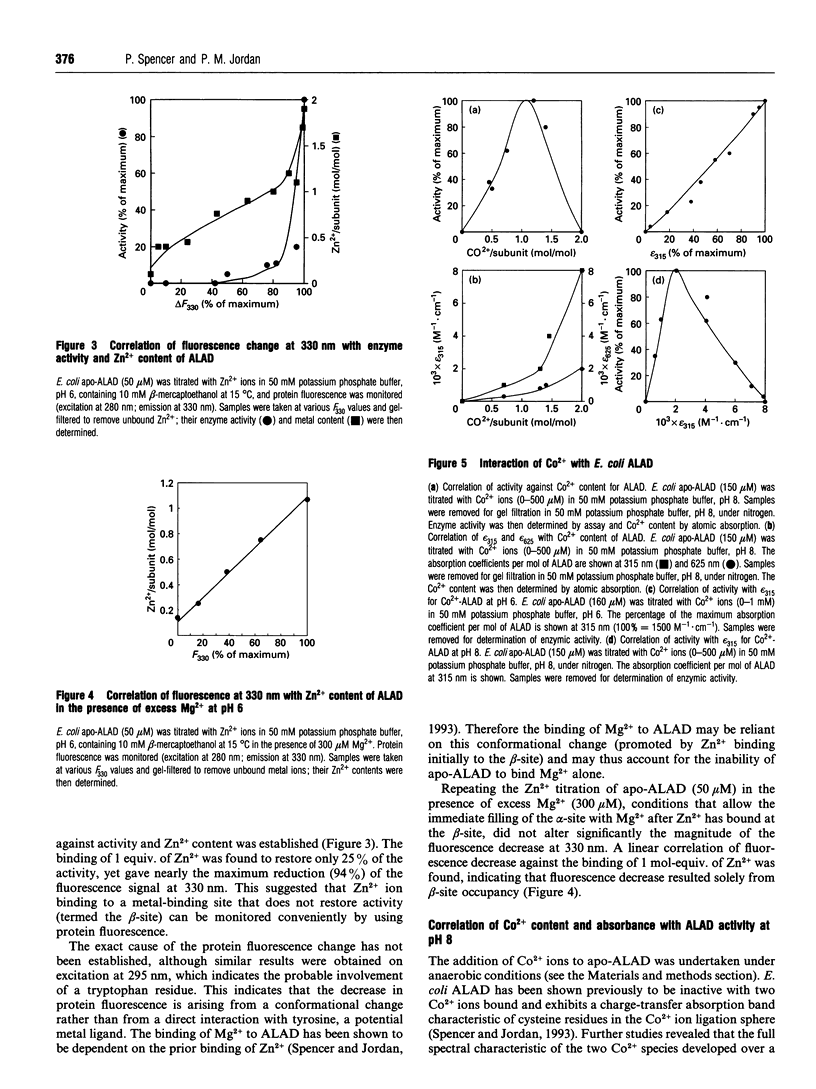
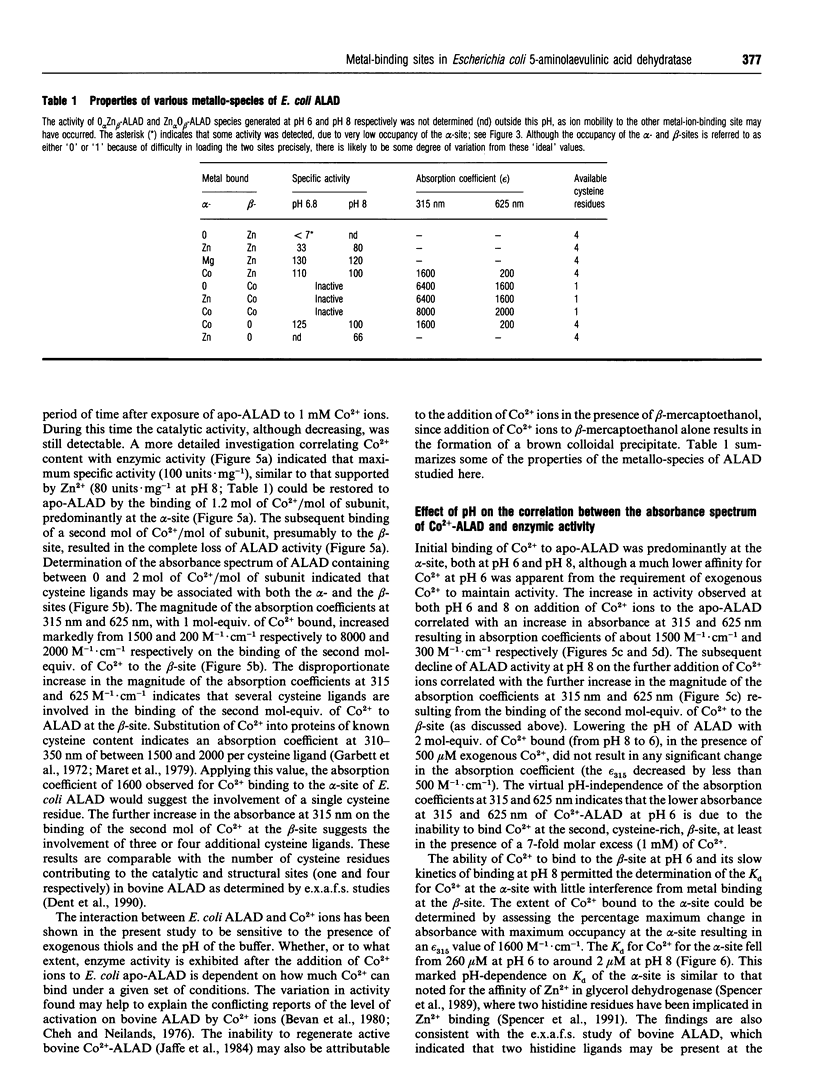
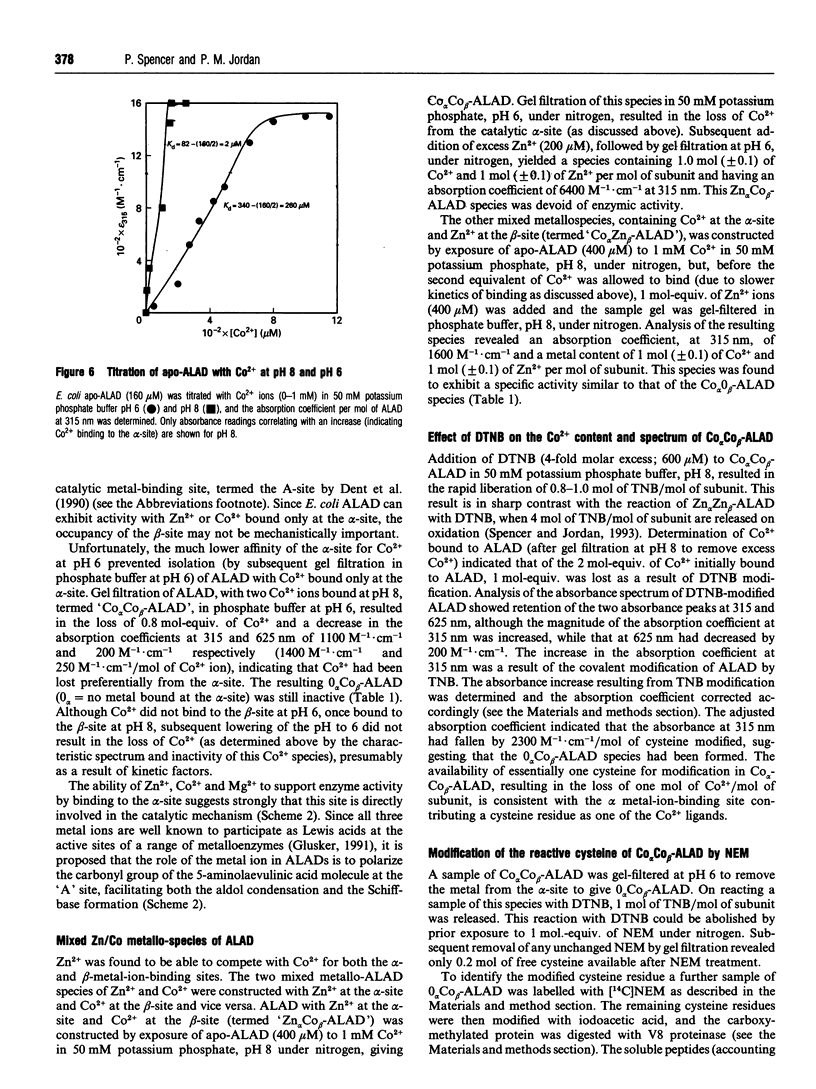
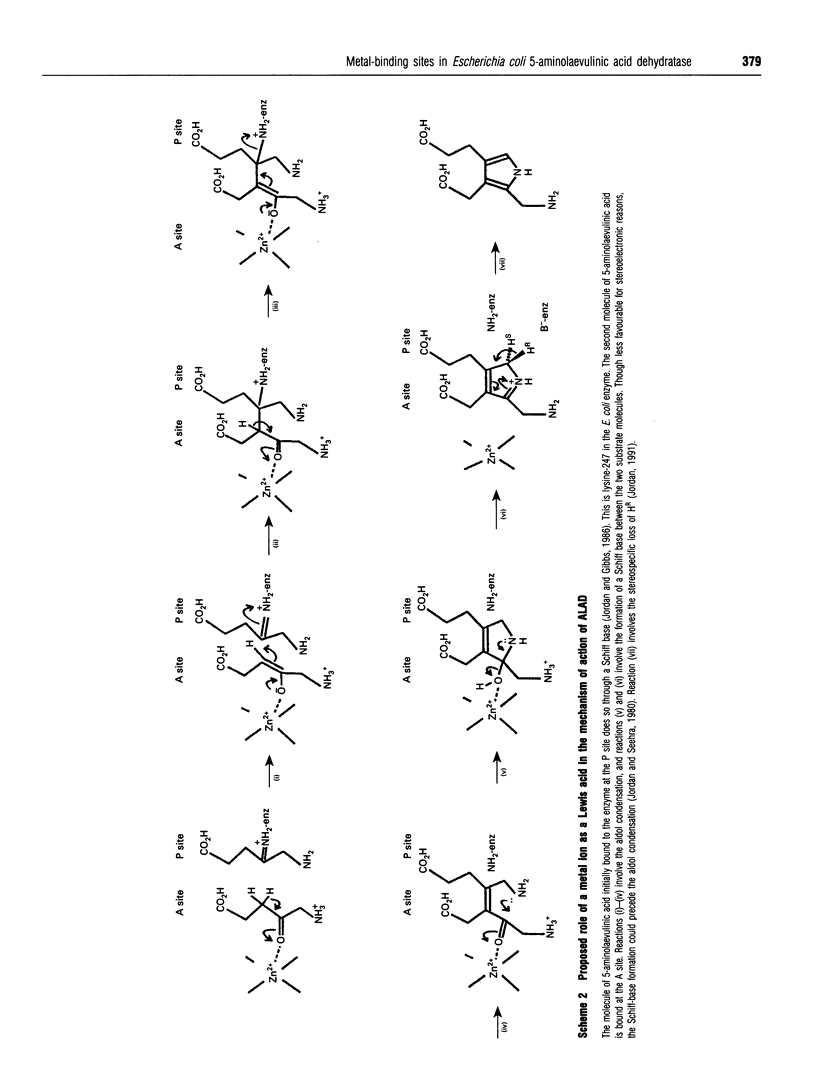
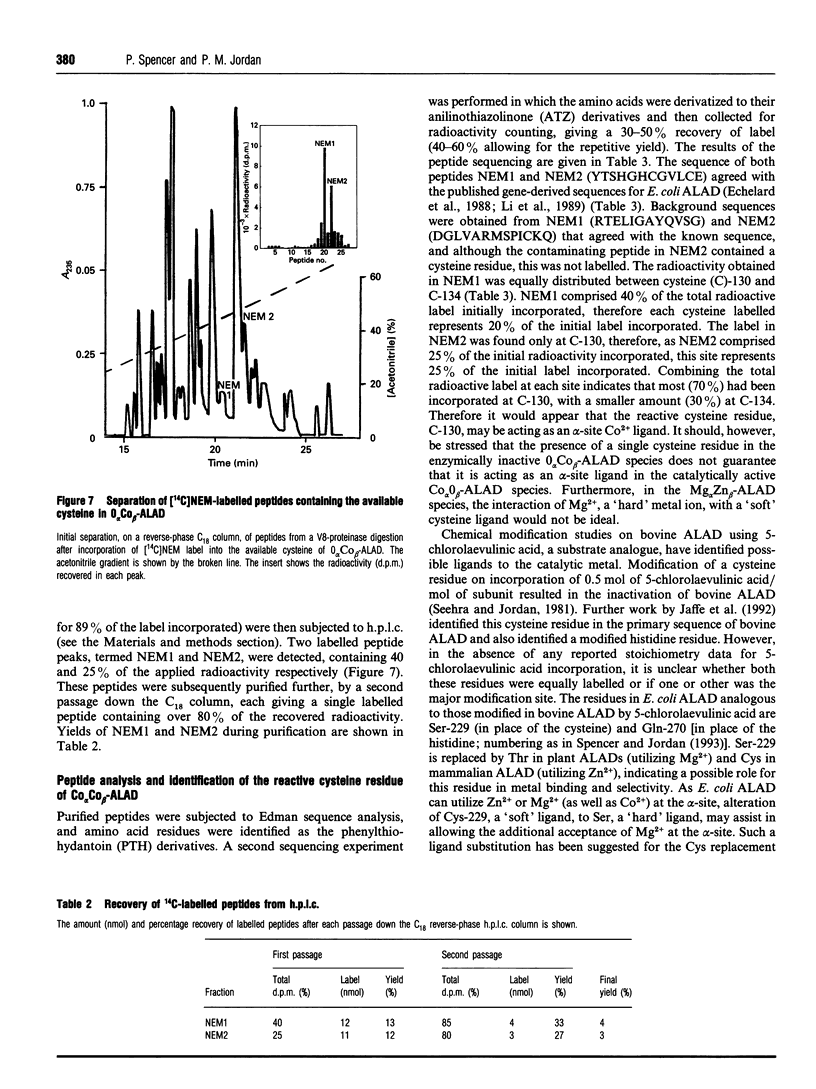
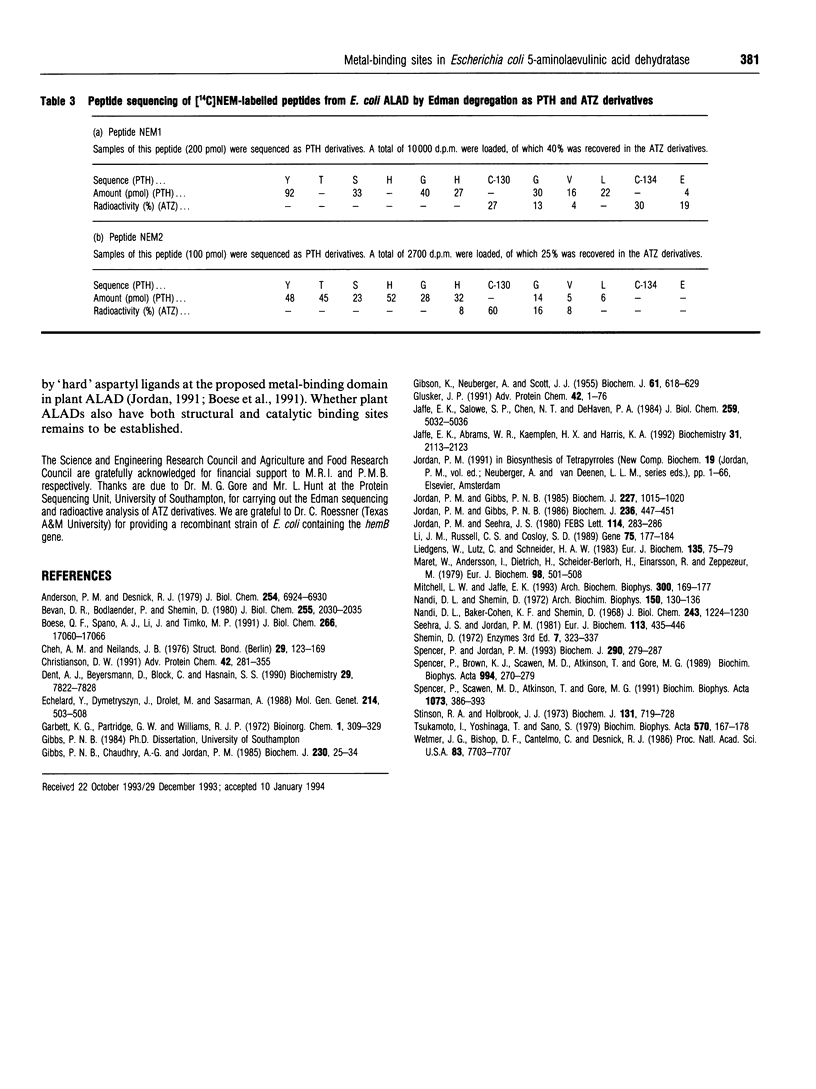
Two distinct metal-binding sites, termed alpha and beta, have been characterized in 5-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase from Escherichia coli. The alpha-site binds a Zn2+ ion that is essential for catalytic activity. This site can also utilize other metal ions able to function as a Lewis acid in the reaction mechanism, such as Mg2+ or Co2+. The beta-site is exclusively a transition-metal-ion-binding site thought to be involved in protein conformation, although a metal bound at this site only appears to be essential for activity if Mg2+ is to be bound at the alpha-site. The alpha- and beta-sites may be distinguished from one another by their different abilities to bind divalent-metal ions at different pH values. The occupancy of the beta-site with Zn2+ results in a decrease of protein fluorescence at pH 6. Occupancy of the alpha- and beta-sites with Co2+ results in u.v.-visible spectral changes. Spectroscopic studies with Co2+ have tentatively identified three cysteine residues at the beta-site and one at the alpha-site. Reaction with N-ethyl[14C]maleimide preferentially labels cysteine-130 at the alpha-site when Co2+ occupies the beta-site.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. M., Desnick R. J. Purification and properties of delta-aminolevulinate dehydrase from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6924–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan D. R., Bodlaender P., Shemin D. Mechanism of porphobilinogen synthase. Requirement of Zn2+ for enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2030–2035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boese Q. F., Spano A. J., Li J. M., Timko M. P. Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Identification of an unusual metal-binding domain in the plant enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17060–17066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson D. W. Structural biology of zinc. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:281–355. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60538-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent A. J., Beyersmann D., Block C., Hasnain S. S. Two different zinc sites in bovine 5-aminolevulinate dehydratase distinguished by extended X-ray absorption fine structure. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7822–7828. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echelard Y., Dymetryszyn J., Drolet M., Sasarman A. Nucleotide sequence of the hemB gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):503–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00330487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The purification and properties of delta-aminolaevulic acid dehydrase. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):618–629. doi: 10.1042/bj0610618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs P. N., Chaudhry A. G., Jordan P. M. Purification and properties of 5-aminolaevulinate dehydratase from human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):25–34. doi: 10.1042/bj2300025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs P. N., Jordan P. M. Identification of lysine at the active site of human 5-aminolaevulinate dehydratase. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):447–451. doi: 10.1042/bj2360447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glusker J. P. Structural aspects of metal liganding to functional groups in proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:1–76. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60534-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. K., Abrams W. R., Kaempfen H. X., Harris K. A., Jr 5-Chlorolevulinate modification of porphobilinogen synthase identifies a potential role for the catalytic zinc. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):2113–2123. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. K., Salowe S. P., Chen N. T., DeHaven P. A. Porphobilinogen synthase modification with methylmethanethiosulfonate. A protocol for the investigation of metalloproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5032–5036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Gibbs P. N. Mechanism of action of 5-aminolaevulinate dehydratase from human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):1015–1020. doi: 10.1042/bj2271015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Seehra J. S. 13C NMR as a probe for the study of enzyme-catalysed reactions: mechanism of action of 5-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 2;114(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. M., Russell C. S., Cosloy S. D. The structure of the Escherichia coli hemB gene. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90394-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liedgens W., Lütz C., Schneider H. A. Molecular properties of 5-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase from Spinacia oleracea. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):75–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maret W., Andersson I., Dietrich H., Schneider-Bernlöhr H., Einarsson R., Zeppezauer M. Site-specific substituted cobalt(II) horse liver alcohol dehydrogenases. Preparation and characterization in solution, crystalline and immobilized state. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):501–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell L. W., Jaffe E. K. Porphobilinogen synthase from Escherichia coli is a Zn(II) metalloenzyme stimulated by Mg(II). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jan;300(1):169–177. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi D. L., Baker-Cohen K. F., Shemin D. Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1224–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seehra J. S., Jordan P. M. 5-Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase: alkylation of an essential thiol in the bovine-liver enzyme by active-site-directed reagents. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):435–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P., Bown K. J., Scawen M. D., Atkinson T., Gore M. G. Isolation and characterisation of the glycerol dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 23;994(3):270–279. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P., Jordan P. M. Purification and characterization of 5-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase from Escherichia coli and a study of the reactive thiols at the metal-binding domain. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 15;290(Pt 1):279–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2900279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P., Scawen M. D., Atkinson T., Gore M. G. The identification of a structurally important cysteine residue in the glycerol dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 4;1073(2):386–393. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson R. A., Holbrook J. J. Equilibrium binding of nicotinamide nucleotides to lactate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):719–728. doi: 10.1042/bj1310719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto I., Yoshinaga T., Sano S. The role of zinc with special reference to the essential thiol groups in delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase of bovine liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 12;570(1):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G., Bishop D. F., Cantelmo C., Desnick R. J. Human delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase: nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7703–7707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


