Abstract
In order better to understand the pathophysiology of the equine form of emphysema, two elastinolytic enzymes from horse neutrophils, referred to as proteinases 2A and 2B, have been extensively characterized and compared with the human neutrophil proteinases, proteinase-3 and elastase. Specificity studies using both the oxidized insulin B-chain and synthetic peptides revealed that cleavage of peptide bonds with P1 alanine or valine residues was preferred. Further characterization of the two horse elastases by N-terminal sequence and reactive-site analyses indicated that proteinases 2A and 2B have considerable sequence similarity to each other, to proteinase-3 from human neutrophils (proteinase 2A), to human neutrophil elastase (proteinase 2B) and to a lesser extent to pig pancreatic elastase. Horse and human elastases differed somewhat in their interaction with some natural protein proteinase inhibitors. For example, in contrast with its action on human neutrophil elastase, aprotinin did not inhibit either of the horse proteinases. However, the Val15, alpha-aminobutyric acid-15 (Abu15), alpha-aminovaleric acid-15 (Nva15) and Ala15 reactive-site variants of aprotinin were good inhibitors of proteinase 2B (Ki < 10(-9) M) but only weak inhibitors of proteinase 2A (Ki > 10(-7) M). In summary, despite these differences, the horse neutrophil elastases were found to resemble closely their human counterparts, thus implicating them in the pathological degradation of connective tissue in chronic lung diseases in the equine species.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardelt W. Inactivation of some pancreatic and leucocyte elastases by peptide chloromethyl ketones and alkyl isocyanates. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 15;67(2):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80355-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. J., Travis J. Human leukocyte granule elastase: rapid isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):836–841. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieth J. G. Pathophysiological interpretation of kinetic constants of protease inhibitors. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980;16 (Suppl):183–197. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-08-027379-2.50020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
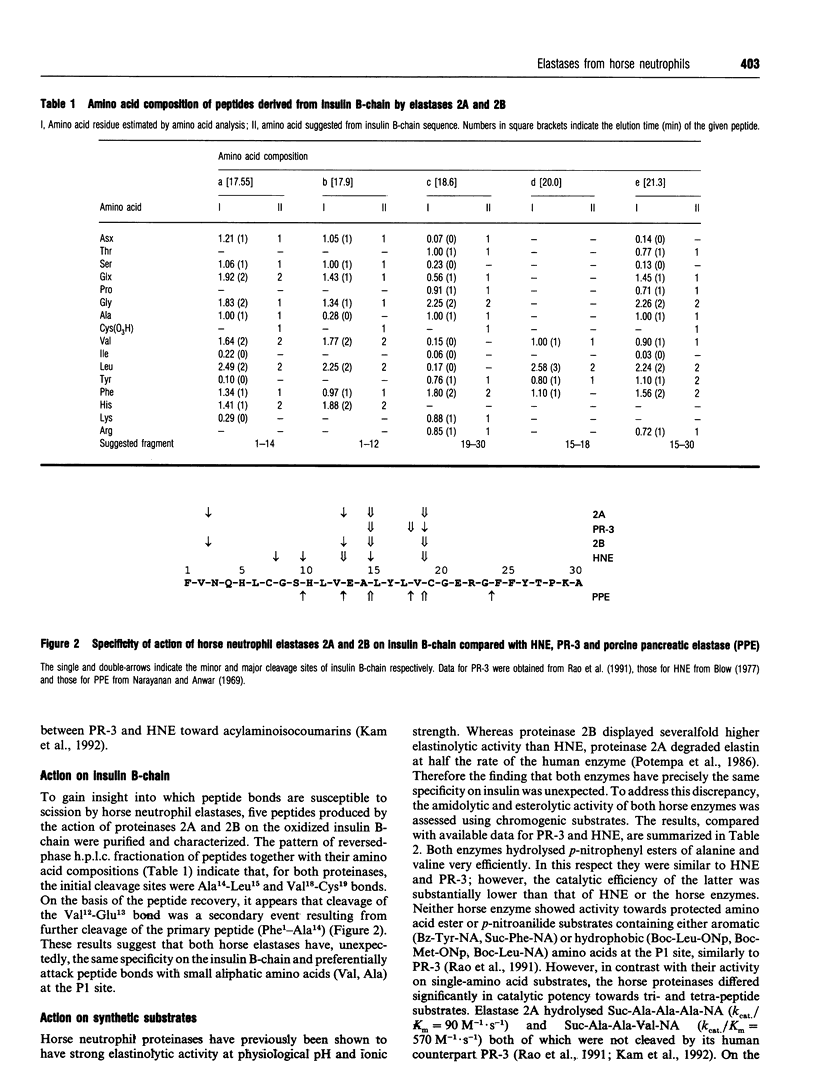
- Blow A. M. Action of human lysosomal elastase on the oxidized B chain of insulin. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 1;161(1):13–16. doi: 10.1042/bj1610013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Meyer E., Jr, Powers J. C. Human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: X-ray crystal structures, mechanism, substrate specificity, and mechanism-based inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):1951–1963. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bories D., Raynal M. C., Solomon D. H., Darzynkiewicz Z., Cayre Y. E. Down-regulation of a serine protease, myeloblastin, causes growth arrest and differentiation of promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90752-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
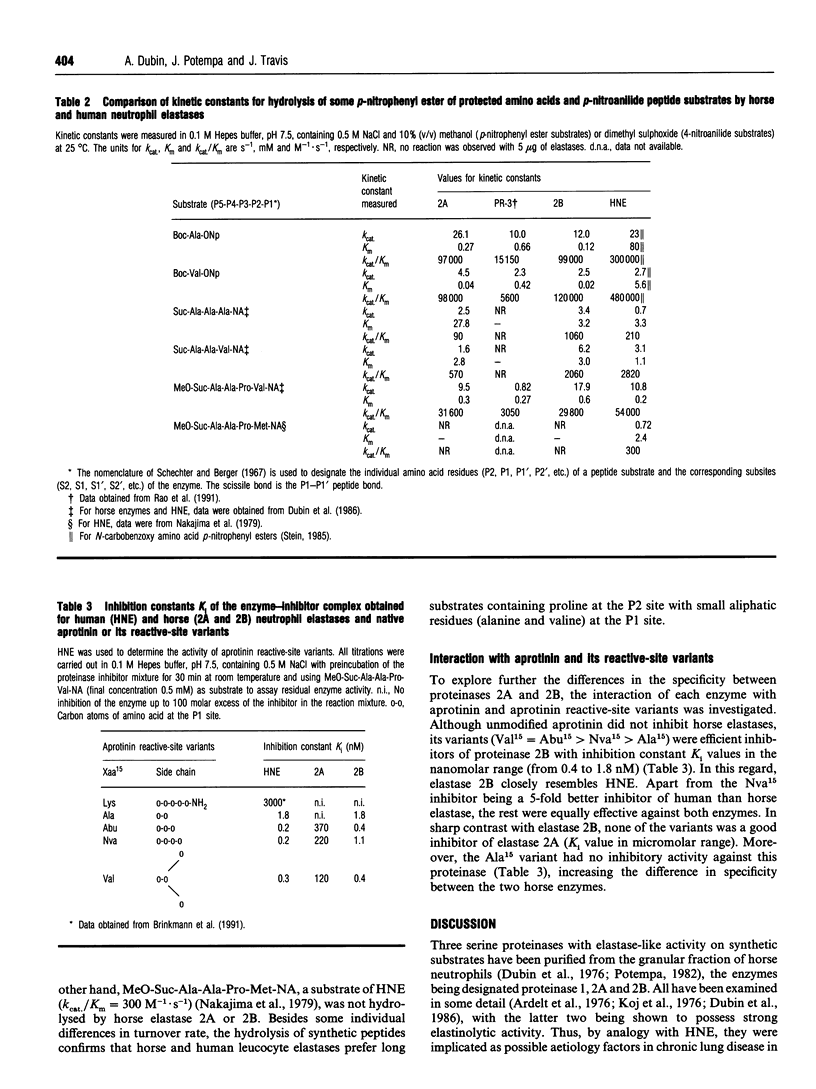
- Brinkmann T., Schnierer S., Tschesche H. Recombinant aprotinin homologue with new inhibitory specificity for cathepsin G. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):95–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks S. P. A simple computer program with statistical tests for the analysis of enzyme kinetics. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):906–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker M. J., Groutas W. C., Hoidal J. R., Rao N. V. Human neutrophil proteinase 3: mapping of the substrate binding site using peptidyl thiobenzyl esters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1318–1324. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91375-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burki N. K., Davenport P. W., Safdar F., Zechman F. W. The effects of airway anesthesia on magnitude estimation of added inspiratory resistive and elastic loads. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):2–4. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.2P2.S2a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli D., Detmers P. A., Nathan C. F., Gabay J. E. Azurocidin and a homologous serine protease from neutrophils. Differential antimicrobial and proteolytic properties. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):904–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI114518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli D., Melchior M., Fu Y., Nakata M., Shuman H., Nathan C., Gabay J. E. Cloning of cDNA for proteinase 3: a serine protease, antibiotic, and autoantigen from human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Koj A., Chudzik J. Isolation and some molecular parameters of elastase-like normal proteinases from horse blood leucocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):389–396. doi: 10.1042/bj1530389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Potempa J., Schnebli H. P., Koj A. Comparison of specificity of human and horse leucocyte proteinases with synthetic peptide substrates. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 1986;24(2):157–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin A., Travis J., Enghild J. J., Potempa J. Equine leukocyte elastase inhibitor. Primary structure and identification as a thymosin-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6576–6583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Scott R. W., Campanelli D., Griffith J., Wilde C., Marra M. N., Seeger M., Nathan C. F. Antibiotic proteins of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerger H. Chronic pulmonary disease in the horse. Equine Vet J. 1973 Jan;5(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. R., Tyler W. S. Chronic alveolar emphysema in the horse. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1969;13:59–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmeding R., van der Schoot C. E., ten Bokkel Huinink D., Hack C. E., van den Ende M. E., Kallenberg C. G., von dem Borne A. E. Wegener's granulomatosis autoantibodies identify a novel diisopropylfluorophosphate-binding protein in the lysosomes of normal human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1577–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI114335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Tissue injury in inflammation. Oxidants, proteinases, and cationic proteins. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):669–674. doi: 10.1172/JCI112869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastase in tissue injury. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:207–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J., Lüdemann J., Utecht B., Gross W. L. Wegener's autoantigen decoded. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):520–520. doi: 10.1038/346520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette J. C., Charles L. A., Falk R. J. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies: disease associations, molecular biology, and pathophysiology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:193–221. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette J. C., Hoidal J. R., Falk R. J. Specificity of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies for proteinase 3. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2263–2264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenberg C. G., Tervaert J. W., van der Woude F. J., Goldschmeding R., von dem Borne A. E., Weening J. J. Autoimmunity to lysosomal enzymes: new clues to vasculitis and glomerulonephritis? Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90159-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam C. M., Kerrigan J. E., Dolman K. M., Goldschmeding R., Von dem Borne A. E., Powers J. C. Substrate and inhibitor studies on proteinase 3. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80340-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao R. C., Wehner N. G., Skubitz K. M., Gray B. H., Hoidal J. R. Proteinase 3. A distinct human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteinase that produces emphysema in hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1963–1973. doi: 10.1172/JCI113816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Chudzik J., Dubin A. Substrate specificity and modifications of the active centre of elastase-like neutral proteinases from horse blood leucocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):397–402. doi: 10.1042/bj1530397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Powers J. C., Ashe B. M., Zimmerman M. Mapping the extended substrate binding site of cathepsin G and human leukocyte elastase. Studies with peptide substrates related to the alpha 1-protease inhibitor reactive site. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4027–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan A. S., Anwar R. A. The specificity of purified porcine pancreatic elastase. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):11–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1140011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Ahmad M. F., Arnaout M. A. Wegener's granulomatosis autoantigen is a novel neutrophil serine proteinase. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):1888–1893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Dubin A., Seemüller U., Schnebli H. P., Koj A. Inhibition of horse leucocyte proteinases by eglin, a proteinase inhibitor from leeches. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1985;44(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potempa J., Korzus E., Dubin A., Silberring J. Elastinolytic activity of horse leukocyte proteinases. Comparison with elastases from human leukocytes and porcine pancreas. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 1986;24(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. V., Wehner N. G., Marshall B. C., Gray W. R., Gray B. H., Hoidal J. R. Characterization of proteinase-3 (PR-3), a neutrophil serine proteinase. Structural and functional properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9540–9548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selak M. A. Neutrophil elastase potentiates cathepsin G-induced platelet activation. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Nov 10;68(5):570–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha S., Watorek W., Karr S., Giles J., Bode W., Travis J. Primary structure of human neutrophil elastase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2228–2232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedly L. A., Tonnesen M. G., Sandhaus R. A., Haslett C., Guthrie L. A., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M., Worthen G. S. Neutrophil-mediated injury to endothelial cells. Enhancement by endotoxin and essential role of neutrophil elastase. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1233–1243. doi: 10.1172/JCI112426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. L. Catalysis by human leukocyte elastase: III. Steady-state kinetics for the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl esters. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Feb 1;236(2):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Fellenberg R., Kohler L., Grünig G., Pellegrini A. Comparison of neutrophil elastases and of neutrophil protease inhibitors in the horse and man. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2480–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


