Abstract
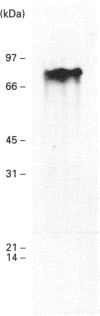
A lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-hydrolysing lysophospholipase was purified from rat brain and characterized. This membrane-bound lysophospholipase was solubilized by using n-octyl glucoside and purified by sequential cation, hydrophobic and gel-filtration chromatography. The purified protein has a mass of 80 kDa as assayed by SDS/PAGE. This lysophospholipase catalysed the hydrolysis of a variety of lysophosphatidic acids, but with different rates, depending on the length and degree of saturation of the sn-1 acyl group (1-oleoyl-LPA approximately 1-stearoyl-LPA > 1-palmitoyl-LPA > 1-myristoyl-LPA). This enzyme had no-measurable catalytic activity when other lysophospholipids, monoacylglycerol or phosphatidic acid were used as substrates. On the basis of its chromatographic properties, substrate specificity and cellular localization, we conclude that this lysophospholipase differs from those previously purified and speculate that it has an important function in terminating biological responses to LPA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durieux M. E., Lynch K. R. Signalling properties of lysophosphatidic acid. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jun;14(6):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garsetti D. E., Ozgür L. E., Steiner M. R., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Isolation and characterization of three lysophospholipases from the murine macrophage cell line WEHI 265.1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 2;1165(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90191-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garsetti D. E., Steiner M. R., Holtsberg F., Ozgür L. E., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Comparison of six mammalian lysophospholipases. J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garsetti D., Holtsberg F., Steiner M. R., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Butyric acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells increases the expression of a single lysophospholipase. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):831–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2880831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Kindom S. E., Peterson D. A., Peller J., Krantz K. E., White J. G. Lysophosphatidic acids. Influence on platelet aggregation and intracellular calcium flux. Am J Pathol. 1979 Aug;96(2):423–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Robinson P. Identification of the molecular species of lysophosphatidic acid produced when platelets are stimulated by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 20;1001(3):282–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. W., Sobel B. E. Lysophosphatidylcholine metabolism in the rabbit heart. Characterization of metabolic pathways and partial purification of myocardial lysophospholipase-transacylase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6702–6708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Moolenaar W. H., Van Duijn B. Lysophosphatidic acid is a chemoattractant for Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1857–1861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidic acid, but not phosphatidic acid, is a potent Ca2(+)-mobilizing stimulus for fibroblasts. Evidence for an extracellular site of action. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12232–12239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The phosphatidylinositol cycle and the regulation of arachidonic acid production. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):367–369. doi: 10.1038/292367a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Simon M. F., Douste-Blazy L. Phosphatidic and lysophosphatidic acid production in phospholipase C-and thrombin-treated platelets. Possible involvement of a platelet lipase. Biochimie. 1978 Sep 29;60(6-7):653–661. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80784-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., MacNulty E. E., Palmer S., Wakelam M. J. Differences in the regulation of endothelin-1- and lysophosphatidic-acid-stimulated Ins(1,4,5)P3 formation in rat-1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2800609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel R. J., Honeyman T. W., McMahon K. K., Serio R., Clark R. B. Inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation in hamster adipocytes with phosphatidic acid: differences and similarities with alpha adrenergic effects. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(6):437–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- She H. S., Garsetti D. E., Steiner M. R., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. The substrate specificities of four different lysophospholipases as determined by a novel fluorescence assay. Biochem J. 1994 Feb 15;298(Pt 1):23–29. doi: 10.1042/bj2980023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. F., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Human platelet aggregation induced by 1-alkyl-lysophosphatidic acid and its analogs: a new group of phospholipid mediators? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1743–1750. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tigyi G., Miledi R. Lysophosphatidates bound to serum albumin activate membrane currents in Xenopus oocytes and neurite retraction in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21360–21367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumura A., Fukuzawa K., Isobe J., Tsukatani H. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced aggregation of human and feline platelets: structure-activity relationship. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumura A., Fukuzawa K., Tsukatani H. Contractile actions of lysophosphatidic acids with a chemically-defined fatty acyl group on longitudinal muscle from guinea-pig ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;34(8):514–516. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1982.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT W. Pharamacologically active acidic phospholipids and glycolipids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Apr;12:415–420. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. Y., Deems R. A., Dennis E. A. Lysophospholipases I and II from P388D1 macrophage-like cell line. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:456–468. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97171-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. Y., Dennis E. A. Purification and characterization of a lysophospholipase from a macrophage-like cell line P388D1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9965–9972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J. G., van den Bosch H., Aarsman A. J., van Deenen L. L. Studies on lysophospholipases. II. Substrate specificity of a lysolecithin hydrolyzing carboxylesterase from beef pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J. G., van den Bosch H., Rijken D., van Deenen L. L. Studies on lysophospholipases. 3. The complete purification of two proteins with lysophospholipase activity from beef liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 16;369(1):50–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Hordijk P. L., Medema R. H., Bos J. L., Moolenaar W. H. Pertussis toxin-sensitive activation of p21ras by G protein-coupled receptor agonists in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1257–1261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., van Rijswijk A., Jalink K., van der Bend R. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., Moolenaar W. H. Mitogenic action of lysophosphatidic acid and phosphatidic acid on fibroblasts. Dependence on acyl-chain length and inhibition by suramin. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2810163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bend R. L., de Widt J., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H., van Blitterswijk W. J. The biologically active phospholipid, lysophosphatidic acid, induces phosphatidylcholine breakdown in fibroblasts via activation of phospholipase D. Comparison with the response to endothelin. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 1;285(Pt 1):235–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2850235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]