Abstract
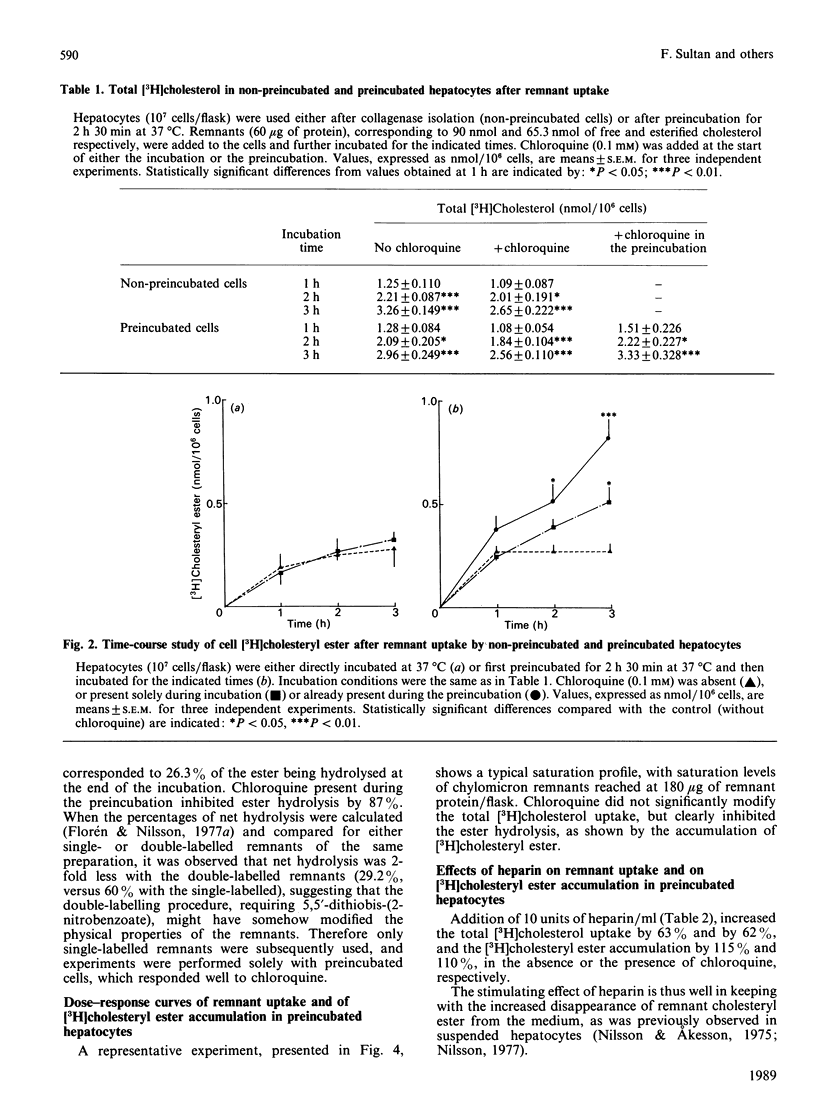
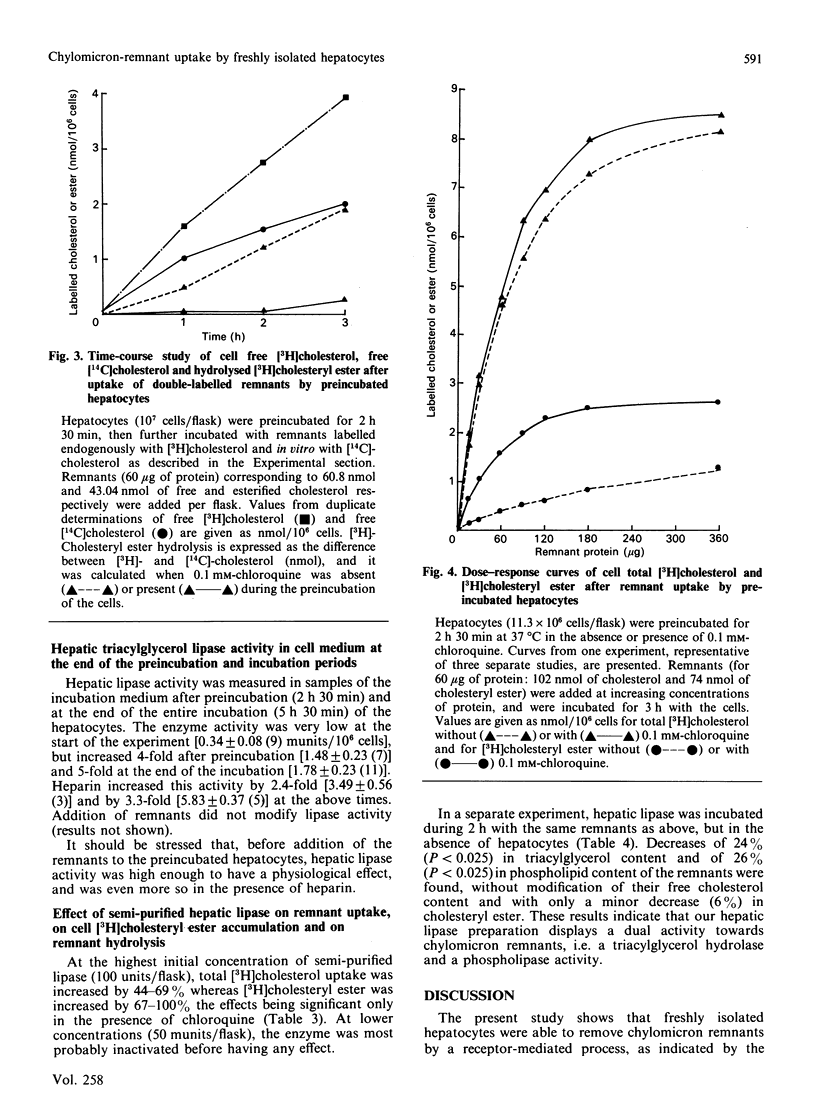
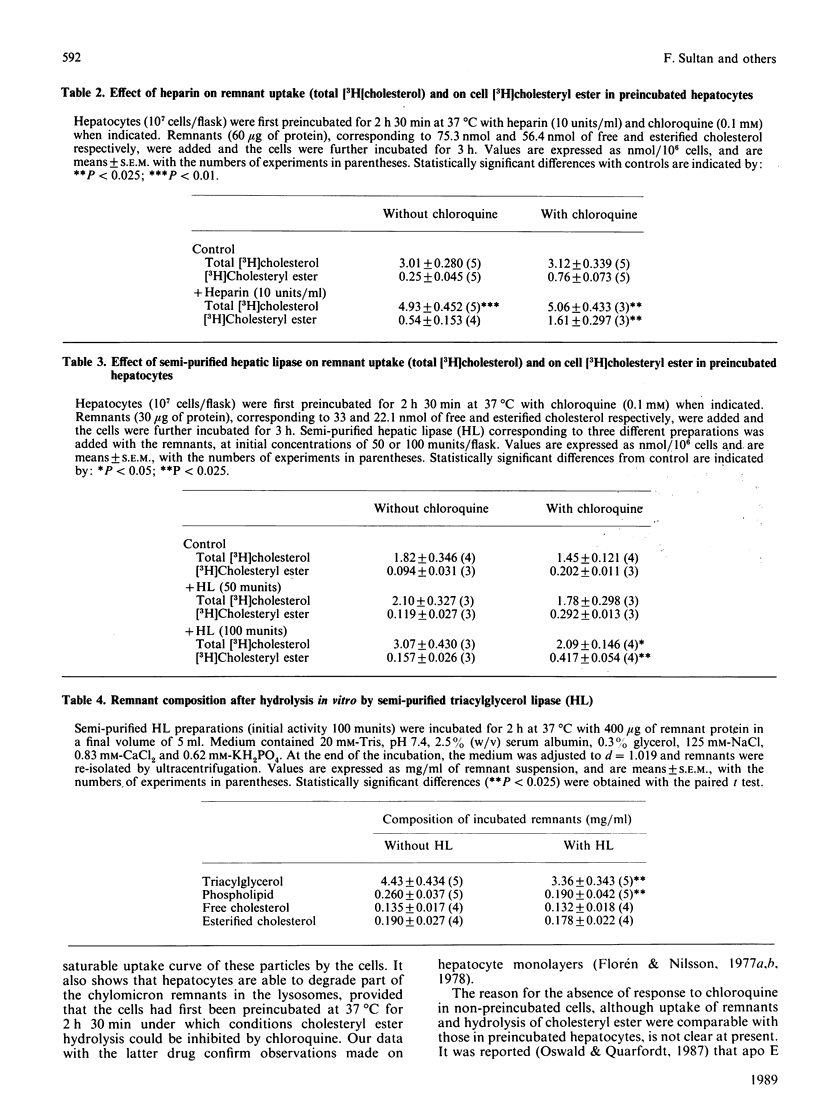
Chylomicron remnants labelled biologically with [3H]cholesterol were efficiently taken up by freshly isolated hepatocytes during a 3 h incubation in Krebs bicarbonate medium. Their [3H]cholesteryl ester was hydrolysed (74% net hydrolysis), and 0.1 mM-chloroquine could partially inhibit this hydrolysis, provided that hepatocytes were first preincubated for 2 h 30 min at 37 degrees C. This hydrolysis was also measured in preincubated cells with remnants double-labelled (3H and 14C) on their free cholesterol moiety; [3H]cholesterol arising from [3H]cholesteryl ester hydrolysis was recovered in the free [3H]cholesterol pool. A dose-response study showed saturation of remnant uptake at 180 micrograms of remnant protein/10(7) cells. Heparin (10 units/ml) increased remnant uptake by 63% (P less than 0.01), [3H]cholesteryl ester accumulation in the cell pellet by 110% (P less than 0.025) and hepatic lipase activity secreted in the medium by 2.4-fold (P less than 0.01) and by 3.3-fold (P less than 0.01) at the end of the preincubation and incubation periods respectively. Addition of 100 munits of semi-purified hepatic lipase preparation/flask stimulated remnant uptake by 44-69%, and [3H]cholesteryl ester accumulation in the presence of chloroquine by 2.1-fold (P less than 0.025). When hepatic lipase was incubated solely with the remnants, it decreased their triacylglycerol and phospholipid contents by 24% and 26% respectively. Thus freshly isolated hepatocytes may be used to study chylomicron-remnant uptake. Hepatic lipase, which seems to underly the stimulating effect of heparin, facilitates remnant uptake in vitro, and this could be mediated by at least one (or both) of its hydrolytic properties.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. M., Nervi F. O., Dietschy J. M. Rate constants for the uptake of cholesterol from various intestinal and serum lipoprotein fractions by the liver of the rat in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 23;486(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbeeny C. M., Rifici V. A. The uptake of chylomicron remnants and very low density lipoprotein remnants by the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9662–9666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Havinga J. R., Ihrke G., Hui D. Y., Wernette-Hammond M. E., Turck C. W., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E-binding proteins isolated from dog and human liver. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):288–297. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.3.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher J. D., Sisson P. J., Waite M. Degradation of mono-oleoylglycerol, trioleoylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine in emulsions and lipoproteins by rat hepatic acylglycerol lipase. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):343–351. doi: 10.1042/bj2290343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Kotlar T. J. Hepatic uptake of phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons in vivo. Comparison with the uptake of chylomicron remnants. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):547–553. doi: 10.1042/bj2000547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrella M., Cooper A. D. High affinity binding of chylomicron remnants to rat liver plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):338–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D. The metabolism of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):464–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggy B. P., Bensadoun A. Enrichment of apolipoprotein B-48 in the LDL density class following in vivo inhibition of hepatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 27;877(2):252–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalet C., Fehlmann M., Debey P. Use of Percoll density gradient centrifugation for preparing isolated rat hepatocytes having long-term viability. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 1;122(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Binding, interiorization and degradation of cholesteryl ester-labelled chylomicron-remmant particles by rat hepatocyte monolayers. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):483–494. doi: 10.1042/bj1680483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Degradation of chylomicron remnant cholesteryl ester by rat hepatocyte monolayers. Inhibition by chloroquine and colchicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):520–528. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Some properties of the chylomicron remnant uptake by rat hepatocyte monolayers. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1979;14(3):281–287. doi: 10.3109/00365527909179884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Uptake and degradation of iodine-labelled chylomicron remnant particles by monolayers of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):827–838. doi: 10.1042/bj1740827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funke H., Boyles J., Weisgraber K. H., Ludwig E. H., Hui D. Y., Mahley R. W. Uptake of apolipoprotein E-containing high density lipoproteins by hepatic parenchymal cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Sep-Oct;4(5):452–461. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.5.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H., Kalkman C., Zonneveld A. J., Hülsmann W. C. Secretion of triacylglycerol hydrolase activity by isolated parenchymal rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H., van Berkel T. J., Hülsmann W. C. Binding of liver lipase to parenchymal and non-parenchymal rat liver cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E., Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Cell-density-dependent uptake of chylomicron remnants in rat hepatocyte monolayers. Effects of compactin and mevalonic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 13;917(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen G. L., Daggy B., Bensadoun A. Triacylglycerol lipase, monoacylglycerol lipase and phospholipase activities of highly purified rat hepatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 12;710(3):464–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Hradek G. T., Hornick C., Renaud G., Windler E. E., Havel R. J. Uptake and processing of remnants of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins by rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1984 Nov;25(11):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalopissis A. D., Griglio S., Malewiak M. I., Rozen R., Liepvre X. L. Very-low-density-lipoprotein secretion by isolated hepatocytes of fat-fed rats. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 15;198(2):373–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1980373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landin B., Nilsson A., Twu J. S., Schotz M. C. A role for hepatic lipase in chylomicron and high density lipoprotein phospholipid metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1984 Jun;25(6):559–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitersdorf E., Stein O., Stein Y. Synthesis and secretion of triacylglycerol lipase by cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 6;794(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenich C. M., Ross A. C. Chylomicron remnant-vitamin A metabolism by the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. J Lipid Res. 1987 Feb;28(2):183–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippiello P. M., Sisson P. J., Waite M. The uptake and metabolism of chylomicron-remnant lipids by rat liver parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells in vitro. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):395–401. doi: 10.1042/bj2320395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Akesson B. Uptake of chyle cholesterol esters and intact triglycerides by suspended hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80891-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A. Effects of anti-microtubular agents and cycloheximide on the metabolism of chylomicron cholesteryl esters by hepatocyte suspensions. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):367–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1620367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Ehnholm C., Florén C. H. Uptake and degradation of rat chylomicron remnants, produced in vivo and in vitro, in rat hepatocyte monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):408–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noël S. P., Dupras R. The kinetic parameters of the uptake of very-low-density lipoprotein remnant cholesteryl esters by perfused rat livers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 29;754(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald B., Quarfordt S. Effect of apoE on triglyceride emulsion interaction with hepatocyte and hepatoma G2 cells. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jul;28(7):798–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald B., Shelburne F., Landis B., Linker A., Quarfordt S. The relevance of glycosaminoglycan sulfates to Apo E induced lipid uptake by hepatocyte monolayers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80348-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persoon N. L., Hülsmann W. C., Jansen H. Structural modulation of salt-resistant rat-liver lipase alters the relative phospholipase and triacylglycerol hydrolase activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 13;917(1):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudel L. L., Morris M. D. Determination of cholesterol using o-phthalaldehyde. J Lipid Res. 1973 May;14(3):364–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustan A. C., Nossen J. O., Blomhoff J. P., Drevon C. A. Release of hepatic lipase and very low density lipoprotein by cultured rat hepatocytes. Int J Biochem. 1986;18(10):909–916. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(86)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Estrich D. L., Wood P. D., Kinsell L. W. Evaluation of gel chromatography for plasma lipoprotein fractionation. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jul;11(4):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonderwoerd K., Hülsmann W. C., Jansen H. Regulation of liver lipase. I. Evidence for several regulatory sites, studied in corticotrophin-treated rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 20;754(3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonderwoerd K., Hülsmann W. C., Jansen H. Stabilization of liver lipase in vitro by heparin or by binding to non-parenchymal liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 24;665(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. I. Effect of Ca 2+ on enzymatic dispersion of isolated, perfused liver. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Oct;74(2):450–454. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel T. J., Kruijt J. K., Scheek L. M., Groot P. H. Effect of apolipoproteins E and C-III on the interaction of chylomicrons with parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells from rat liver. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):71–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2160071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel T. J., Kruijt J. K., Van Gent T., Van Tol A. Saturable high affinity binding, uptake and degradation of rat plasma lipoproteins by isolated parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;665(1):22–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Sparrow J. T. Human apolipoprotein E. Determination of the heparin binding sites of apolipoprotein E3. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2068–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Greeve J., Daerr W. H., Greten H. Binding of rat chylomicrons and their remnants to the hepatic low-density-lipoprotein receptor and its role in remnant removal. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):553–561. doi: 10.1042/bj2520553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Preyer S., Greten H. Influence of lysophosphatidylcholine on the C-apolipoprotein content of rat and human triglyceride-rich lipoproteins during triglyceride hydrolysis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):658–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI112624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Regulation of the hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the rat. Opposing effects of homologous apolipoprotein E and individual C apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8303–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol A., van Gent T., Jansen H. Degradation of high density lipoprotein by heparin-releasable liver lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]