Abstract
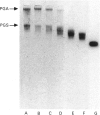
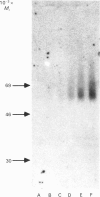
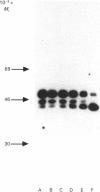
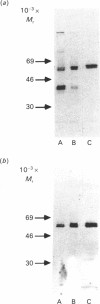
Cartilage proteoglycan aggregates were subjected to degradation by a metalloproteinase, capable of degrading proteoglycan, released from cartilage in culture. This proteinase was demonstrated to be immunologically identical with fibroblast stromelysin. An early release of hyaluronic acid-binding region and large glycosaminoglycan-attachment regions was observed. With increasing time the glycosaminoglycan-attachment regions were digested into smaller fragments and the hyaluronic acid-binding regions accumulated. The degradation of link proteins also occurred concomitantly with these events. Link proteins were converted into a component of similar size to that of the smallest native link protein component. N-Terminal sequence analysis of the three human link protein components indicated that they are all derived from the same protein core, which is closely homologous to that of the rat chondrosarcoma link protein. The two larger link proteins (Mr 48,000 and 44,000) contain the same N-terminal sequence, but they differ by the apparent presence of an N-linked oligosaccharide at residue 6 of the largest link protein component. The smallest link protein (Mr 41,000), however, has an N-terminal sequence equivalent to that commencing at residue 17 in the larger link proteins. It was found that the cartilage metalloproteinase cleaves link proteins in human neonatal cartilage proteoglycan aggregates at the His-16-Ile-17 bond, the same position at which the smallest link protein component appears to be derived naturally from the two larger link protein components. These results suggest that stromelysin secreted by chondrocytes can account for the increased accumulation of hyaluronic acid-binding regions and much of the degradation of link protein observed during aging within human articular cartilage.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. R., Caterson B. The isolation and characterization of the link proteins from proteoglycan aggregates of bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2387–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter J. A., Rosenberg L. C. Electron microscopic studies of cartilage proteoglycans. Direct evidence for the variable length of the chondroitin sulfate-rich region of proteoglycan subunit core protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9830–9839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. K., Golds E. E., Mort J. S., Roughley P. J. Human articular cartilage secretes characteristic metal dependent proteinases upon stimulation by mononuclear cell factor. J Rheumatol. 1986 Feb;13(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. K., Roughley P. J., Mort J. S. The action of human articular-cartilage metalloproteinase on proteoglycan and link protein. Similarities between products of degradation in situ and in vitro. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):117–122. doi: 10.1042/bj2370117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. R., Murphy G., Werb Z. Stromelysin, a connective tissue-degrading metalloendopeptidase secreted by stimulated rabbit synovial fibroblasts in parallel with collagenase. Biosynthesis, isolation, characterization, and substrates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12367–12376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deák F., Kiss I., Sparks K. J., Argraves W. S., Hampikian G., Goetinck P. F. Complete amino acid sequence of chicken cartilage link protein deduced from cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3766–3770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K., Sasaki M., Horigan E., Hassell J. R., Yamada Y. Complete primary structure of the rat cartilage proteoglycan core protein deduced from cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17757–17767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golds E. E., Santer V., Killackey J., Roughley P. J. Mononuclear cell factors stimulate the concomitant secretion of distinct latent proteoglycan, gelatin and collagen degrading enzymes from human skin fibroblasts and synovial cells. J Rheumatol. 1983 Dec;10(6):861–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley C. J., Lowther D. A. Extracellular matrix metabolism by chondrocytes. III. Modulation of proteoglycan synthesis by extracellular levels of proteoglycan in cartilage cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 7;500(1):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Sommarin Y., Hedbom E., Wieslander J., Larsson B. Assay of proteoglycan populations using agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;151(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Glédic S., Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Jollès P. Identity of the protein cores of the two link proteins from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Localization of their sugar moieties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14759–14761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Caterson B., Poole A. R., Roughley P. J. The origin of human cartilage proteoglycan link-protein heterogeneity and fragmentation during aging. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):805–812. doi: 10.1042/bj2320805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Poole A. R., Roughley P. J. Age-related changes in the structure of proteoglycan link proteins present in normal human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):269–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2140269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Stephens P. E., Smith B. J., Docherty A. J. Stromelysin is an activator of procollagenase. A study with natural and recombinant enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):265–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2480265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J. Characterization of a specific antiserum to rabbit stromelysin and demonstration of the synthesis of collagenase and stromelysin by stimulated rabbit articular chondrocytes. Coll Relat Res. 1986 Oct;6(4):351–363. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(86)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. J., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. The primary structure of link protein from rat chondrosarcoma proteoglycan aggregate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3519–3535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., De Luca S., Lohmander S., Hascall V. C. Structures of N-linked and O-linked oligosaccharides on proteoglycan monomer isolated from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10920–10927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollivierre F., Gubler U., Towle C. A., Laurencin C., Treadwell B. V. Expression of IL-1 genes in human and bovine chondrocytes: a mechanism for autocrine control of cartilage matrix degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 30;141(3):904–911. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Mörgelin M., Wiedemann H., Beardmore-Gray M., Dunham D., Hardingham T., Heinegård D., Timpl R., Engel J. Extended and globular protein domains in cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):763–772. doi: 10.1042/bj2450763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol J. P., Loyau G. Interleukin-1 and osteoarthritis. Life Sci. 1987 Sep 7;41(10):1187–1198. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J. A comparative study of the glycosaminoglycan-peptides obtained after degradation of cartilage proteoglycan by different proteinases, and their use in the characterization of different proteoglycans. Connect Tissue Res. 1978;6(3):145–153. doi: 10.3109/03008207809152624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Mort J. S. Ageing and the aggregating proteoglycans of human articular cartilage. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 Oct;71(4):337–344. doi: 10.1042/cs0710337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The heterogeneity of link proteins isolated from human articular cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J., Poole A. R. Identification of a hyaluronic acid-binding protein that interferes with the preparation of high-buoyant-density proteoglycan aggregates from adult human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj2310129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thonar E. J., Sweet M. B. An oligosaccharide component in proteoglycans of articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 1;584(2):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Kronberger A., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. Human skin fibroblast stromelysin: structure, glycosylation, substrate specificity, and differential expression in normal and tumorigenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6725–6729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr, Selzer M. G. Two latent metalloproteases of human articular cartilage that digest proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3633–3638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]